Abstract
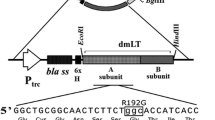
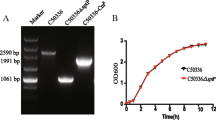
To protect chickens from typhoid caused by Salmonella enterica serovar Gallinarum (S. Gallinarum), the attenuated 9R strain has been used in the field as a vaccine. However, safety concerns have been raised because the mutations in 9R are undefined while its efficacy is still a question under debate. A global regulator, ppGpp, synthesized by RelA and SpoT, has been shown to induce various virulence genes in S. Gallinarum (Jeong et al., 2008). In this study, two mutant strains defective in ppGpp-synthesis were constructed in wild-type S. Gallinarum (ΔppGpp) and 9R strain (9R-ΔppGpp) backgrounds and tested as live vaccines in chickens. After oral inoculation, the LD50 values of ΔppGpp and 9R-ΔppGpp were approximately 5×1010 colony forming unit (CFU) similarly as 9R strain, which was ∼105-fold higher than that of the wildtype S. Gallinarum strain. Immunological analyses revealed immunization with either of the two attenuated ppGpp-defective strains induced significant antibody responses, the production of antibody-secreting B cells in blood, proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the spleen, and splenic expression of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IFN-γ and TGF-β4, at levels comparable to the 9R strain. Chickens immunized with the mutants (1×108 CFU) were 80% protected against oral challenge with 1×109 wild-type virulent bacteria (4,000-fold LD50 dose), similar to the level of protection achieved by 9R immunization. Based on these data, live attenuated ΔppGpp-defective strains may serve as novel vaccines to control fowl typhoid in chickens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altier, C. 2005. Genetic and environmental control of salmonella invasion. J. Microbiol. 43, 85–92.
Alvarez, M.T., N. Ledesma, G. Tellez, J.L. Molinari, and P. Tato. 2003. Comparison of the immune responses against Salmonella enterica serovar Gallinarum infection between naked neck chickens and a commercial chicken line. Avian Pathol. 32, 193–203.
Babu, U., R.A. Dalloul, M. Okamura, H.S. Lillehoj, H. Xie, R.B. Raybourne, D. Gaines, and R.A. Heckert. 2004. Salmonella enteritidis clearance and immune responses in chickens following Salmonella vaccination and challenge. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 101, 251–257.
Babu, U., M. Scott, M.J. Myers, M. Okamura, D. Gaines, H.F. Yancy, H. Lillehoj, R.A. Heckert, and R.B. Raybourne. 2003. Effects of live attenuated and killed Salmonella vaccine on T-lymphocyte mediated immunity in laying hens. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 91, 39–44.
Barrow, P.A., M.B. Huggins, and M.A. Lovell. 1994. Host specificity of Salmonella infection in chickens and mice is expressed in vivo primarily at the level of the reticuloendothelial system. Infect. Immun. 62, 4602–4610.
Barrow, P.A., M.A. Lovell, and A. Berchieri. 1990. Immunisation of laying hens against Salmonella enteritidis with live attenuated vaccines. Vet. Rec. 126, 241–242.
Beal, R.K., C. Powers, P. Wigley, P.A. Barrow, and A.L. Smith. 2004a. Temporal dynamics of the cellular, humoral and cytokine responses in chickens during primary and secondary infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Avian Pathol. 33, 25–33.
Beal, R.K., P. Wigley, C. Powers, S.D. Hulme, P.A. Barrow, and A.L. Smith. 2004b. Age at primary infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in the chicken influences persistence of infection and subsequent immunity to re-challenge. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 100, 151–164.
Berndt, A. and U. Methner. 2001. Gamma/delta T cell response of chickens after oral administration of attenuated and nonattenuated Salmonella typhimurium strains. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 78, 143–161.
Bohls, R.L., R. Smitha, P.J. Ferroa, N.J. Silvyb, Z. Lia, and E. Collissona. 2006. The use of flow cytometry to discriminate avian lymphocytes from contaminating thrombocytes. Developmental Comparative Immunol. 30, 843–850.
Cashel, M. and J. Gallant. 1968. Control of RNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. I. Amino acid dependence of the synthesis of the substrates of RNA polymerase. J. Mol. Biol. 34, 317–330.
Cashel, M., D.R. Gentry, V.J. Hernandez, and D. Vinella. 1996. The stringent response. ASM Press, Washington, D.C., USA.
Datsenko, K.A. and B.L. Wanner. 2000. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6640–6645.
Dueger, E.L., J.K. House, D.M. Heithoff, and M.J. Mahan. 2001. Salmonella DNA adenine methylase mutants elicit protective immune responses to homologous and heterologous serovars in chickens. Infect. Immun. 69, 7950–7954.
Feberwee, A., T.S. de Vries, A.R. Elbers, and W.A. de Jong. 2000. Results of a Salmonella enteritidis vaccination field trial in broilerbreeder flocks in The Netherlands. Avian Dis. 44, 249–255.
Jeong, J.H., M. Song, S.I. Park, K.O. Cho, J.H. Rhee, and H.E. Choy. 2008. Salmonella enterica serovar gallinarum requires ppGpp for internalization and survival in animal cells. J. Bacteriol. 190, 6340–6350.
Jones, B.D., N. Ghori, and S. Falkow. 1994. Salmonella typhimurium initiates murine infection by penetrating and destroying the specialized epithelial M cells of the Peyer’s patches. J. Exp. Med. 180, 15–23.
Jones, M.A., P. Wigley, K.L. Page, S.D. Hulme, and P.A. Barrow. 2001. Salmonella enterica serovar Gallinarum requires the Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 type III secretion system but not the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 type III secretion system for virulence in chickens. Infect. Immun. 69, 5471–5476.
Kaiser, P., L. Rothwell, E.E. Galyov, P.A. Barrow, J. Burnside, and P. Wigley. 2000. Differential cytokine expression in avian cells in response to invasion by Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella gallinarum. Microbiology 146, 3217–3226.
Kemeny, D.M. and S.J. Challacombe. 1988. ELISA and Other Solid Phase Immunoassays. John Wiley and Sons Ltd., Chichester, UK.
Kim, C.J., K.V. Nagaraja, and B.S. Pomeroy. 1991. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of Salmonella enteritidis infection in chickens. Am. J. Vet. Res. 52, 1069–1074.
Kogut, M.H., L. Rothwell, and P. Kaiser. 2003. Differential regulation of cytokine gene expression by avian heterophils during receptormediated phagocytosis of opsonized and nonopsonized Salmonella enteritidis. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 23, 319–327.
Lee, A.K., C.S. Detweiler, and S. Falkow. 2000. OmpR regulates the two-component system SsrA-ssrB in Salmonella pathogenicity island 2. J. Bacteriol. 182, 771–781.
Lee, Y.J., I.P. Mo, and M.S. Kang. 2007. Protective efficacy of live Salmonella gallinarum 9R vaccine in commercial layer flocks. Avian Pathol. 36, 495–498.
Lucas, R.L. and C.A. Lee. 2000. Unravelling the mysteries of virulence gene regulation in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 36, 1024–1033.
Lundin, B.S., C. Johansson, and A.M. Svennerholm. 2002. Oral immunization with a Salmonella enterica serovar typhi vaccine induces specific circulating mucosa-homing CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells in humans. Infect. Immun. 70, 5622–5627.
Marcus, S.L., J.H. Brumell, C.G. Pfeifer, and B.B. Finlay. 2000. Salmonella pathogenicity islands: big virulence in small packages. Microb. Infect. 2, 145–156.
Na, H.S., H.J. Kim, H.C. Lee, Y. Hong, J.H. Rhee, and H.E. Choy. 2006. Immune response induced by Salmonella typhimurium defective in ppGpp synthesis. Vaccine 24, 2027–2034.
Pizarro-Cerda, J. and K. Tedin. 2004. The bacterial signal molecule, ppGpp, regulates Salmonella virulence gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 52, 1827–1844.
Reed, L.J. and H. Muench. 1938. A simple method for estimating fifty percent end points. Am. J. Hyg. 27, 493–497.
Salerno-Goncalves, R., M.F. Pasetti, and M.B. Sztein. 2002. Characterization of CD8(+) effector T cell responses in volunteers immunized with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi strain Ty21a typhoid vaccine. J. Immunol. 169, 2196–2203.
Sands, M.K. and R.B. Roberts. 1952. The effects of a tryptophanhistidine deficiency in a mutant of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 63, 505–511.
Shivaprasad, H.L. 2000. Fowl typhoid and pullorum disease. Rev. Sci. Tech. 19, 405–424.
Silva, E.N., G.H. Snoeyenbos, O.M. Weinack, and C.F. Smyser. 1981. Studies on the use of 9R strain of Salmonella gallinarum as a vaccine in chickens. Avian Dis. 25, 38–52.
Smith, H.W. 1956. The use of live vaccines in experimental Salmonella gallinarum infection in chickens with observations on their interference effect. J. Hyg. (Lond). 54, 419–432.
Song, M., H.J. Kim, E.Y. Kim, M. Shin, H.C. Lee, Y. Hong, J.H. Rhee, H. Yoon, S. Ryu, S. Lim, and H.E. Choy. 2004. ppGppdependent stationary phase induction of genes on Salmonella pathogenicity island 1. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 34183–34190.
Wigley, P., S.D. Hulme, N. Bumstead, and P.A. Barrow. 2002. In vivo and in vitro studies of genetic resistance to systemic salmonellosis in the chicken encoded by the SAL1 locus. Microb. Infect. 4, 1111–1120.
Wigley, P., S.D. Hulme, C. Powers, R.K. Beal, A. Berchieri, Jr., A. Smith, and P. Barrow. 2005. Infection of the reproductive tract and eggs with Salmonella enterica serovar pullorum in the chicken is associated with suppression of cellular immunity at sexual maturity. Infect. Immun. 73, 2986–2990.
Woodward, M.J., G. Gettinby, M.F. Breslin, J.D. Corkish, and S. Houghton. 2002. The efficacy of Salenvac, a Salmonella enterica subsp. Enterica serotype Enteritidis iron-restricted bacterin vaccine, in laying chickens. Avian Pathol. 31, 383–392.
Yuan, L., L.A. Ward, B.I. Rosen, T.L. To, and L.J. Saif. 1996. Systematic and intestinal antibody-secreting cell responses and correlates of protective immunity to human rotavirus in a gnotobiotic pig model of disease. J. Virol. 70, 3075–3083.
Zhang-Barber, L., A.K. Turner, and P.A. Barrow. 1999. Vaccination for control of Salmonella in poultry. Vaccine 17, 2538–2545.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, SI., Jeong, JH., Choy, H.E. et al. Immune response induced by ppGpp-defective Salmonella enterica serovar Gallinarum in chickens. J Microbiol. 48, 674–681 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0179-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0179-6