Abstract
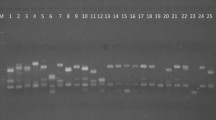
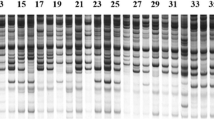
Present investigation was carried out to evaluate genetic diversity among 38 M6 population of oat cv. JO-1. To validate the observed morpho-physiological variations, these lines were analyzed with 21 ISSR primers. A total of 132 loci were amplified by these 21 ISSR markers and 116 loci were found to be polymorphic (87.87 %). The genetic similarity coefficient values among 39 oat genotypes based on ISSR analysis ranged from 0.305 to 0.957. The cluster analysis divided the oat genotypes into two groups. Mutants JMO 81 and JMO 82 were found to be most divergent, hence can be used as parents in breeding program for the development of superior cultivars.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atak C, Celik O, Acik L (2011) Genetic analysis of Rhododendron mutants using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). Pak J Bot 43(2):1173–1182
Babaei A, Nematzadeh GA, Avagyan V, Hamidreza S, Petrodi H (2010) Radio sensitivity studies of morpho- physiological characteristics in some Iranian rice varieties (Oryza sativa L.) in M1 generation. Afr J Agric Res 5(16):2124–2130
Chao S, Zhang W, Dubcovsky J, Sorrells M (2007) Evaluation of genetic diversity and genome-wide linkage disequilibrium among US wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) germplasm representing different market classes. Crop Sci 47(3):1018–1030
De Souza VQ, Pereira AS, Kopp MM, Coimbra JLM, Carvalho FIF, Luz VK, Oliveira AC (2005) Genetic dissimilarity in oat (Avena sativa L.) tolerant and sensitive mutants to organic acids. Bragantia 64(4):569–575
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12(1):13–15
Edmé SJ, Comstock JC, Miller JD, Tai PYP (2005) Determination of DNA content and genome size in sugarcane. J Amer Soc Sugarcane Tech 25:1–16
Garris AJ, Tai TH, Coburn J, Kresovich S, McCouch SR (2005) Genetic structure and diversity in Oryza sativa L. Genetics 169(3):1631–1638
Govindaraj M, Vetriventhan M, Srinivasan M (2015) Importance of genetic diversity assessment in crop plants and its recent advances: an overview of its analytical perspectives. Genetics Res Int. doi:10.1155/2015/431487
Gowda MVC, Nadaf HL, Sheshagiri R (1996) The role of mutations in intraspecific differentiation of ground nut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Euphytica 90:105–113
Hautea DM, Molina GC, Balatero CH, Coronado NB, Perez EB, Alvarez MTH, Canama AO, Akuba RH, Quilloy RB, Frankie RB, Caspillo CS (2004) Analysis of induced mutants of Philippine with molecular markers. In: Jain SM, Swennen R (eds) Banana improvement: cellular, molecular biology and induced mutations. http://www.fao.org/docrep/007/ae216e/ae216e07.htm#bm07
Khan IA, Bibi S, Yasmin S, Khatri A, Seema N, Afghan S (2010) Genetic variability in mutated population of sugarcane clone nia-98 through molecular markers (RAPD and TRAP). Pak J Bot 42(1):605–614
Miri SM, Mousavi A, Naghavi MR, Khiabani BN (2014) Molecular analysis of musa mutants resistant to salinity by microsatellite markers. Trakia J Sci 2:114–120
Mudibu J, Nkongolo KKC, Mehes-Smith M, Kalonji-Mbuyi A (2011) Genetic analysis of soybean genetic pool using ISSR merker: effect of gamma radiation on genetic variability. Int J Plant Breed Genet 5(3):235–245
Oliver RE, Obert DE, Hu G, Bonman JM, Jackson EW (2010) Development of oat-based markers from barley and wheat microsatellites. Genome 6:458-471
Rohlf FJ (2000) NTSYSpc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 2.1. Exeter Software, NY
Roldan-Ruiz I, Dendauw J, Vanbockstaele E, Depicker A, De Loose M (2000) AFLP markers reveal high polymorphic rates in ryegrasses (Lolium spp.). Mol Breed 6:125–134
Ruwali Y, Singh K, Kumar S, Kumar L (2013) Molecular diversity analysis in selected fodder and dual purpose oat (Avena sativa L.) genotypes by using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). Afr J Biotechnol 12:3425–3429
Tanhuanpaa P, Kalendar R, Laurila J, Schulman AH, Manninen O, Kiviharju E (2006) Generation of SNP markers for short straw in oat (Avena sativa L.). Genome 49:282–287
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, P., Tiwari, S., Tripathi, N. et al. Polymorphism analysis in advanced mutant population of oat (Avena sativa L.) using ISSR markers. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 22, 115–120 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-015-0333-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-015-0333-z