Abstract
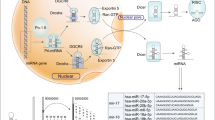
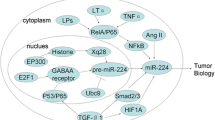
MicroRNAs (miRs) are short and highly conserved non-coding RNAs molecules consisting of 18–25 nucleotides that regulate gene expression at post-transcriptional level by direct binding to complementary binding sites within the 3′untranslated region (3′UTR) of target mRNAs. New evidences have demonstrated that miRNAs play an important role in diverse physiological processes, including regulating cell growth, apoptosis, metastasis, drug resistance, and invasion. In chromosomes 11 and 22 of the miR-130 family, paralogous miRNA sequences, miR-130a and miR-130b are situated, respectively. MiR-130a has participated in different pathogenesis, including hepatocellular carcinoma, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, glioblastoma, prostate carcinoma, leukemia, etc. Most important of all, more and more evidences indicate that miR-130a is associated with drug resistance and acts as an intermediate in PI3 K/Akt/PTEN/mTOR, Wnt/β-catenin and NF-kB/PTEN drug resistance signaling pathways. Drug resistance has emerged as a major obstacle to successful treatment of cancer nowadays and in this review, we will reveal the function of miR-130a in cancer, especially in drug resistance. Therefore, it will provide a new therapeutic target for the treatment of cancer, especially in chemotherapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre Lindsey A, Bray Freddie, Siegel Rebecca L, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108.
Xiong J, Wei B, Ye Q, Liu W. MiR-30a-5p/UBE3C axis regulates breast cancer cell proliferation and migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;pii:S0006–291X(16)30381–3. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.03.069.
Wang D, Qiu C, Zhang H, Wang J, Cui Q, Yin Y. Human microRNA oncogenes and tumor suppressors show significantly different biological patterns: from functions to targets. PLoS One. 2010;5:e13067.
Giannakakis A, Coukos G, Hatzigeorgiou A, Sandaltzopoulos R, Zhang L. miRNA genetic alterations in human cancers. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2007;7:1375–86.
Zhang HD, Jiang LH, Sun DW, Tang JH. MiR-139-5p: promising biomarker for cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:1355–65.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136:215–33.
Chen X, Lu P, Wang DD, Yang SJ, Wu Y, Shen HY. The role of miRNAs in drug resistance and prognosis of breast cancer formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. Gene. 2016;595:221–6.
Suresh S, McCallum L, Lu W, Lazar N, Perbal B, Irvine AE. MicroRNAs 130a/b are regulated by BCR-ABL and downregulate expression of CCN3 in CML. J Cell Commun Signal. 2011;5:183–91.
Ishihara K, Sasaki D, Tsuruda K, Inokuchi N, Nagai K, Hasegawa H, et al. Impact of miR-155 and miR-126 as novel biomarkers on the assessment of disease progression and prognosis in adult T-cell leukemia. Cancer Epidemiol. 2012;36:560–5.
Sand M, Skrygan M, Sand D, Georgas D, Hahn SA, Gambichler T, et al. Expression of microRNAs in basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:847–55.
Jiang H, Yu WW, Wang LL, Peng Y. MiR-130a acts as a potential diagnostic biomarker and promotes gastric cancer migration, invasion and proliferation by targeting RUNX3. Oncol Rep. 2015;34:1153–61.
Wang XC, Tian LL, Wu HL, Jiang XY, Du LQ, Zhang H, et al. Expression of miRNA-130a in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Am J Med Sci. 2010;340:385–8.
Chen J, Yan D, Wu W, et al. MicroRNA-130a promotes the metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of osteosarcoma by targeting PTEN. Oncol Rep. 2016;35:3285–92.
Liu SG, Qin XG, Zhao BS, Zhu J, Ye W, Shu Q. Differential expression of miRNAs in esophageal cancer tissue. Oncol Lett. 2013;5:1639–42.
Ratert N, Meyer HA, Jung M. miRNA profiling identifies candidate mirnas for bladder cancer diagnosis and clinical outcome. J Mol Diagn. 2013;15:695–705.
Zhang X, Huang L, Zhao Y, Tan W. Downregulation of miR-130a contributes to cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells by targeting X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) directly. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2013;45:995–1001.
Li B, Huang P, Qiu J, Liao Y, Hong J, Yuan Y. MicroRNA-130a is down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and associates with poor prognosis. Med Oncol. 2014;31:230.
Pan Y, Wang R, Zhang F, Chen Y, Lv Q, Long G, et al. MicroRNA-130a inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration in human breast cancer by targeting the RAB5A. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:384–93.
He L, Wang HY, Zhang L, Huang L, Li JD, Xiong Y, et al. Prognostic significance of low DICER expression regulated by miR-130a in cervical cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1205.
Qiu S, Lin S, Hu D, Feng Y, Tan Y, Peng Y. Interactions of miR-323/miR-326/miR-329 and miR-130a/miR-155/miR-210 as prognostic indicators for clinical outcome of glioblastoma patients. J Transl Med. 2013;11:10.
Boll K, Reiche K, Kasack K, Mörbt N, Kretzschmar AK, Tomm JM, et al. MiR-130a, miR-203 and miR-205 jointly repress key oncogenic pathways and are downregulated in prostate carcinoma. Oncogene. 2013;32:277–85.
Kovaleva V, Mora R, Park YJ, Plass C, Chiramel AI, Bartenschlager R, et al. miRNA-130a targets ATG2B and DICER1 to inhibit autophagy and trigger killing of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 2012;72:1763–72.
Cui XY, Guo YJ, Yao HR. Analysis of microRNA in drug- resistant breast cancer cell line MCF-7/ADR. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2008;28:1813–5.
Chen C, Wang HJ, Yang LY, Jia XB, Xu P, Chen J, et al. Expression of MiR-130a in serum samples of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer and its association with platinum resistance. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016;47:60–3.
Zhou YM, Liu J, Sun W. MiR-130a overcomes gefitinib resistance by targeting met in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15:1391–6.
Yuan WX, Gui YX, Na WN, et al. Circulating microRNA-125b and microRNA-130a expression profiles predict chemoresistance to R-CHOP in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. Oncol Lett. 2016;11:423–32.
Liu Y, Li Y, Wang R, Chao J, Yang X. MiR-130a-3p regulates cell migration and invasion via inhibition of Smad4 in gemcitabine resistant hepatoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016;35:19.
Xu N, Shen C, Luo Y, Xia L, Xue F, Xia Q, Zhang J. Upregulated miR-130a increases drug resistance by regulating RUNX3 and Wnt signaling in cisplatin-treated HCC cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;425:468–72.
Fujita Y, Kojima T, Kawakami K, Mizutani K, Kato T, Deguchi T, et al. miR-130a activates apoptotic signaling through activation of caspase-8 in taxane-resistant prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 2015;75:1568–78.
Lanzetti L, Palamidessi A, Areces L, Areces L, Scita G, Di Fiore PP. Rab5 is a signalling GTPase involved in actin remodelling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Nature. 2004;429:309–14.
Li QL, Ito K, Sakakura C, Ki Inoue, Chi XZ, Lee KY, et al. Causal relationship between the loss of RUNX3 expression and gastric cancer. Cell. 2002;109:113–24.
Jo MJ, Lee JR, Cho IJ, Kim YW, Kim SC. Roots of Erigeron annuus attenuate acute inflammation as mediated with the inhibition of NF- kappa B-associated nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 production. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:297427.
Park SW, Cho C, Cho BN, Kim Y, Goo TW, Kim YI. 15-deoxy-delta12,14-prostaglandin J 2 down-regulates activin-induced activin receptor, smad, and cytokines expression via suppression of NF- kappa B and MAPK signaling in HepG2 cells. PPAR Res. 2013;2013:751261.
Ling H, Gray CB, Zambon AC, Grimm M, Gu Y, Dalton N, et al. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II deltamediates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through nuclear factor-kappaB. Circ Res. 2013;112:935–44.
Zhang J, Chen J, Yang J, Xu CW, Pu P, Ding JW, et al. Resveratrol attenuates oxidative stress induced by balloon injury in the rat carotid artery through actions on the ERK1/2 and NF-kappa B pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;31:230–41.
Zhang J, Wu H, Li P, Zhao Y, Liu M, Tang H. NF-κB-modulated miR-130a targets TNF-α in cervical cancer cells. J Transl Med. 2014;12:155.
Feng Y, Zhou S, Li G, Hu C, Zou W, Zhang H, et al. Nuclear factor-κB-dependent microRNA-130a upregulation promotes cervical cancer cell growth by targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016;598:57–65.
Majetschak M, Obertacke U, Schade FU, Bardenheuer M, Voggenreiter G, Bloemeke B, et al. Tumor necrosis factor gene polymorphisms, leukocyte function, and sepsis susceptibility in blunt trauma patients. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002;9:1205–11.
Balkwill F, Joffroy C. TNF: a tumor-suppressing factor or a tumor promoting factor? Future Oncol. 2010;6:1833–6.
Hagemann T, Robinson SC, Schulz M, Trümper L, Balkwill FR, Binder C. Enhanced invasiveness of breast cancer cell lines upon co-cultivation with macrophages is due to TNF-α dependent up-regulation of matrix metalloproteases. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25:1543–9.
Vu TH, Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: effectors of development and normal physiology. Genes Dev. 2000;14:2123–33.
Zucker S, Vacirca J. Role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in colorectal cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2004;23:101–17.
Häger M, Pedersen CC, Larsen MT, Andersen MK, Hother C, Grønbæk K, et al. MicroRNA-130a-mediated down-regulation of Smad4 contributes to reduced sensitivity to TGF-β1 stimulation in granulocytic precursors. Blood. 2011;118:6649–59.
Chang CW, Yu JC, Hsieh YH, Yao CC, Chao JI, Chen PM, et al. MicroRNA-30a increases tight junction protein expression to suppress the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by targeting Slug in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:16462–78.
Parsons R, Simpson L. PTEN and cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 2003;222:147–66.
Nielsen-Preiss SM, Silva SR, Gillette JM. Role of PTEN and Akt in the regulation of growth and apoptosis in human osteoblastic cells. J Cell Biochem. 2003;90:964–75.
Hu Y, Xu S, Jin W, Yi Q, Wei W. Effect of the PTEN gene on adhesion, invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2014;32:1741–7.
Wang Z, Dai X, Chen Y, et al. MiR-30a-5p is induced by Wnt/β-catenin pathway and promotes glioma cell invasion by repressing NCAM. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;465:374–80.
Wang W, Lin H, Zhou L, Sun C, Zhu Q, Zhao H, et al. MicroRNA-30a-3p inhibits tumor proliferation, invasiveness and metastasis and is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014;40:1586–94.
Li WF, Dai H, Ou Q, Zuo GQ, Liu CA. Overexpression of microRNA-30a-5p inhibits liver cancer cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting MTDH/PTEN/AKT pathway. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:5885–95.
Schlessinger K, Hall A, Tolwinski N. Wnt signaling pathways meet Rho GTPases. Genes. 2009;23:265–77.
Scheel C, Eaton EN, Li SH, Reinhardt F, Kah KJ, Bell G, et al. Paracrine and autocrine signals induce and maintain mesenchymal and stem cell states in the breast. Cell. 2011;145:926–40.
Sharrard RM, Maitland NJ. Alternative splicing of the human PTEN/MMAC1/TEP1 gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1494:282–5.
Maehama T, Dixon JE. The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:13375–8.
Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME. Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev. 1999;13:2905–27.
Testa JR, Bellacosa A. AKT plays a central role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:10983–5.
Jacinto E, Facchinetti V, Liu D, Soto N, Wei S, Jung SY, et al. SIN1/MIP1 maintains rictor-mTOR complex integrity and regulates Akt phosphorylation and substrate specificity. Cell. 2006;127:125–37.
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Sengupta S, Sheen JH, Hsu PP, Bagley AF, et al. Prolonged rapamycin treatment inhibits mTORC2 assembly and Akt/PKB. Mol Cell. 2006;22:159–68.
Vazquez F, Sellers WR. The PTEN tumor suppressor protein: an antagonist of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1470:M21–35.
Yang L, Li N, Wang H, Jia X, Wang X, Luo J. Altered microRNA expression in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells and upregulation of miR-130a associated with MDR1/P-glycoprotein-mediated drug resistance. Oncol Rep. 2012;28:592–600.
Li NW, Wang HJ, Yang LY, Jia XB, Chen C, Wang X. Regulatory effects and associated mechanisms of miR-130a molecules on cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer A2780 cell lines. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013;44:865–70.
Li N, Yang L, Wang H, Yi T, Jia X, Chen C, Xu P. MiR-130a and MiR-374a function as novel regulators of cisplatin resistance in human ovarian cancer A2780 cells. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0128886.
Hu M, Liu Y, Deng C, Han R, Jia Y, Liu S, et al. Enhanced invasiveness in multidrug resistant leukemic cells is associated with overexpression of P-glycoprotein and cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Leuk Lymphoma. 2011;52:1302–11.
Gottesman MM, Ling V. The molecular basis of multidrug resistance in cancer: the early years of P-glycoprotein research. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:998–1009.
Li Z, Hu S, Wang J, Cai J, Xiao L, Yu L, et al. MiR-27a modulates MDR1/Pglycoprotein expression by targeting HIPK2 in human ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 2010;119:125–30.
Ma JJ, Chen BL, Xin XY. XIAP gene downregulation by small interfering RNA inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and reverses the cisplatin resistance of ovarian carcinoma. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009;146:222–6.
Sasaki H, Sheng Y, Kotsuji F, Tsang BK. Down-regulation of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein induces apoptosis in chemoresistant human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000;60:5659–66.
Suda K, Murakami I, Katayama T, Tomizawa K, Osada H, Sekido Y, et al. Reciprocal and complementary role of MET amplification and EGFR T790 M mutation in acquired resistance to kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:5489–98.
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 2007;316:1039–43.
Peruzzi B, Bottaro DP. Targeting the c-Met signaling pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:3657–60.
Garofalo M, Di Leva G, Romano G, Nuovo G, Suh SS, Ngankeu A, et al. miR-221&222 regulate TRAIL resistance and enhance tumorigenicity through PTEN and TIMP3 downregulation. Cancer Cell. 2009;16:498–509.
Acunzo M, Visone R, Romano G, Veronese A, Lovat F, Palmieri D, et al. miR-130a targets MET and induces TRAIL-sensitivity in NSCLC by downregulating miR-221 and 222. Oncogene. 2012;31:634–42.
Chen CX, Hu Y, Li L. NRP1 is targeted by miR-130a and miR-130b, and is associated with multidrug resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer based on integrated gene network analysis. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13:188–96.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Hd., Jiang, Lh., Sun, Dw. et al. The role of miR-130a in cancer. Breast Cancer 24, 521–527 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-017-0776-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-017-0776-x