Abstract
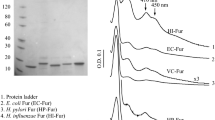
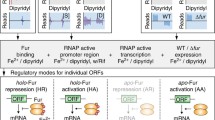
The Ferric Uptake Regulator (Fur) is a transcriptional regulator that is conserved across a broad number of bacterial species and has been shown to regulate expression of iron uptake and storage genes. Additionally, Fur has been shown to be an important colonization factor of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. In H. pylori, Fur-dependent regulation appears to be unique in that Fur is able to act as a transcriptional repressor when bound to iron as well as in its iron free (apo) form. To date, apo-regulation has not been identified in any other bacterium. To determine whether Fur from other species has the capacity for apo-regulation, we investigated the ability of Fur from Escherichia coli, Campylobacter jejuni, Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Vibrio cholerae to complement both iron-bound and apo-Fur regulation within the context of a H. pylori fur mutant. We found that while some Fur species (E. coli, C. jejuni, and V. cholerae) complemented iron-bound regulation, apo-regulation was unable to be complemented by any of the examined species. These data suggest that despite the conservation among bacterial Fur proteins, H. pylori Fur contains unique structure/function features that make it novel in comparison to Fur from other species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alm, R.A., L.S. Ling, D.T. Moir, B.L. King, E.D. Brown, P.C. Doig, D.R. Smith, and et al. 1999. Genomic-sequence comparison of two unrelated isolates of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 397, 176–180.
Andrews, S.C., A.K. Robinson, and F. Rodriguez-Quinones. 2003. Bacterial iron homeostasis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 27, 215–237.
Baltrus, D.A., M.R. Amieva, A. Covacci, T.M. Lowe, D.S. Merrell, K.M. Ottemann, M. Stein, N.R. Salama, and K. Guillemin. 2009. The complete genome sequence of Helicobacter pylori strain G27. J. Bacteriol. 191, 447–448.
Bender, K.S., H.C. Yen, C.L. Hemme, Z. Yang, Z. He, Q. He, J. Zhou, K.H. Huang, E.J. Alm, T.C. Hazen, A.P. Arkin, and J.D. Wall. 2007. Analysis of a ferric uptake regulator (Fur) mutant of Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 5389–5400.
Bereswill, S., S. Greiner, A.H. van Vliet, B. Waidner, F. Fassbinder, E. Schiltz, J.G. Kusters, and M. Kist 2000. Regulation of ferritinmediated cytoplasmic iron storage by the ferric uptake regulator homolog (Fur) of Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 182, 5948–5953.
Bereswill, S., F. Lichte, S. Greiner, B. Waidner, F. Fassbinder, and M. Kist. 1999. The ferric uptake regulator (Fur) homologue of Helicobacter pylori: functional analysis of the coding gene and controlled production of the recombinant protein in Escherichia coli. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 188, 31–40.
Bijlsma, J.J., A.L.M. Lie, I.C. Nootenboom, C.M. Vandenbroucke-Grauls, and J.G. Kusters. 2000. Identification of loci essential for the growth of Helicobacter pylori under acidic conditions. J. Infect. Dis. 182, 1566–1569.
Bijlsma, J.J., B. Waidner, A.H. Vliet, N.J. Hughes, S. Hag, S. Bereswill, D.J. Kelly, C.M. Vandenbroucke-Grauls, M. Kist, and J.G. Kusters. 2002. The Helicobacter pylori homologue of the ferric uptake regulator is involved in acid resistance. Infect. Immun. 70, 606–611.
Blaser, M.J. 1998. Helicobacter pylori and gastric diseases. BMJ 316, 1507–1510.
Bury-Mone, S., J.M. Thiberge, M. Contreras, A. Maitournam, A. Labigne, and H. De Reuse. 2004. Responsiveness to acidity via metal ion regulators mediates virulence in the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Microbiol. 53, 623–638.
Campanella, J.J., L. Bitincka, and J. Smalley. 2003. MatGAT: an application that generates similarity/identity matrices using protein or DNA sequences. BMC Bioinformatics 4, 29.
Carpenter, B., H. Gancz, S. Benoit, S. Evans, P.S.J. Michel, R. Maier, and D.S. Merrell. (2010 Submitted). Mutagenesis of conserved amino acids of Helicobacter pylori Fur reveals residues important for function.
Carpenter, B.M., T.K. McDaniel, J.M. Whitmire, H. Gancz, S. Guidotti, S. Censini, and D.S. Merrell. 2007. Expanding the Helicobacter pylori genetic toolbox: modification of an endogenous plasmid for use as a transcriptional reporter and complementation vector. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 7506–7514.
Carpenter, B.M., J.M. Whitmire, and D.S. Merrell. 2009. This is not your mother’s repressor: the complex role of fur in pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 77, 2590–2601.
de Lorenzo, V., S. Wee, M. Herrero, and J.B. Neilands. 1987. Operator sequences of the aerobactin operon of plasmid ColVK30 binding the ferric uptake regulation (fur) repressor. J. Bacteriol. 169, 2624–2630.
Delany, I., R. Ieva, A. Soragni, M. Hilleringmann, R. Rappuoli, and V. Scarlato. 2005. In vitro analysis of protein-operator interactions of the NikR and fur metal-responsive regulators of coregulated genes in Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 187, 7703–7715.
Delany, I., A.B. Pacheco, G. Spohn, R. Rappuoli, and V. Scarlato. 2001a. Iron-dependent transcription of the frpB gene of Helicobacter pylori is controlled by the Fur repressor protein. J. Bacteriol. 183, 4932–4937.
Delany, I., G. Spohn, R. Rappuoli, and V. Scarlato. 2001b. The Fur repressor controls transcription of iron-activated and -repressed genes in Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Microbiol. 42, 1297–1309.
Dubrac, S. and D. Touati. 2000. Fur positive regulation of iron superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli: functional analysis of the sodB promoter. J. Bacteriol. 182, 3802–3808.
Ernst, J.F., R.L. Bennett, and L.I. Rothfield. 1978. Constitutive expression of the iron-enterochelin and ferrichrome uptake systems in a mutant strain of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 135, 928–934.
Ernst, F.D., S. Bereswill, B. Waidner, J. Stoof, U. Mader, J.G. Kusters, E.J. Kuipers, M. Kist, A.H. van Vliet, and G. Homuth. 2005a. Transcriptional profiling of Helicobacter pylori Fur- and iron-regulated gene expression. Microbiology 151, 533–546.
Ernst, F.D., G. Homuth, J. Stoof, U. Mader, B. Waidner, E.J. Kuipers, M. Kist, J.G. Kusters, S. Bereswill, and A.H. van Vliet. 2005b. Ironresponsive regulation of the Helicobacter pylori iron-cofactored superoxide dismutase SodB is mediated by Fur. J. Bacteriol. 187, 3687–3692.
Fiorini, F., S. Stefanini, P. Valenti, E. Chiancone, and D. De Biase. 2008. Transcription of the Listeria monocytogenes fri gene is growth-phase dependent and is repressed directly by Fur, the ferric uptake regulator. Gene 410, 113–121.
Gancz, H., S. Censini, and D.S. Merrell. 2006. Iron and pH homeostasis intersect at the level of Fur regulation in the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 74, 602–614.
Gutteridge, J.M., G.J. Quinlan, and T.W. Evans. 2001. The iron paradox of heart and lungs and its implications for acute lung injury. Free Radic Res. 34, 439–443.
Hantke, K. 1984. Cloning of the repressor protein gene of ironregulated systems in Escherichia coli K12. Mol. Gen. Genet 197, 337–341.
Hantke, K. 2001. Iron and metal regulation in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 4, 172–177.
Heidelberg, J.F., J.A. Eisen, W.C. Nelson, R.A. Clayton, M.L. Gwinn, R.J. Dodson, D.H. Haft and et al. 2000. DNA sequence of both chromosomes of the cholera pathogen Vibrio cholerae. Nature 406, 477–483.
Heidelberg, J.F., R. Seshadri, S.A. Haveman, C.L. Hemme, I.T. Paulsen, J.F. Kolonay, J.A. Eisen and et al. 2004. The genome sequence of the anaerobic, sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough. Nat. Biotechnol. 22, 554–559.
Holmes, K., F. Mulholland, B.M. Pearson, C. Pin, J. McNicholl-Kennedy, J.M. Ketley, and J.M. Wells. 2005. Campylobacter jejuni gene expression in response to iron limitation and the role of Fur. Microbiology 151, 243–257.
Horsburgh, M.J., E. Ingham, and S.J. Foster. 2001. In Staphylococcus aureus, fur is an interactive regulator with PerR, contributes to virulence, and is necessary for oxidative stress resistance through positive regulation of catalase and iron homeostasis. J. Bacteriol. 183, 468–475.
Horton, R.M., S.N. Ho, J.K. Pullen, H.D. Hunt, Z. Cai, and L.R. Pease. 1993. Gene splicing by overlap extension. Methods Enzymol. 217, 270–279.
Litwin, C.M. and S.B. Calderwood. 1994. Analysis of the complexity of gene regulation by fur in Vibrio cholerae. J. Bacteriol. 176, 240–248.
Masse, E. and S. Gottesman. 2002. A small RNA regulates the expression of genes involved in iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 4620–4625.
Masse, E., H. Salvail, G. Desnoyers and M. Arguin. 2007. Small RNAs controlling iron metabolism. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 10, 140–145.
McArthur, K.E. and M. Feldman. 1989. Gastric acid secretion, gastrin release, and gastric emptying in humans as affected by liquid meal temperature. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 49, 51–54.
Merrell, D.S., L.J. Thompson, C.C. Kim, H. Mitchell, L.S. Tompkins, A. Lee, and S. Falkow. 2003. Growth phase-dependent response of Helicobacter pylori to iron starvation. Infect. Immun. 71, 6510–6525.
Mey, A.R., S.A. Craig, and S.M. Payne. 2005. Characterization of Vibrio cholerae RyhB: the RyhB regulon and role of ryhB in biofilm formation. Infect. Immun. 73, 5706–5719.
Ochsner, U.A., A.I. Vasil, and M.L. Vasil. 1995. Role of the ferric uptake regulator of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the regulation of siderophores and exotoxin A expression: purification and activity on iron-regulated promoters. J. Bacteriol. 177, 7194–7201.
Parkhill, J., B.W. Wren, K. Mungall, J.M. Ketley, C. Churcher, D. Basham, T. Chillingworth, and et al. 2000. The genome sequence of the food-borne pathogen Campylobacter jejuni reveals hypervariable sequences. Nature 403, 665–668.
Perna, N.T., G. Plunkett, 3rd, V. Burland, B. Mau, J.D. Glasner, D.J. Rose, G.F. Mayhew, and et al. 2001. Genome sequence of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Nature 409, 529–533.
Pohl, E., J.C. Haller, A. Mijovilovich, W. Meyer-Klaucke, E. Garman, and M.L. Vasil. 2003. Architecture of a protein central to iron homeostasis: crystal structure and spectroscopic analysis of the ferric uptake regulator. Mol. Microbiol. 47, 903–915.
Ratledge, C. and L.G. Dover. 2000. Iron metabolism in pathogenic bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 54, 881–941.
Seyler, R.W., Jr., J.W. Olson, and R.J. Maier. 2001. Superoxide dismutase-deficient mutants of Helicobacter pylori are hypersensitive to oxidative stress and defective in host colonization. Infect. Immun. 69, 4034–4040.
Sheikh, M.A. and G.L. Taylor. 2009. Crystal structure of the Vibriocholerae ferric uptake regulator (Fur) reveals insights into metal co-ordination. Mol. Microbiol. 72, 1208–1220.
Spiegelhalder, C., B. Gerstenecker, A. Kersten, E. Schiltz, and M. Kist. 1993. Purification of Helicobacter pylori superoxide dismutase and cloning and sequencing of the gene. Infect. Immun. 61, 5315–5325.
Stover, C.K., X.Q. Pham, A.L. Erwin, S.D. Mizoguchi, P. Warrener, M.J. Hickey, F.S. Brinkman, and et al. 2000. Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature 406, 959–964.
Sun, K., S. Cheng, M. Zhang, F. Wang, and L. Sun. 2008. Cys-92, Cys-95, and the C-terminal 12 residues of the Vibrio harveyi ferric uptake regulator (Fur) are functionally inessential. J. Microbiol. 46, 670–680.
Thompson, L.J., D.S. Merrell, B.A. Neilan, H. Mitchell, A. Lee, and S. Falkow. 2003. Gene expression profiling of Helicobacter pylori reveals a growth-phase-dependent switch in virulence gene expression. Infect. Immun. 71, 2643–2655.
van Vliet, A.H., J. Stoof, S.W. Poppelaars, S. Bereswill, G. Homuth, M. Kist, E.J. Kuipers, and J.G. Kusters. 2003. Differential regulation of amidase- and formamidase-mediated ammonia production by the Helicobacter pylori fur repressor. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 9052–9057.
van Vliet, A.H., J. Stoof, R. Vlasblom, S.A. Wainwright, N.J. Hughes, D.J. Kelly, S. Bereswill, and et al. 2002. The role of the Ferric Uptake Regulator (Fur) in regulation of Helicobacter pylori iron uptake. Helicobacter 7, 237–244.
Wang, G., P. Alamuri, and R.J. Maier. 2006. The diverse antioxidant systems of Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Microbiol. 61, 847–860.
Wilderman, P.J., N.A. Sowa, D.J. FitzGerald, P.C. FitzGerald, S. Gottesman, U.A. Ochsner, and M.L. Vasil. 2004. Identification of tandem duplicate regulatory small RNAs in Pseudomonas aeruginosa involved in iron homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 9792–9797.
Xiao, B., W. Li, G. Guo, B. Li, Z. Liu, K. Jia, Y. Guo, X. Mao, and Q. Zou. 2009a. Identification of small noncoding RNAs in Helicobacter pylori by a bioinformatics-based approach. Curr. Microbiol. 58, 258–263.
Xiao, B., W. Li, G. Guo, B.S. Li, Z. Liu, B. Tang, X.H. Mao, and Q.M. Zou. 2009b. Screening and identification of natural antisense transcripts in Helicobacter pylori by a novel approach based on RNase I protection assay. Mol. Biol. Rep. 36, 1853–1858.
Xiao, B., Z. Liu, B.S. Li, B. Tang, W. Li, G. Guo, Y. Shi, F. Wang, Y. Wu, W.D. Tong, H. Guo, X.H. Mao, and Q.M. Zou. 2009c. Induction of microRNA-155 during Helicobacter pylori infection and its negative regulatory role in the inflammatory response. J. Infect. Dis. 200, 916–925.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miles, S., Carpenter, B.M., Gancz, H. et al. Helicobacter pylori apo-Fur regulation appears unconserved across species. J Microbiol. 48, 378–386 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0022-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0022-0