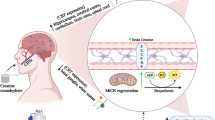
Abstract
It is increasingly evident that bidirectional interactions exist among the gastrointestinal tract, the enteric nervous system, and the central nervous system. Recent preclinical and clinical trials have shown that gut microbiota plays an important role in these gut-brain interactions. Furthermore, alterations in gut microbiota composition may be associated with pathogenesis of various neurological disorders, including stress, autism, depression, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. Therefore, the concepts of the microbiota-gut-brain axis is emerging. Here, we review the role of gut microbiota in bidirectional interactions between the gut and the brain, including neural, immune-mediated, and metabolic mechanisms. We highlight recent advances in the understanding of probiotic modulation of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders via the gut-brain axis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, J.B., Johansen, L.J., Powell, L.D., Quig, D., and Rubin, R.A. 2011. Gastrointestinal flora and gastrointestinal status in children with autism-comparisons to typical children and correlation with autism severity. BMC Gastroenterol. 11, 22.
Aizawa, E., Tsuji, H., Asahara, T., Takahashi, T., Teraishi, T., Yoshida, S., Ota, M., Koga, N., Hattori, K., and Kunugi, H. 2016. Possible association of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus in the gut microbiota of patients with major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 202, 254–257.
Akbari, E., Asemi, Z., Daneshvar Kakhaki, R., Bahmani, F., Kouchaki, E., Tamtaji, O.R., Hamidi, G.A., and Salami, M. 2016. Effect of probiotic supplementation on cognitive function and metabolic status in Alzheimer’s disease: A randomized, double-blind and controlled trial. Front. Aging Neurosci. 8, 256.
Bailey, M.T. and Coe, C.L. 1999. Maternal separation disrupts the integrity of the intestinal microflora in infant rhesus monkeys. Dev. Psychobiol. 35, 146–155.
Bailey, M.T., Dowd, S.E., Galley, J.D., Hufnagle, A.R., Allen, R.G., and Lyte, M. 2011. Exposure to a social stressor alters the structure of the intestinal microbiota: implications for stressor-induced immunomodulation. Brain Behav. Immun. 25, 397–407.
Bailey, M.T., Dowd, S.E., Parry, N.M., Galley, J.D., Schauer, D.B., and Lyte, M. 2010. Stressor exposure disrupts commensal microbial populations in the intestines and leads to increased colonization by Citrobacter rodentium. Infect. Immun. 78, 1509–1519.
Bailey, M.T., Lubach, G.R., and Coe, C.L. 2004. Prenatal stress alters bacterial colonization of the gut in infant monkeys. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 38, 414–421.
Banks, W.A. 2005. Blood-brain barrier transport of cytokines: a mechanism for neuropathology. Curr. Pharm. Des. 11, 973–984.
Barrett, E., Ross, R.P., O’Toole, P.W., Fitzgerald, G.F., and Stanton, C. 2012. γ-Aminobutyric acid production by culturable bacteria from the human intestine. J. Appl. Microbiol. 113, 411–417.
Bengmark, S. 2013. Gut microbiota, immune development and function. Pharmacol. Res. 69, 87–113.
Benton, D., Williams, C., and Brown, A. 2007. Impact of consuming a milk drink containing a probiotic on mood and cognition. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 61, 355–361.
Bercik, P., Denou, E., Collins, J., Jackson, W., Lu, J., Jury, J., Deng, Y., Blennerhassett, P., Macri, J., McCoy, K.D., et al. 2011a. The intestinal microbiota affect central levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor and behavior in mice. Gastroenterology 141, 599–609.
Bercik, P., Park, A.J., Sinclair, D., Khoshdel, A., Lu, J., Huang, X., Deng, Y., Blennerhassett, P.A., Fahnestock, M., Moine, D., et al. 2011b. The anxiolytic effect of Bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 involves vagal pathways for gut-brain communication. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 23, 1132–1139.
Berer, K. and Krishnamoorthy, G. 2012. Commensal gut flora and brain autoimmunity: A love or hate affair? Acta Neuropathol. 123, 639–651.
Bermudez-Brito, M., Plaza-Diaz, J., Munoz-Quezada, S., Gomez-Llorente, C., and Gil, A. 2012. Probiotic mechanisms of action. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 61, 160–174.
Boursi, B., Mamtani, R., Haynes, K., and Yang, Y.X. 2016. Parkinson’s disease and colorectal cancer risk-A nested case control study. Cancer Epidemiol. 43, 9–14.
Bravo, J.A., Forsythe, P., Chew, M.V., Escaravage, E., Savignac, H.M., Dinan, T.G., Bienenstock, J., and Cryan, J.F. 2011. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 16050–16055.
Bravo, J.A., Julio-Pieper, M., Forsythe, P., Kunze, W., Dinan, T.G., Bienenstock, J., and Cryan, J.F. 2012. Communication between gastrointestinal bacteria and the nervous system. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 12, 667–672.
Browning, K.N., Verheijden, S., and Boeckxstaens, G.E. 2017. The vagus nerve in appetite regulation, mood, and intestinal inflammation. Gastroenterology 152, 730–744.
Bu, X.L., Yao, X.Q., Jiao, S.S., Zeng, F., Liu, Y.H., Xiang, Y., Liang, C.R., Wang, Q.H., Wang, X., Cao, H.Y., et al. 2015. A study on the association between infectious burden and Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 22, 1519–1525.
Carabotti, M., Scirocco, A., Maselli, M.A., and Severi, C. 2015. The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann.Gastroenterol. 28, 203–209.
Cassani, E., Barichella, M., Cancello, R., Cavanna, F., Iorio, L., Cereda, E., Bolliri, C., Zampella Maria, P., Bianchi, F., Cestaro, B., et al. 2015. Increased urinary indoxyl sulfate (indican): New insights into gut dysbiosis in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism. Relat. Disord. 21, 389–393.
Cassani, E., Privitera, G., Pezzoli, G., Pusani, C., Madio, C., Iorio, L., and Barichella, M. 2011. Use of probiotics for the treatment of constipation in Parkinson’s disease patients. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 57, 117–121.
Choi, H.J., Lee, N.K., and Paik, H.D. 2015. Health benefits of lactic acid bacteria isolated from kimchi, with respect to immunomodulatory effects. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 24, 783–789.
Clarke, M.B., Hughes, D.T., Zhu, C., Boedeker, E.C., and Sperandio, V. 2006. The QseC sensor kinase: a bacterial adrenergic receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 10420–10425.
Cohen, L.J., Esterhazy, D., Kim, S.H., Lemetre, C., Aguilar, R.R., Gordon, E.A., Pickard, A.J., Cross, J.R., Emiliano, A.B., Han, S.M., et al. 2017. Commensal bacteria make GPCR ligands that mimic human signalling molecules. Nature 549, 48–53.
Coury, D.L., Ashwood, P., Fasano, A., Fuchs, G., Geraghty, M., Kaul, A., Mawe, G., Patterson, P., and Jones, N.E. 2012. Gastrointestinal conditions in children with autism spectrum disorder: developing a research agenda. Pediatrics 130 Suppl 2, S160–S168.
Cryan, J.F. and Dinan, T.G. 2012. Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 701–712.
De Angelis, M., Piccolo, M., Vannini, L., Siragusa, S., De Giacomo, A., Serrazzanetti, D.I., Cristofori, F., Guerzoni, M.E., Gobbetti, M., and Francavilla, R. 2013. Fecal microbiota and metabolome of children with autism and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. PLoS One 8, e76993.
Desbonnet, L., Garrett, L., Clarke, G., Bienenstock, J., and Dinan, T.G. 2008. The probiotic Bifidobacteria infantis: An assessment of potential antidepressant properties in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 43, 164–174.
Desbonnet, L., Garrett, L., Clarke, G., Kiely, B., Cryan, J.F., and Dinan, T.G. 2010. Effects of the probiotic Bifidobacterium infantis in the maternal separation model of depression. Neuroscience 170, 1179–1188.
Deshmukh, H.S., Liu, Y., Menkiti, O.R., Mei, J., Dai, N., O’Leary, C.E., Oliver, P.M., Kolls, J.K., Weiser, J.N., and Worthen, G.S. 2014. The microbiota regulates neutrophil homeostasis and host resistance to Escherichia coli K1 sepsis in neonatal mice. Nat. Med. 20, 524–530.
Diamond, B., Huerta, P.T., Tracey, K., and Volpe, B.T. 2011. It takes guts to grow a brain: Increasing evidence of the important role of the intestinal microflora in neuro-and immune-modulatory functions during development and adulthood. Bioessays 33, 588–591.
Donato, K.A., Gareau, M.G., Wang, Y.J., and Sherman, P.M. 2010. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG attenuates interferon-γ and tumour necrosis factor-a-induced barrier dysfunction and pro-inflammatory signalling. Microbiology 156, 3288–3297.
Emery, D.C., Shoemark, D.K., Batstone, T.E., Waterfall, C.M., Coghill, J.A., Cerajewska, T.L., Davies, M., West, N.X., and Allen, S.J. 2017. 16S rRNA next generation sequencing analysis shows bacteria in Alzheimer’s post-mortem brain. Front. Aging Neurosci. 9, 195.
Erny, D., de Angelis, A.L.H., Jaitin, D., Wieghofer, P., Staszewski, O., David, E., Keren-Shaul, H., Mahlakoiv, T., Jakobshagen, K., and Buch, T. 2015. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 965–977.
Felger, J.C. and Lotrich, F.E. 2013. Inflammatory cytokines in depression: neurobiological mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neuroscience 246, 199–229.
Finegold, S.M., Dowd, S.E., Gontcharova, V., Liu, C., Henley, K.E., Wolcott, R.D., Youn, E., Summanen, P.H., Granpeesheh, D., Dixon, D., et al. 2010. Pyrosequencing study of fecal microflora of autistic and control children. Anaerobe 16, 444–453.
Forsyth, C.B., Shannon, K.M., Kordower, J.H., Voigt, R.M., Shaikh, M., Jaglin, J.A., Estes, J.D., Dodiya, H.B., and Keshavarzian, A. 2011. Increased intestinal permeability correlates with sigmoid mucosa a-synuclein staining and endotoxin exposure markers in early Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 6, e28032.
Frost, G., Sleeth, M.L., Sahuri-Arisoylu, M., Lizarbe, B., Cerdan, S., Brody, L., Anastasovska, J., Ghourab, S., Hankir, M., Zhang, S., et al. 2014. The short-chain fatty acid acetate reduces appetite via a central homeostatic mechanism. Nat. Commun. 5, 3611.
Furusawa, Y., Obata, Y., Fukuda, S., Endo, T.A., Nakato, G., Takahashi, D., Nakanishi, Y., Uetake, C., Kato, K., Kato, T., et al. 2013. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature 504, 446–450.
Gagliano, H., Delgado-Morales, R., Sanz-Garcia, A., and Armario, A. 2014. High doses of the histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate trigger a stress-like response. Neuropharmacology 79, 75–82.
Gill, S.R., Pop, M., Deboy, R.T., Eckburg, P.B., Turnbaugh, P.J., Samuel, B.S., Gordon, J.I., Relman, D.A., Fraser-Liggett, C.M., and Nelson, K.E. 2006. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science 312, 1355–1359.
Goehler, L.E., Park, S.M., Opitz, N., Lyte, M., and Gaykema, R.P. 2008. Campylobacter jejuni infection increases anxiety-like behavior in the holeboard: possible anatomical substrates for viscerosensory modulation of exploratory behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 22, 354–366.
Goldstone, A.P. 2006. The hypothalamus, hormones, and hunger: alterations in human obesity and illness. Prog. Brain Res. 153, 57–73.
Golubeva, A.V., Crampton, S., Desbonnet, L., Edge, D., O’Sullivan, O., Lomasney, K.W., Zhdanov, A.V., Crispie, F., Moloney, R.D., Borre, Y.E., et al. 2015. Prenatal stress-induced alterations in major physiological systems correlate with gut microbiota composition in adulthood. Psychoneuroendocrinology 60, 58–74.
Grenham, S., Clarke, G., Cryan, J.F., and Dinan, T.G. 2011. Brain-gutmicrobe communication in health and disease. Front. Physiol. 2, 94.
Grossi, E., Melli, S., Dunca, D., and Terruzzi, V. 2016. Unexpected improvement in core autism spectrum disorder symptoms after long-term treatment with probiotics. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 4, 2050313x16666231.
Guthrie, G.D. and Nicholson-Guthrie, C.S. 1989. γ-Aminobutyric acid uptake by a bacterial system with neurotransmitter binding characteristics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 7378–7381.
Harach, T., Marungruang, N., Duthilleul, N., Cheatham, V., Mc Coy, K.D., Frisoni, G., Neher, J.J., Fak, F., Jucker, M., Lasser, T., et al. 2017. Reduction of Aβ amyloid pathology in APPPS1 transgenic mice in the absence of gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 7, 41802.
Hardy, J. and Selkoe, D.J. 2002. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297, 353–356.
Hemarajata, P., Gao, C., Pflughoeft, K.J., Thomas, C.M., Saulnier, D.M., Spinler, J.K., and Versalovic, J. 2013. Lactobacillus reuteri-specific immunoregulatory gene rsiR modulates histamine production and immunomodulation by Lactobacillus reuteri. J. Bacteriol. 195, 5567–5576.
Hill, C., Guarner, F., Reid, G., Gibson, G.R., Merenstein, D.J., Pot, B., Morelli, L., Canani, R.B., Flint, H.J., Salminen, S., et al. 2014. Expert consensus document. The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 11, 506–514.
Holzer, P. and Farzi, A. 2014. Neuropeptides and the microbiotagut-brain axis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 817, 195–219.
Horn, T. and Klein, J. 2013. Neuroprotective effects of lactate in brain ischemia: dependence on anesthetic drugs. Neurochem. Int. 62, 251–257.
Hosoi, T., Okuma, Y., and Nomura, Y. 2002. The mechanisms of immune-to-brain communication in inflammation as a drug target. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 1, 257–262.
Hsiao, E.Y., McBride, S.W., Hsien, S., Sharon, G., Hyde, E.R., McCue, T., Codelli, J.A., Chow, J., Reisman, S.E., Petrosino, J.F., et al. 2013. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 155, 1451–1463.
Inan, M.S., Rasoulpour, R.J., Yin, L., Hubbard, A.K., Rosenberg, D.W., and Giardina, C. 2000. The luminal short-chain fatty acid butyrate modulates NF-kB activity in a human colonic epithelial cell line. Gastroenterology 118, 724–734.
Janik, R., Thomason, L.A.M., Stanisz, A.M., Forsythe, P., Bienenstock, J., and Stanisz, G.J. 2016. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals oral Lactobacillus promotion of increases in brain GABA, N-acetyl aspartate and glutamate. Neuroimage 125, 988–995.
Jiang, H., Ling, Z., Zhang, Y., Mao, H., Ma, Z., Yin, Y., Wang, W., Tang, W., Tan, Z., Shi, J., et al. 2015. Altered fecal microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 48, 186–194.
Kabouridis, P.S., Lasrado, R., McCallum, S., Chng, S.H., Snippert, H.J., Clevers, H., Pettersson, S., and Pachnis, V. 2015. Microbiota controls the homeostasis of glial cells in the gut lamina propria. Neuron 85, 289–295.
Kaluzna-Czaplinska, J. and Blaszczyk, S. 2012. The level of arabinitol in autistic children after probiotic therapy. Nutrition 28, 124–126.
Kang, D.W., Park, J.G., Ilhan, Z.E., Wallstrom, G., Labaer, J., Adams, J.B., and Krajmalnik-Brown, R. 2013. Reduced incidence of Prevotella and other fermenters in intestinal microflora of autistic children. PLoS One 8, e68322.
Kato-Kataoka, A., Nishida, K., Takada, M., Kawai, M., Kikuchi-Hayakawa, H., Suda, K., Ishikawa, H., Gondo, Y., Shimizu, K., Matsuki, T., et al. 2016. Fermented milk containing Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota preserves the diversity of the gut microbiota and relieves abdominal dysfunction in healthy medical students exposed to academic stress. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 82, 3649–3658.
Kawashima, K., Misawa, H., Moriwaki, Y., Fujii, Y.X., Fujii, T., Horiuchi, Y., Yamada, T., Imanaka, T., and Kamekura, M. 2007. Ubiquitous expression of acetylcholine and its biological functions in life forms without nervous systems. Life Sci. 80, 2206–2209.
Keshavarzian, A., Green, S.J., Engen, P.A., Voigt, R.M., Naqib, A., Forsyth, C.B., Mutlu, E., and Shannon, K.M. 2015. Colonic bacterial composition in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 30, 1351–1360.
Kimura, I., Ozawa, K., Inoue, D., Imamura, T., Kimura, K., Maeda, T., Terasawa, K., Kashihara, D., Hirano, K., Tani, T., et al. 2013. The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43. Nat. Commun. 4, 1829.
Kunze, W.A., Mao, Y.K., Wang, B., Huizinga, J.D., Ma, X., Forsythe, P., and Bienenstock, J. 2009. Lactobacillus reuteri enhances excitability of colonic AH neurons by inhibiting calcium-dependent potassium channel opening. J. Cell Mol. Med. 13, 2261–2270.
Landete, J.M., De las Rivas, B., Marcobal, A., and Munoz, R. 2008. Updated molecular knowledge about histamine biosynthesis by bacteria. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 48, 697–714.
Lim, S.K., Kwon, M.S., Lee, J., Oh, Y.J., Jang, J.Y., Lee, J.H., Park, H.W., Nam, Y.D., Seo, M.J., Roh, S.W., et al. 2017. Weissella cibaria WIKIM28 ameliorates atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions by inducing tolerogenic dendritic cells and regulatory T cells in BALB/c mice. Sci. Rep. 7, 40040.
Liu, X., Cao, S., and Zhang, X. 2015. Modulation of gut microbiotabrain axis by probiotics, prebiotics, and diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 63, 7885–7895.
Louveau, A., Smirnov, I., Keyes, T.J., Eccles, J.D., Rouhani, S.J., Peske, J.D., Derecki, N.C., Castle, D., Mandell, J.W., Lee, K.S., et al. 2015. Structural and functional features of central nervous system lymphatic vessels. Nature 523, 337–341.
Lyte, M. 2011. Probiotics function mechanistically as delivery vehicles for neuroactive compounds: Microbial endocrinology in the design and use of probiotics. BioEssays 33, 574–581.
Macfabe, D.F. 2012. Short-chain fatty acid fermentation products of the gut microbiome: implications in autism spectrum disorders. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 23, 19260.
Macfarlane, S. and Macfarlane, G.T. 2003. Regulation of short-chain fatty acid production. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 62, 67–72.
Macpherson, A.J. and Uhr, T. 2004. Compartmentalization of the mucosal immune responses to commensal intestinal bacteria. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1029, 36–43.
McCusker, R.H. and Kelley, K.W. 2013. Immune-neural connections: how the immune system’s response to infectious agents influences behavior. J. Exp. Biol. 216, 84–98.
McVey Neufeld, K.A., Mao, Y.K., Bienenstock, J., Foster, J.A., and Kunze, W.A. 2013. The microbiome is essential for normal gut intrinsic primary afferent neuron excitability in the mouse. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 25, e183–e188.
Messaoudi, M., Lalonde, R., Violle, N., Javelot, H., Desor, D., Nejdi, A., Bisson, J.F., Rougeot, C., Pichelin, M., Cazaubiel, M., et al. 2011a. Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 105, 755–764.
Messaoudi, M., Violle, N., Bisson, J.F., Desor, D., Javelot, H., and Rougeot, C. 2011b. Beneficial psychological effects of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in healthy human volunteers. Gut microbes 2, 256–261.
Meuer, K., Pitzer, C., Teismann, P., Kruger, C., Goricke, B., Laage, R., Lingor, P., Peters, K., Schlachetzki, J.C., Kobayashi, K., et al. 2006. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor is neuroprotective in a model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 97, 675–686.
Miller, A.H., Haroon, E., Raison, C.L., and Felger, J.C. 2013. Cytokine targets in the brain: impact on neurotransmitters and neurocircuits. Depress. Anxiety 30, 297–306.
Mountzouris, K.C., Tsirtsikos, P., Kalamara, E., Nitsch, S., Schatzmayr, G., and Fegeros, K. 2007. Evaluation of the efficacy of a probiotic containing Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Enterococcus, and Pediococcus strains in promoting broiler performance and modulating cecal microflora composition and metabolic activities. Poult. Sci. 86, 309–317.
O’Mahony, L., McCarthy, J., Kelly, P., Hurley, G., Luo, F., Chen, K., O’Sullivan, G.C., Kiely, B., Collins, J.K., Shanahan, F., et al. 2005. Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium in irritable bowel syndrome: symptom responses and relationship to cytokine profiles. Gastroenterology 128, 541–551.
O’Mahony, S.M., Marchesi, J.R., Scully, P., Codling, C., Ceolho, A.M., Quigley, E.M., Cryan, J.F., and Dinan, T.G. 2009. Early life stress alters behavior, immunity, and microbiota in rats: implications for irritable bowel syndrome and psychiatric illnesses. Biol. Psychiatry 65, 263–267.
Obermeier, B., Daneman, R., and Ransohoff, R.M. 2013. Development, maintenance and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Med. 19, 1584–1596.
Overduin, J., Schoterman, M.H., Calame, W., Schonewille, A.J., and Ten Bruggencate, S.J. 2013. Dietary galacto-oligosaccharides and calcium: effects on energy intake, fat-pad weight and satiety-related, gastrointestinal hormones in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 109, 1338–1348.
Özogul, F. 2011. Effects of specific lactic acid bacteria species on biogenic amine production by foodborne pathogen. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 46, 478–484.
Parracho, H.M., Bingham, M.O., Gibson, G.R., and McCartney, A.L. 2005. Differences between the gut microflora of children with autistic spectrum disorders and that of healthy children. J. Med. Microbiol. 54, 987–991.
Prakash, A., Medhi, B., and Chopra, K. 2013. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor (GCSF) improves memory and neurobehavior in an amyloid-beta induced experimental model of Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 110, 46–57.
Psichas, A., Sleeth, M.L., Murphy, K.G., Brooks, L., Bewick, G.A., Hanyaloglu, A.C., Ghatei, M.A., Bloom, S.R., and Frost, G. 2015. The short chain fatty acid propionate stimulates GLP-1 and PYY secretion via free fatty acid receptor 2 in rodents. Int. J. Obes. (Lond) 39, 424–429.
Rafiki, A., Boulland, J.L., Halestrap, A.P., Ottersen, O.P., and Bergersen, L. 2003. Highly differential expression of the monocarboxylate transporters MCT2 and MCT4 in the developing rat brain. Neuroscience 122, 677–688.
Rhee, S.H., Pothoulakis, C., and Mayer, E.A. 2009. Principles and clinical implications of the brain-gut-enteric microbiota axis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6, 306–314.
Rios-Covian, D., Ruas-Madiedo, P., Margolles, A., Gueimonde, M., de Los Reyes-Gavilan, C.G., and Salazar, N. 2016. Intestinal short chain fatty acids and their link with diet and human health. Front. Microbiol. 7, 185.
Sarkar, A., Lehto, S.M., Harty, S., Dinan, T.G., Cryan, J.F., and Burnet, P.W. 2016. Psychobiotics and the manipulation of bacteria-gutbrain signals. Trends Neurosci. 39, 763–781.
Savignac, H.M., Kiely, B., Dinan, T.G., and Cryan, J.F. 2014. Bifidobacteria exert strain-specific effects on stress-related behavior and physiology in BALB/c mice. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 26, 1615–1627.
Scheperjans, F., Aho, V., Pereira, P.A., Koskinen, K., Paulin, L., Pekkonen, E., Haapaniemi, E., Kaakkola, S., Eerola-Rautio, J., Pohja, M., et al. 2015. Gut microbiota are related to Parkinson’s disease and clinical phenotype. Mov. Disord. 30, 350–358.
Shyu, W.C., Lin, S.Z., Yang, H.I., Tzeng, Y.S., Pang, C.Y., Yen, P.S., and Li, H. 2004. Functional recovery of stroke rats induced by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-stimulated stem cells. Circulation 110, 1847–1854.
Song, Y., Liu, C., and Finegold, S.M. 2004. Real-time PCR quantitation of clostridia in feces of autistic children. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 6459–6465.
Steenbergen, L., Sellaro, R., van Hemert, S., Bosch, J.A., and Colzato, L.S. 2015. A randomized controlled trial to test the effect of multispecies probiotics on cognitive reactivity to sad mood. Brain Behav. Immun. 48, 258–264.
Stilling, R.M., Dinan, T.G., and Cryan, J.F. 2014. Microbial genes, brain & behaviour -epigenetic regulation of the gut-brain axis. Genes Brain Behav. 13, 69–86.
Strati, F., Cavalieri, D., Albanese, D., De Felice, C., Donati, C., Hayek, J., Jousson, O., Leoncini, S., Renzi, D., Calabro, A., et al. 2017. New evidences on the altered gut microbiota in autism spectrum disorders. Microbiome 5, 24.
Sudo, N., Chida, Y., Aiba, Y., Sonoda, J., Oyama, N., Yu, X.N., Kubo, C., and Koga, Y. 2004. Postnatal microbial colonization programs the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system for stress response in mice. J. Physiol. 558, 263–275.
Sun, B.L., Wang, L.H., Yang, T., Sun, J.Y., Mao, L.L., Yang, M.F., Yuan, H., Colvin, R.A., and Yang, X.Y. 2017. Lymphatic drainage system of the brain: A novel target for intervention of neurological diseases. Prog. Neurobiol. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.08.007 (in press).
Surwase, S.N. and Jadhav, J.P. 2011. Bioconversion of L-tyrosine to L-DOPA by a novel bacterium Bacillus sp. JPJ. Amino Acids 41, 495–506.
Thayer, J.F. and Sternberg, E.M. 2009. Neural concomitants of immunity-focus on the vagus nerve. Neuroimage 47, 908–910.
Thomas, C.M., Hong, T., van Pijkeren, J.P., Hemarajata, P., Trinh, D.V., Hu, W., Britton, R.A., Kalkum, M., and Versalovic, J. 2012. Histamine derived from probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri suppresses TNF via modulation of PKA and ERK signaling. PLoS One 7, e31951.
Tillisch, K. 2014. The effects of gut microbiota on CNS function in humans. Gut Microbes 5, 404–410.
Tillisch, K., Labus, J., Kilpatrick, L., Jiang, Z., Stains, J., Ebrat, B., Guyonnet, D., Legrain-Raspaud, S., Trotin, B., Naliboff, B., et al. 2013. Consumption of fermented milk product with probiotic modulates brain activity. Gastroenterology 144, 1394–1401.e4.
Tremaroli, V. and Backhed, F. 2012. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 489, 242–249.
Vetulani, J. 2013. Early maternal separation: a rodent model of depression and a prevailing human condition. Pharmacol. Rep. 65, 1451–1461.
Vogt, N.M., Kerby, R.L., Dill-McFarland, K.A., Harding, S.J., Merluzzi, A.P., Johnson, S.C., Carlsson, C.M., Asthana, S., Zetterberg, H., and Blennow, K. 2017. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 7, 13537.
Wallner, S., Peters, S., Pitzer, C., Resch, H., Bogdahn, U., and Schneider, A. 2015. The granulocyte-colony stimulating factor has a dual role in neuronal and vascular plasticity. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 3, 48.
Wang, L., Christophersen, C.T., Sorich, M.J., Gerber, J.P., Angley, M.T., and Conlon, M.A. 2011. Low relative abundances of the mucolytic bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila and Bifidobacterium spp. in feces of children with autism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 6718–6721.
Wang, L., Christophersen, C.T., Sorich, M.J., Gerber, J.P., Angley, M.T., and Conlon, M.A. 2013. Increased abundance of Sutterella spp. and Ruminococcus torques in feces of children with autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Autism 4, 42.
Wang, Y. and Kasper, L.H. 2014. The role of microbiome in central nervous system disorders. Brain. Behav. Immun. 38, 1–12.
Westfall, S., Lomis, N., Kahouli, I., Dia, S.Y., Singh, S.P., and Prakash, S. 2017. Microbiome, probiotics and neurodegenerative diseases: deciphering the gut brain axis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 74, 3769–3787.
Williams, B.B., Van Benschoten, A.H., Cimermancic, P., Donia, M.S., Zimmermann, M., Taketani, M., Ishihara, A., Kashyap, P.C., Fraser, J.S., and Fischbach, M.A. 2014. Discovery and characterization of gut microbiota decarboxylases that can produce the neurotransmitter tryptamine. Cell Host Microbe 16, 495–503.
Yang, N.J. and Chiu, I.M. 2017. Bacterial signaling to the nervous system through toxins and metabolites. J. Mol. Biol. 429, 587–605.
Yano, J.M., Yu, K., Donaldson, G.P., Shastri, G.G., Ann, P., Ma, L., Nagler, C.R., Ismagilov, R.F., Mazmanian, S.K., and Hsiao, E.Y. 2015. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 161, 264–276.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, N., Yun, M., Oh, Y.J. et al. Mind-altering with the gut: Modulation of the gut-brain axis with probiotics. J Microbiol. 56, 172–182 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-018-8032-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-018-8032-4