Abstract
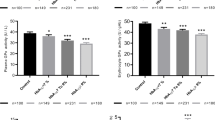
Increased oxidative stress is a widely accepted participant in the development and progression of diabetes and its complications. The present study has been undertaken to evaluate oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus and effect of vitamin E supplementation on oxidative stress. In all 120 subjects were enrolled in the present study, 40 subjects are age and sex matched controls. Test group comprised of clinically diagnosed (n = 80) type 2 diabetic patients. Biochemical parameters like serum MDA, nitric oxide, superoxide dismutase, erythrocyte reduced glutathione and platelet aggregation were analyzed in control and diabetic group. Test group is further categorized as Group I (n = 40) diabetics were treated by only hypoglycemic drugs and Group II (n = 40) diabetics were treated by hypoglycemic drugs with vitamin E supplementation. All above biochemical parameters were again reassessed after 3 months follow-up in both group and its values were compared with its respective baseline levels. The study shows, reduction of oxidative stress, improvement in antioxidant enzymes and endothelial dysfunction in group II, those were on treatment of hypoglycemic drugs along with vitamin E supplementation. Hence the present study may conclude that vitamin E supplementation along with hypoglycemic drugs may be beneficial to type 2 DM patients to minimize vascular complications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maitra A, Abbas. Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease, 7th ed. 2004. p. 1191–2.
Irshad M, Chaudhari PS. Oxidant and antioxidant system: role and significance in human body. Indian J Exp Biol. 2002;40:1233–9.
Ramakrishna V, Jailkhani R. Evaluation of oxidative stress in Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM) patients. Diagn Pathol. 2007;2:22. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-2-22.
Heistad Donald D. Oxidative stress and vascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;26:689–95.
Coesention F, Luscher TF. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1998;32(Suppl 13):554–61.
Powers AC. In: Kasper D, Braunwald E, et al., editors. Diabetes mellitus in Harrison’s principles of internal medicine, 16th ed. McGraw-Hill Companies; 2008. p. 2161–2.
Trinder P. Determination of glucose in blood using glucose oxidase with an alternative oxygen acceptor. Ann Clin Biochem. 1969;6:24–7.
Trivelli LA, Ranney HM, Lai HT. Hemoglobin components in patients with diabetes mellitus. New Engl J Med. 1971;284:353–7.
Marklund S, Marklund G. A simple assay for superoxide dismutase using autooxidation of pyrogallol. Eur J Biochem. 1974;47:469–72.
Cortas NK, Wakid NW. Determination of inorganic nitrate in serum and urine by a kinetic cadmium reduction method. Clin Chem. 1990;36(8):1440–3.
Wilbur KM, Bernheim F, Shapiro OW. The thiobarbituric acid method for mlaondialdehyde estimation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1943;250:305–13.
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM. Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med. 1963;61:882–8.
Born GVR. Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal. Nature. 1962;194:927–9.
Dalle-Donne I, et al. Biomarkers of oxidative damage in human disease. Clin Chem. 2006;52(4):601–23.
Wolff SP. Diabetes mellitus and free radicals. Br Med Bull. 1993;49(3):432–642.
Maritim AC, Sanders RA, Watkins JB. Diabetes, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: a review. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2003;17:24–38.
Pieper GM. Review of alterations in endothelial nitric oxide production in diabetes. Hypertension. 1998;31:1047–60.
Ceriello A. A hyperglycemia: the bridge between non enzymatic glycation and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Diabetes Nutr Metab. 1999;12(1):42–6.
Nobar R, Pour R. Total antioxidant capacity, superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase in diabetic patients. Med J Islam Acad Sci. 1999;12(4):109–14.
Gryglewski RJ, Botting RM, Vane JR. Mediators produced by endothelial cell. Hypertension. 1988;12:465–92.
Chin JH, Azhar S, Hoffman BB. Inactivation of endothelial derived relaxing factor by oxidized lipoproteins. J Clin Investig. 1992;89:10–8.
Sharma A, Kharb S, Chugh SN, Kakkar R, Singh GP. Evaluation of oxidative stress before and after control of glycemia and after vitamin E supplementation in diabetic patients. Metabolism. 2000;49:160–2.
Barbagallo M, Dominguez LJ, Tagliamonte MR, Resrich LM, Paolisso G. Effects of vitamin E and glutathione on glucose metabolism: role of magnesium. Hypertension. 1999;34:1002–6.
Watanabe J, Umela F, Wakasug H, Ibayashi H. Effect of vitamin E on platelet aggregation in diabetes mellitus. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1984;143:161–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shinde, S.N., Dhadke, V.N. & Suryakar, A.N. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Follow-up Along with Vitamin E Supplementation. Ind J Clin Biochem 26, 74–77 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-010-0041-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-010-0041-y