Abstract
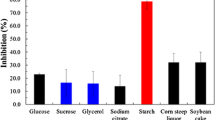
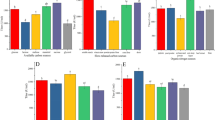
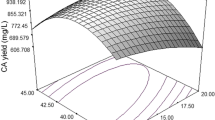
Antifungal lipopeptide produced by Bacillus sp. BH072 was extracted from fermentation liquor and determined as iturin A by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). For industrial-scale production, the yield of iturin A was improved by optimizing medium components and fermentation conditions. A one-factor test was conducted; fermentation conditions were then optimized by response surface methodology (RSM) to obtain the following: temperature, 29.5°C; pH 6.45; inoculation quantity, 6.7%; loading volume, 100 ml (in 500 ml flasks); and rotary speed, 150 rpm. Under these conditions, the mass concentration of iturin A was increased from 45.30 mg/ml to 47.87 mg/ml. The following components of the medium were determined: carbon sources (glucose, fructose, sucrose, xylose, rhamnose, and soluble starch); nitrogen sources (peptone, soybean meal, NH4Cl, urea, and ammonium citrate); and metal ions (Zn2+, Fe3+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Ca2+, and K+). The effects of these components on iturin A production were observed in LB medium. We selected sucrose, soybean meal, and Mg2+ for RSM to optimize the conditions because of several advantages, including maximum iturin A production, high antifungal activity, and low cost. The optimum concentrations of these components were 0.98% sucrose, 0.94% soybean meal, and 0.93% Mg2+. After iturin A production was optimized by RSM, the mass concentration reached 52.21 mg/ml. The antifungal specific activity was enhanced from 350.11 AU/mg to 513.92 AU/mg, which was 46.8% higher than the previous result. The present study provides an important experimental basis for the industrial-scale production of iturin A and the agricultural applications of Bacillus sp. BH072.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asaka, O. and Shoda, M. 1996. Biocontrol of Rhizoctonia solani Damping-Off of Tomato with Bacillus subtilis RB14. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62, 4081–4085.
Besson, F. and Michel, G. 1987. Isolation and characterization of new iturins: iturin D and iturin E. J. Antibiot. 40, 437–442.
Bonmatin, J.M., Laprevote, O., Peypoux, F. 2003. Diversity among microbial cyclic lipopeptides: Iturins and surfactins. Activity-structure relationships to design new bioactive agents. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen 6, 541–556.
Box, G.E.P. and Wilson, K.B. 1951. On the experimental attainment of optimum conditions. J. Royal. Statist. Soc. (Ser. B). 13, 1–5.
Buchanan, R.L. and Philips, J.G. 1990. Response surface model for predicting the effects of temperature, pH, sodium chloride content, sodium nitrite concentration and atmosphere on the growth of Listeria monocutogenes. J. Food Protect. 53, 370–374.
Chen, H., Wang, L., Su, C.X., Gong, G.H., Wang, P., and Yu, Z.L. 2008. Isolation and characterization of lipopeptide antibiotics produced by Bacillus subtilis. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 47, 180–186.
Delcambe, L., Peypoux, F., and Besson, F. 1977. Structure of iturin and iturin-like substances [proceedings]. Biochem. Soc. T. 5, 1122–1124.
Eshita, S.M., Roberto, N.H., Beale, J.M., Mamiya, B.M., and Workman, R.F. 1995. Bacillomycin L(c), a new antibiotic of the iturin group-isolations, structures, and antifungal activities of the congeners. J. Antibiot. 48, 1240–1247.
Fábio, C.S., Danilo, D.F., Hilario, C.M., Flávia, M.L.P., Patrizia, P., and Attilio, C. 2006. Use of response surface methodology for optimization of xylitol production by the new yeast strain Debaryomyces hansenii UFV-170. J. Food Eng. 76, 376–386.
Gangadharan, R., Anandan, V., and Zhang, G. 2008. Optimizing the functionalization process for nanopillar enhanced electrodes with GOx/PPY for glucose detection. Nanotechnology 19, 1–7.
Gu, X.B., Zheng, Z.M., Yu, H.Q., Wang, J., Liang, F.L., and Liu, R.L. 2005. Optimization of medium constituents for a novel lipopeptide production by Bacillus subtilis MO-01 by a response surface method. Process Biochem. 40, 3196–3201.
Haltrich, D., Press, M., and Steiner, W. 1993. Optimization of a culture medium for increased xylanase production by a wild strain of Schizophyllum commune. Enzyme Microbiol. Technol. 15, 854–859.
Huang, X.Q., Wang, Y.F., Cui, Y.H., and Hua, X. 2010. Optimization of antifungal effect of surfactin and iturin to Penicillium notatum in syrup of peach by RSM. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 16, 63–69.
Katz, E. and Demain, A.C. 1977. The peptide antibiotics of Bacillus: chemistry, biogenesis, and possible functions. Bacteriol. Rev. 41, 449–474.
Kim, P.I., Ryu, J., Kim, Y.H., and Chi, Y.T. 2010. Production of biosurfactant lipopeptides Iturin A Fengycin and Surfactin A from Bacillus subtilis CMB32 for control of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 20, 138–145.
Kuo, C.Y. 2006. Optimization of cultivation conditions for iturin A production by Bacillus subtilis using solid state fermentation. Master Thesis. Da-Yeh University, Taiwan.
Maget-Dana, R. and Peypoux, F. 1994. Iturins, a special class of pore-forming lipopeptides: biological and physicochemical properties. Toxicol. 87, 151–174.
Mizumoto, S. and Shoda, M. 2007. Medium optimization of antifungal lipopeptide, iturin A, production by Bacillus subtilis in solid-state fermentation by response surface methodology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 76, 101–108.
Motta, A.S. and Brandelli, A. 2002. Characterization of an antibacterial peptide produced by Brevibacterium linens. J. Appl. Microbiol. 92, 63–70.
Mullai, P., Yogeswari, M.K., and Sridevi, K. 2013. Optimisation and enhancement of biohydrogen production using nickel nanoparticles-A novel approach. Bioresour. Technol. 141, 212–219.
Nihorimbere, V., Cawoy, H., Seyer, A., Brunelle, A., Thonart, P., and Ongena, M. 2012. Impact of rhizosphere factors on cyclic lipopeptide signature from the plant beneficial strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens S499. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 79, 176–191.
Ongena, M. and Jacques, P. 2008. Bacillus lipopeptides: versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol. Trends Microbiol. 16, 115–125.
Ongena, M., Jacques, P., Toure, Y., Destain, J., Jabrane, A., and Thonart, P. 2005. Involvement of fengycin-type lipopeptides in the multifaceted biocontrol potential of Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 69, 29–38.
Peypoux, F., Bonmatin, J.M., and Wallach, J. 1999. Recent trends in the biochemistry of surfactin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 51, 553–563.
Phae, C.G. and Shoda, M. 1990. Investigation of optimal conditions for foam separation of iturin, and antifungal peptide produced by Bacillus subtilis. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 71, 118–121.
Phae, C.G. and Shoda, M. 1991. A new fungus which degrades hydrogen sulfide, methanethiol, dimethyl sulfide and dimethyl disulfide. Biotechnol. Lett. 13, 375–380.
Phae, C.G., Shoda, M., and Kita, N. 1992. Biological control of crown and root rot and bacterial wilt of tomato by Bacillus subtilis NB22. Annal. Phytopathol. Society Japan 58, 329–339.
Prapulla, S.G., Jacob, S., Chand, N., Rajalakshmi, D., and Karanth, N.G. 1992. Maximization of lipid production by rhodotroula gracilis CFR-1 using response surface methodology. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 40, 965–969.
Romero, D., de Vicentev, A., Rakotoalyv, R.H., Dufour, S.E., Veening, J.W., Arrebola, E., Cazorla, F.M., Kuipers, O.P., Paquot, M., and Perez-Garcia, A. 2007. The iturin and fengycin families of lipopeptides are key factors in antagonism of Bacillus subtilis toward Podosphaera fusca. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 20, 430–440.
Roongsawang, N., Washio, K., and Morikawa, M. 2011. Diversity of nonribosomal peptide synthetases involved in the biosynthesis of lipopeptide biosurfactants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12, 141–172.
Shih, I.L. and Shen, M.H. 2006. Application of response surface methodology to optimize production of poly(e-lysine) by streptomyces albulus IFO14147. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 39, 15–21.
Shih, I.L., Van, Y.T., and Chang, Y.N. 2002. Application of statistical experimental methods to optimize production of poly(g-glutamic acid) by Bacillus licheniformis CCRC 12826. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 31, 213–220.
Tenoux, I., Besson, F., and Michel, G. 1991. Studies on the antifungal antibiotics: bacillomycin D and bacillomycin D methylester. Microbios 67, 187–193.
Toure, Y., Ongena, M., Jacques, P., Guiro, A., and Thonart, P.J. 2004. Role of lipopeptides produced by Bacillus subtilis GA1 in the reduction of grey mould disease caused by Botrytis cinerea on apple. Appl. Microbiol. 96, 1151–1160.
Yang, J., Ji, J.Y., Kang, Z.S., and Huang, L.L. 2012. Optimization of fermentation conditions of antifungal lipopeptide produced by Bacillus subtilis E1R-j. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinia. 21, 54–60.
Yao, D.H., Ji, Z.X., Wang, C.J., Qi, G.F., Zhang, L.L., Ma, X., and Chen, S.W. 2012. Co-producing iturin A and poly-c-glutamic acid from rapeseed meal under solid state fermentation by the newly isolated Bacillus subtilis strain 3–10. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 28, 985–991.
Zhang, Y., Zhang, Q.J., Feng, X.H., Li, S., Xia, J., and Xu, H. 2012. A novel agar diffusion assay for qualitative and quantitative estimation of epsilon-polylysine in fermentation broths and foods. Food Res. Int. 48, 49–56.
Zhao, P.C., Quan, C.S., Jin, L.M., Wang, L.N., Wang, J.H., and Fan, S.D. 2013a. Effects of critical medium components on the production of antifungal lipopeptides from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Q-426 exhibiting excellent biosurfactant properties. World J. Microb. Biotechnol. 29, 401–409.
Zhao, X., Zhou, Z.J., Han, Y., Wang, Z.Z., Fan, J., and Xiao, H.Z. 2013b. Isolation and identification of antifungal peptides from Bacillus BH072, a novel bacterium isolated from honey. Microbiol. Res. 168, 598–606.
Zhao, Z., Wang, Q., Wang, K., Brian, K., Liu, C., and Gu, Y. 2010. Study of the antifungal activity of Bacillus vallismortis ZZ185 in vitro and identification of its antifungal components. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 292–297.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Han, Y., Tan, Xq. et al. Optimization of antifungal lipopeptide production from Bacillus sp. BH072 by response surface methodology. J Microbiol. 52, 324–332 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-014-3354-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-014-3354-3