Abstract
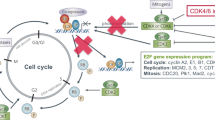
Endocrine therapy is the mainstay of treatment for patients with estrogen receptor positive (ER+)/HER2-negative (HER2−) metastatic breast cancer (MBC). Many clinicians consider the sequential endocrine therapy is gold standard strategy because of better outcome and the maintenance of a better quality of life (QOL) for MBC patients. However, clinical practice shall be changed according to development of CDK4/6 inhibitor in current. CDK4/6 is key kinase which promote the cell cycle, and especially the expression of cyclin D1 and the activation of CDK4/6 to drive breast cancer proliferation. Currently positive data of several clinical trials using three CDK4/6 inhibitors (palbocilcib, ribociclib, abemaciclib) were published and primary endpoint were met in all phase III studies. Therefore, practice change of endocrine therapy has been achieved in ER positive MBC. This review will present clinical trial data, including both the efficacy and safety of CDK4/6 inhibitors for MBC, and describe the designs of the mainly ongoing clinical trials examining CDK4/6 inhibitors for the treatment of MBC and EBC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Finn RS, Aleshin A, Slamon DJ. Targeting the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) 4/6 in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016;18:17.
Finn RS, Dering J, Conklin D, et al. PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase4/6inhibitor, preferentially inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11:77.
Chen P, Lee NV, Hu W, et al. Spectrum and degree of CDK drug interactions predicts clinical performance. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016;15(10):2273–81.
Flaherty KT, Lorusso PM, Demichele A, et al. Phase I, dose-escalation trial of the oral cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor PD 0332991, administered using a 21-day schedule in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:568–76.
Tamura K, Mukai H, Naito Y, et al. Phase I study of palbociclib, a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor, in Japanese patients. Cancer Sci. 2016;107(6):755–63.
Finn RS, Crown JP, Lang I, et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone as first-line treatment of oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1/TRIO-18): a randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(1):25–35.
Finn RS, Martin M, Rugo HP, et al. Palbociclib and letrozole in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1925–36.
Turner NC, Ro J, André F, et al. Palbociclib in hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. NEJM. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1505270.
Fujiwara Y, Tamura K, Kondo S, et al. Phase 1 study of abemaciclib, an inhibitor of CDK4 and 6, as a single agent for Japanese patients with advanced cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016;78(2):281–8.
Dickler MN, Tolaney SM, Rugo HS, et al. MONARCH 1, A Phase II Study of abemaciclib, a CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitor, as a single agent, in patients with refractory HR+/HER2− metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-17-0754 (Epub ahead of print).
Sledge GW Jr, Toi M, Neven P, et al. MONARCH 2: abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant in women with HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer who had progressed while receiving endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(25):2875–84.
Goetz MP, Toi M, Campone M, et al. MONARCH 3: abemaciclib as initial therapy for advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(32):3638–46.
Infante JR, Cassier PA, Gerecitano JF, et al. A PhaseI study of the cyclin-dependent kinase4/6 inhibitor ribociclib (LEE011) in patients with advanced solid tumors and lymphomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(23):5696–705.
Hortobagyi GN, Stemmer SM, Burris HA, et al. Ribociclib as first-line therapy for HR-positive, advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(18):1738–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
I have conflict of interest about this paper to declare as follow Honoraria: Pfizer. Research Fund (registration study fee): Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly.
About this article
Cite this article
Iwata, H. Clinical development of CDK4/6 inhibitor for breast cancer. Breast Cancer 25, 402–406 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-017-0827-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-017-0827-3