Abstract
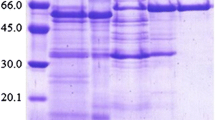
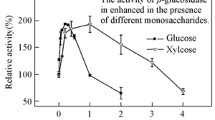
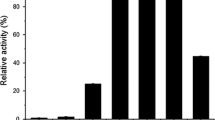
An α-glucosidase enzyme produced by the fungus Thermoascus aurantiacus CBMAI 756 was purified by ultra filtration, ammonium sulphate precipitation, and chromatography using Q Sepharose, Sephacryl S-200, and Superose 12 columns. The apparent molecular mass of the enzyme was 83 kDa as determined in gel electrophoresis. Maximum activity was observed at pH 4.5 at 70°C. Enzyme showed stability stable in the pH range of 3.0–9.0 and lost 40% of its initial activity at the temperatures of 40, 50, and 60°C. In the presence of ions Na+, Ba2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Al3+, Zn2+, Ca2+ this enzyme maintained 90–105% of its maximum activity and was inhibited by Cr3+, Ag+, and Hg2+. The enzyme showed a transglycosylation property, by the release of oligosaccharides after 3 h of incubation with maltose, and specificity for short maltooligosaccharides and α-PNPG. The Km measured for the α-glucosidase was 0.07 μM, with a Vmax of 318.0 μmol/min/mg.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anindyawati, T., Y.G. Ann, K. Ito, M. Izzuka, and N. Minamiura. 1998. Two kinds of novel α-glucosidases from Aspergillus awamori KT-11: their purifications, properties, and specificities. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 85, 465–469.
Bergmeyer, H.U. and E. Bernt. 1974. Methods of enzymatic analysis, pp. 1205–1215. In H.U. Bergmeyer (ed.). Verlag Chimie/Academic Press, New York, N.Y., USA.
Blum, H., H. Bier, and H.J. Gross. 1987. Improved silver staining of plant-proteins, RNA and DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Eletrophoresis 8, 93–99.
Bravo-Torres, J.C., J.C. Villagómez-Castro, C. Calvo-Méndez, A. Flores-Carreón, and E. López-Romero. 2004. Purification and biochemical characterization of a membrane-bound α-glucosidase from the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Int. J. Parasitol. 34, 455–462.
Brienzo, M., V. Arantes, and A.M.F. Milagres. 2008. Enzymology of the thermophilic ascomycetous fungus Thermoascus aurantiacus. Fungal Biol. Rev. 22, 120–130.
Carvalho, A.F.A., A.Z. Gonçalves, R. Silva, and E. Gomes. 2006. A specific short dextrin-hydrolyzing extracellular glucosidase from the thermophilic fungus Thermoascus aurantiacus 179-5. J. Microbiol. 44, 276–283.
Chiba, S. 1997. Molecular mechanism in α-glucosidase and glucoamylase. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 61, 1233–1239.
Constantino, H.R., S.H. Brown, and R.M. Kelly. 1990. Purification and characterization of an α-glucosidase from a hyperthermophilic archaebacterium, Pyrococcus furiosus, exhibiting a temperature optimum of 105 to 115°C. J. Bacteriol. 172, 3654–3660.
Dubois, M., K.A. Gilles, J.K. Hamilton, P.A. Robers, and F. Smith. 1956. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 28, 350–356.
Ezeji, T.C. and H. Bahl. 2006. Purification, characterization, and synergistic action of phytate-resistant α-amylase and α-glucosidase from Geobacillus thermodenitrificans HRO10. J. Biotechnol. 125, 27–38.
Faridmoayer, A. and C.H. Scaman. 2004. An improved purification procedure for soluble processing α-glucosidase I from Saccharomyces cerevisiae overexpressing CWH41. Protein Expr. Purif. 33, 11–18.
Fernánez-Arrojo, L., D. Marín, A.G. Segura, D. Linde, M. Alcalde, P. Gutiérrez-Alonso, I. Ghazi, F.J. Plou, M. Fernandéz-lobato, and A. Ballesteros. 2007. Transformation of maltose into prebiotic isomaltooligosaccharides by a novel α-glucosidase from Xantophyllomyces dendrorhous. Process Biochem. 42, 1530–1536.
Fontana, J.D., M. Gebara, M. Blumel, H. Schneider, C.R. Mackenzie, and K.G. Johnson. 1988. α-4-O-methyl-glucuronidase component of xylanolytic complexes. Methods Enzymol. 169, 560–571.
Frandsen, T. and B. Svensson. 1998. Plant α-glucosidases of the glycoside hydrolase family 31 molecular properties, substrate specificity, resction mechanism, and comparison with family members of different origin. Plant Mol. Biol. 37, 1–13.
Gabriel, O. and S.F. Wang. 1969. Determination of enzymatic activity in polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 27, 545–554.
Giannesi, G.C., M.L.T.M. Polizeli, H.F. Terzine, and J.A. Jorge. 2006. A novel α-glucosidase from Chaetomium thermophilum var. coprophilum that converts maltose into trehalose: Purification and partial characterization of the enzyme. Process Biochem. 41, 1729–1735.
Hartree, E.F. 1972. Determination of protein: A modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal. Biochem. 48, 422–427.
Herscovics, A. 1999. Processing glycosidases of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1426, 275–285.
Iwata, H., T. Suzuki, and I. Aramaki. 2003. Purification and characterization of rice α-glucosidase, a key enzyme for alcohol fermentation of rice polish. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 95, 106–108.
Kashiwabara, S.S., S. Azuma, M. Tsuduki, and Y. Suzuki. 2000. The primary structure of the subunit in Bacillus thermoamyloliquefaciens KP1071 molecular mass 540,000 homohexameric α-glucosidase II belonging to the glycosyl hydrolae family 31. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 64, 1379–1393.
Kato, N., S. Suyama, M. Shirokane, M. Kato, T. Kobayashi, and N. Tsukagoshi. 2002. Novel α-glucosidase from Aspergillus nidulans with strong transglycosylation activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 1250–1256.
Kim, K.Y., H. Nam, H. Kurihara, and S.M. Kim. 2008. Potent α-glucosidase inhibitors purified from the red alga Grateloupia elliptica. Phytochemistry 69, 2820–2825.
Kumar, S. and T. Satyanarayana. 2003. Purification and kineties of a raw starch-hydrolyzing, termostable, and neutral glucoamylase of the thermophylic mold Thermomucor indicae-seudaticae. Biotechnol. Prog. 19, 936–944.
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural protein during the assembly of head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685.
Leite, R.S.R., E. Gomes, and R. Silva. 2007. Characterization and comparison of thermostability of purified β-glucosidases from a mesophilic Aureobasidium pullulans and a thermophilic Thermoascus aurantiacus. Process Biochem. 42, 1101–1106.
Li, K.B. and K.Y. Chan. 1983. Production and properties of α-glucosidase from Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 46, 1380–1387.
Martino, A., C. Schiraldi, S. Fusco, I. Di Lernia, T. Costabile, T. Pellicano, M. Marotta, and et al. 2001. Properties of the recombinant α-glucosidase from Sulfolobus solfataricus in relation to strach processing. J. Mol. Catal. B-Enzym. 11, 787–794.
Mehta, A., N. Zitzmann, P.M. Rudd, T.M. Block, and R.A. Dwek. 1998. α-Glucosidase inhibitors as potential broad based anti-viral agents. FEBS Lett. 430, 17–22.
Melo, E.B., A.S. Gomes, and I. Carvalho. 2006. α- and β-Glucosidase inhibitors: chemical structure and biological activity. Tetrahedron 62, 10277–10302.
Merheb, C.W., H. Cabral, E. Gomes, and R. Da Silva. 2007. Partial characterization of protease from a thermophilic fungus, Thermoascus aurantiacus, and its hydrolytic activity on bovine casein. Food Chem. 104, 127–131.
Murata, T. and T. Usui. 2006. Enzymatic synthesis of oligosaccharides and neoglycoconjugates. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 70, 1049–1059.
Naested, H., B. Kramhøft, F. Lok, K. Bojsen, S. Yu, and B. Svensson. 2006. Production of enzymatically active recombinant full-length barley high pI α-glucosidase of glycoside family 31 by high celldensity fermentation of Pichia pastoris and affinity purification. Protein Expr. Purif. 46, 56–63.
Nashiru, O., S. Koh, S.Y. Lee, and D.S. Lee. 2001. Novel α-glucosidase from extreme thermophile Thermus caldophilus GK24. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 34, 347–354.
Okuyama, M., Y. Tanimoto, T. Ito, A. Anzai, H. Mori, A. Kimura, H. Matsui, and S. Chiba. 2005. Purification and characterization of the hyper-glycosylated extracellular α-glucosidase from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 37, 472–480.
Palma-Fernandez, E.R.D., E. Gomes, and R. Da Silva. 2002. Purification and characterization of two β-glucosidases from thermophilic fungus Thermoascus aurantiacus. Folia Microbiol. 47, 685–690.
Piller, K., R.M. Daniel, and H.H. Petach. 1996. Properties and stabilization of an extracellular α-glucosidase from the extremely thermophilic archaebacteria Thermococcus strain AN1: enzyme activity at 130°C. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1292, 197–205.
Schiraldi, C., A. Martino, T. Costabile, M. Generoso, M. Marotta, and M. De Rosa. 2004. Glucose production from maltodextrins employing a thermophilic immobilized cell biocatalyst in a packedbed reactor. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 34, 415–421.
Shimba, N., M. Shinagawa, W. Hoshino, H. Yamaguchi, N. Yamada, and E. Suzuki. 2009. Monitoring the hydrolysis and transglycosylation activity of α-glucosidase from Aspergillus niger by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 393, 23–28.
Soro, R.Y., J.K. Diopoh, R.M. Willemot, and D. Combes. 2007. Enzymatic synthesis of polyglucosylfructosides from sucrose alone α-glucosidase isolated from the digestive juice of Archachatina ventricosa (Achatinideae). Enzyme Microb. Technol. 42, 44–51.
Sugimoto, M. and Y. Suzuki. 1994. Hydrolytic action on the mixture of maltose and soluble starch by α-glucosidase from Mucor javanicus IFO4570. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 58, 1535–1536.
Tanaka, Y., T. Aki, Y. Hidaka, Y. Furuya, S. Kawamoto, S. Shigeta, K. Ono, and O. Sizuki. 2002. Purification and characterization of a novel fungal α-glucosidase from Mortirella alliacea with high starch-hydrolitic actvity. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 66, 2415–2423.
Torre-Bouscoulet, M.E., E. López-Romero, R. Balcázar-Orozco, C. Calvo-Méndez, and A. Flores-Carreón. 2004. Partial purification and biochemical characterization of a soluble α-glucosidase II-like activity from Candida albicans. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 236, 123–128.
Vieille, C. and J.G. Zeikus. 2001. Hyperthermophilic enzymes: sources, uses, and molecular mechanisms for thermostability. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 65, 1–43.
Wang, Y., L. Ma, Z. Li, Z. Du, Z. Liu, J. Qin, X. Wang, Z. Huang, L. Gu, and A.S.C. Chen. 2004. Synergetic inhibition of metal ions and genistein on α-glucosidase. FEBS Lett. 576, 46–50.
Watanabe, K., H. Uchino, C. Ohmura, Y. Tanaka, T. Onuma, and R. Kawamori. 2004. Different effects of two α-glucosidase inhibitors, acarbose and voglibose, on serum 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5AG) level. J. Diabetes Complications 18, 183–186.
Yamamoto, T., T. Unno, Y. Watanabe, M. Yamamoto, M. Okuyama, H. Mori, S. Chiba, and A. Kimura. 2004. Purification and characterization of Acremonium implicatum α-glucosidase having regioselectivity for α-1,3-glucosidic linkage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1700, 189–198.
Yamasaki, Y., T. Miyake, and Y. Suzuki. 1973. Properties of crystalline α-glucosidase from Mucor javanicus. Agr. Biol. Chem. 37, 251–259.
Zacharius, R.M., T.E.Z.H. Morrisson, and J.J. Woodlock. 1969. Glycoprotein staing following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 30, 148–152.
Zdzieblo, A. and J. Synowiecki. 2002. New source of the thermostable α-glucosidase suitable for single step starch processing. Food Chem. 79, 485–491.
Zhou, C., Y. Xue, Y. Zhang, Y. Zeng, and Y. Ma. 2009. Recombinant expression and characterization of Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis thermostable α-glucosidase with regioselectivity for high-yield isomaltooligosaccharides synthesis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 19, 1547–1556.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carvalho, A.F.A., Boscolo, M., da Silva, R. et al. Purification and characterization of the α-glucosidase produced by thermophilic fungus Thermoascus aurantiacus CBMAI 756. J Microbiol. 48, 452–459 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-9319-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-9319-2