Abstract
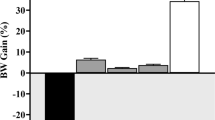
One of the most important complications of diabetes is nephropathy. This study investigates the effects of aqueous garlic extract on inflammation and oxidative stress status in the kidneys of diabetic rats. Male rats were divided into four groups- control rats, diabetic rats, garlic extract-treated diabetic rats, garlic extract-treated normal rats. The glucose, urea, uric acid, and creatinine levels were measured in sera using colorimetric methods. To determine the oxidative stress condition in the kidney tissues, total antioxidant capacity (TAC), malondialdehyde (MDA), and total oxidant status (TOS) were measured using colorimetric methods. Inflammation status was evaluated by the determination of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) gene and protein expression using qRT-PCR and ELISA respectively, while nitric oxide (NO) level in these tissues was measured using the Griess method. Histological examination of Kidneys was carried out by H&E staining. The levels of glucose, urea, and uric acid were found to increase in the serum of diabetic rats and decrease in that of diabetic rats after treatment with garlic. Measurement of MDA, TOS, and TAC revealed oxidative stress in diabetic rats, which improved after receiving the extract. The NO and TNF-α protein levels in diabetic rats were higher than those in control rats. After treatment with garlic, the levels of TNF-α protein and NO became close to the normal levels. Histological results confirmed certain other data as well. Garlic has antioxidant properties; therefore, it can reduce oxidative stress, which plays an important role in the development of diabetic nephropathy. Reduction in oxidative stress has beneficial effects on inflammation because it leads to a decrease in the level of TNF-α.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sivakumar S, Palsamy P, Subramanian SP. Impact of D-pinitol on the attenuation of proinflammatory cytokines, hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative stress and protection of kidney tissue ultrastructure in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2010;188(1):237–45.
Saravanan G, Ponmurugan P. S-allylcysteine improves streptozotocin-induced alterations of blood glucose, liver cytochrome P450 2E1, plasma antioxidant system, and adipocytes hormones in diabetic rats. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2013;11(4):e10927.
Ingaramo PI, Ronco MT, Frances DE, Monti JA, Pisani GB, Ceballos MP, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha pathways develops liver apoptosis in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Mol Immunol. 2011;48(12–13):1397–407.
Nasiri A, Ziamajidi N, Behrouj H, Abbasalipourkabir R, Dehghan A. The effects of aqueous extract of chicory root on steatosis, lipid profile and liver damage enzyme markers in tamoxifen-treated rats. Mol Biochem Diagn J. 2014;1(3):185–94.
Behrouj H, Ziamajidi N, Abbasalipourkabir R, Nasiri A, Solemani Asl S. Therapeutic effect of silybum marianum plant extract on tamoxifen-induced fatty liver in rats. Avicenna J Med Biochem. 2015;3(1):e27160.
Chauhan P, Mahajan S, Kulshrestha A, Shrivastava S, Sharma B, Goswamy HM, Prasad GB. Bougainvillea spectabilis exhibits antihyperglycemic and antioxidant activities in experimental diabetes. J Evid Based Complement Altern Med. 2016;21(3):177–85.
Jaiswal D, Rai PK, Mehta S, Chatterji S, Shukla S, Rai DK, et al. Role of Moringa oleifera in regulation of diabetes-induced oxidative stress. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2013;6(6):426–32.
Rai PK, Jaiswal D, Mehta S, Rai DK, Sharma B, Watal G. Effect of Curcuma longa freeze dried rhizome powder with milk in STZ induced diabetic rats. Indian. J Clin Biochem. 2010;25(2):175–81.
Rai PK, Jaiswal D, Rai DK, Sharma B, Watal G. Antioxidant potential of oral feeding of Cynodon dactylon extract on diabetes induced oxidative stress. J Food Biochem. 2010;34(1):78–92.
Rai PK, Jaiswal D, Rai DK, Sharma B, Watal G. Effect of water extract of Trichosanthes dioica fruits in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2008;23(4):387–90.
Singh VK, Singh DK. Pharmacological effects of garlic (Allium sativum L.). Annu Rev Biomed Sci. 2008;10:6–26.
El-Demerdash FM, Yousef MI, El-Naga NI. Biochemical study on the hypoglycemic effects of onion and garlic in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2005;43(1):57–63.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54.
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem. 1979;95(2):351–8.
Erel O. A new automated colorimetric method for measuring total oxidant status. Clin Biochem. 2005;38(12):1103–11.
Benzie IF, Strain J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem. 1996;239(1):70–6.
Miranda KM, Espey MG, Wink DA. A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide. 2001;5(1):62–71.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8.
Rezagholizadeh L, Pourfarjam Y, Nowrouzi A, Nakhjavani M, Meysamie A, Ziamajidi N, et al. Effect of Cichorium intybus L. on the expression of hepatic NF-κB and IKKβ and serum TNF-α in STZ− and STZ+ niacinamide-induced diabetes in rats. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2016;8(1):1.
Ziamajidi N, Khaghani S, Hassanzadeh G, Vardasbi S, Ahmadian S, Nowrouzi A, et al. Amelioration by chicory seed extract of diabetes- and oleic acid-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) via modulation of PPARalpha and SREBP-1. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;58:198–209.
Shirwaikar A, Rajendran K, Barik R. Effect of aqueous bark extract of Garuga pinnata Roxb. in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced type-II diabetes mellitus. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;107(2):285–90.
Watal G, Dhar P, Srivastava SK, Sharma B. Herbal medicine as an alternative medicine for treating diabetes. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. 2014;2014:1–2.
Singh RK, Sharma B. Certain traditional indian plants and their therapeutic applications: a review. VRI Phytomed. 2013;1(1):1–11.
Eidi A, Eidi M, Esmaeili E. Antidiabetic effect of garlic (Allium sativum L.) in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Phytomedicine. 2006;13(9):624–9.
Liu CT, Sheen LY, Lii CK. Does garlic have a role as an antidiabetic agent? Mol Nutr Food Res. 2007;51(11):1353–64.
Saravanan G, Ponmurugan P. Ameliorative potential of S-allyl cysteine on oxidative stress in STZ induced diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2011;189(1–2):100–6.
Hsu CC, Yen HF, Yin MC, Tsai CM, Hsieh CH. Five cysteine-containing compounds delay diabetic deterioration in Balb/cA mice. J Nutr. 2004;134(12):3245–9.
Navarro JF, Milena FJ, Mora C, Leon C, Claverie F, Flores C, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression in diabetic nephropathy: relationship with urinary albumin excretion and effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition. Kidney Int Suppl. 2005;99:S98–102.
Moriwaki Y, Yamamoto T, Shibutani Y, Aoki E, Tsutsumi Z, Takahashi S, et al. Elevated levels of interleukin-18 and tumor necrosis factor-α in serum of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: relationship with diabetic nephropathy. Metabolism. 2003;52(5):605–8.
Leverkus M, Yaar M, Eller MS, Tang EH, Gilchrest BA. Post-transcriptional regulation of UV induced TNF-α expression. J Investig Dermatol. 1998;110(4):353–7.
MacKenzie S, Fernàndez-Troy N, Espel E. Post-transcriptional regulation of TNF-α during in vitro differentiation of human monocytes/macrophages in primary culture. J Leukoc Biol. 2002;71(6):1026–32.
Boado RJ, Pardridge WM. Glucose deprivation and hypoxia increase the expression of the GLUT1 glucose transporter via a specific mRNA cis-acting regulatory element. J Neurochem. 2002;80(3):552–4.
Acknowledgments
The present study was funded by Vice-chancellor for Research and Technology, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (No. 9312126433).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasiri, A., Ziamajidi, N., Abbasalipourkabir, R. et al. Beneficial Effect of Aqueous Garlic Extract on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Status in the Kidneys of Type 1 Diabetic Rats. Ind J Clin Biochem 32, 329–336 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-016-0621-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-016-0621-6