Abstract
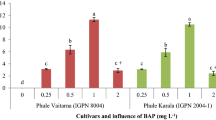
A cephalosporin antibiotic, cefotaxime (Omnatax™) promoted somatic embryogenesis and subsequent shoot regeneration in vitro from spindle in sugarcane irrespective of the genotypes as (CoJ 83, CoJ 88 and CoJ 64) culturered on MS medium with 2,4-D (2.5 mgl−1) and kinetin (0.5 mgl−1). Seven different concentrations of cefotaxime (100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600 and 700 mgl−1) were tested to find the optimal concentration of cefotaxime for somatic embryogenesis from callus cultures. Among the three varieties, calli of variety CoJ 83 incubated on MS medium with 2,4-D (2.5 mgl−1) + kinetin (0.5 mgl−1) + cefotaxime (500 mgl−1) exhibited maximum somatic embryogenesis. To improve shoot regeneration, the callus was transferred to MS medium with BAP (0.5 mgl−1) + kinetin (0.5 mgl−1) in combination with different levels of cefotaxime. Highest frequency of shoot regeneration was observed in callus of CoJ 83 in the presence of 500 mgl−1 cefotaxime. The plantlets could be successfully hardened in polybags and transferred to soil, where they exhibited normal growth. Our results convincingly demonstrated that cefotaxime improves somatic embryogenesis from spindle and regeneration from embryogenic calli of sugarcane and hence can be strongly recommended for rapid and large scale multiplication of sugarcane.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAP:
-
6-benzylaminopurine
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Ddichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- kinetin:
-
6-furfurylaminopurine
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
References
Ahloowalia BS and Maretzki A (1983). Plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis in sugarcane. Plant Cell Rep 2: 21–25
Aoshima Y (2005). Efficient embryogeneses in the callus of tea (Camellia sinensis) enhanced by osmatic stress on antibiotics treatment. Plant Biotechnol., 22: 277–280.
Arencibia AD, Carmona ER, Tellez P, Chan MT, Yu SM, Trujillo LE, and Oramas P (1998). An efficient protocol for sugarcane (Saccharum spp. L.) transformation mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Trans. Res 7: 213–22
Borrelli GM, di Fonzo N and Lupotto E (1992). Effect of cefotaxime on callus culture and plant regeneration in durum wheat. J. Plant Physiol. 140: 372–374
Bower R and Birch RG (1992). Transgenic sugarcane plants via microprojectile bombardment. Plant J. 2: 409–16
Brisibe EA, Miyake H, Taniguchi T and Maeda E (1994). Regulation of somatic embryogenesis in long term callus cultures of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). New Phytol. 126: 301–07
Chahal GS and Gosal SS (2002). Tissue culture in crop development. In: Principles and Procedures of Plant Breeding (Eds. Chahal GS and Gosal SS), Pangbourne, UK: Alpha Science International Ltd. pp 429–456
Danilova SA and Yu ID (2004) The Stimulatory Effect of the Antibiotic Cefotaxime on Plant Regeneration in Maize Tissue Culture. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology 51: 559–562
Grewal D, Gill R, and Gosal SS (2006). Influence of antibiotic cefotaxime on somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in indica rice. Plant Biotech. 1: 1158–1162
Ho WJ and Vasil IK (1983). Somatic embryogenesis in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.): Growth and plant regeneration from embryogenic cell suspension cultures. Ann. Bot, 51:719–26
Kaur A, Gill MS, Ruma D and Gosal SS (2008). Enhanced in vitro shoot multiplication and elongation in sugarcane using cefotaxime. Sugar Tech 10(1): 60–64
Leifert C and Waites WM (1990). Contaminants of plant tissue cultures. Int.Assoc.Plant Tiss. Cult. News. 16:2–13
Lorz H, Gohel E and Brown P (1998). Advances in tissue culture and progress towards genetic transformation of cereals. Plant Breed. 100: 1–25
Mathias RJ and Boyd LA (1986). Cefotaxime stimulates callus growth, embryogenesis and regeneration in haploid breed wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). The Plant Sci. 46: 217–223
Mithias RJ and Mukasa C (1987). The effect of cefotaxime on the growth and regeneration of callus from four varieties of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Plant Cell Reports. 6: 454–457
Murashige T and Skoog F (1962). A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco culture. Plant Physiol. 15: 473–97
Naboras MW, Heyser JW, Dyhes TA and Dehott KJ (1983). Long duration, high-frequency plant regeneration from cereal tissue cultures. Planta, 157(5): 385–391.
Nakano M and Mii M (1993). Antibiotics stimulate somatic embryogenesis without plant growth regulators in several Dianthus cultivars. J. Plant Physiol. 141:721–725
Pius J, George L, Eapen S and Rao PS (1993). Enhanced plant regeneration in pearl millet (Pennisetum americanum) by ethylene inhibitors and cefotaxime. Plant Cell Tiss. Org Cult. 32: 91–96
Rao AM, Sree KP and Kishore PBK (1995). Enhanced plant regeneration in grain and sweet sorghum by asparagine, proline and cefotaxime. Plant Cell Reporters. 15: 72–75
Selwyn S (1980). The beta-lactam antibiotics. Hodder and Stoughton, London pp 56–90
Torregorsa L, Peros JP, Lopaz G and Bouquet A (2000). Effect of hygromycin, kanamycin and phosphinothricin on the embryogenic callus development and axillary micropropagation of Vitis vinifera L. Acta Hort 528: 401–406
Yepes LM and Aldwincle HS (1994). Factors that effect the leaf regeneration efficiency in apple, and effect of antibiotics in morphogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 37: 257–69.
Yu TA, Yeh SD and Yang JS (2001). Effect of carbenecillin and cefotaxime on callus growth and somatic embryogenesis from adventitious roots of papaya. Bot Bull Acad Sin 42: 281–28
Zaghmout OMF and Torello WA (1992). Plant regeneration from callus and protoplasts of perennial rye grass (Lolium perenne L.). J Plant Physiol 140: 101–105
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mittal, P., Gosal, S.S., Senger, A. et al. Impact of cefotaxime on somatic embryogenesis and shoot regeneration in sugarcane. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 15, 257–265 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-009-0029-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-009-0029-3