Abstract
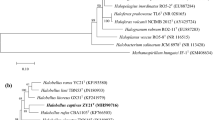
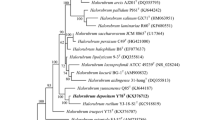
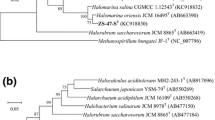
Strain B31T is a Gram-staining-negative, motile, and extremely halophilic archaeon that was isolated from salt-fermented seafood. Its morphology, physiology, biochemical features, and 16S rRNA gene sequence were determined. Phylogenetic analysis of its 16S rRNA gene sequence and composition of its major polar lipids placed this archaeon in the genus Halorubrum of the family Halobacteriaceae. Strain B31T showed 97.3, 97.2, and 96.9 % 16S rRNA similarity to the type strains of Halorubrum alkaliphilum, Hrr. tibetense, and Hrr. vacuolatum, respectively. Its major polar lipids were phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylglycerol phosphate methyl ester (PGP-Me) and sulfated diglycosyl diether (S-DGD). Genomic DNA from strain B31T has a 61.7 mol% G+C content. Analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences, as well as physiological and biochemical tests, identified genotypic and phenotypic differences between strain B31T and other Halorubrum species. The type strain of the novel species is B31T (=JCM 15757T =DSM 19504T).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castillo, A.M., M.C. Gutierrez, M. Kamekura, Y. Xue, Y. Ma, D.A. Cowan, B.E. Jones, W.D. Grant, and A. Ventosa. 2006. Halorubrum orientale sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from Lake Ejinor, Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 2559–2563.
Chun, J., J.H. Lee, Y. Jung, M. Kim, S. Kim, B.K. Kim, and Y.W. Lim. 2007. EzTaxon: a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 2259–2261.
Cui, H.L., D. Tohty, P.J. Zhou, and S.J. Liu. 2006. Halorubrum lipolyticum sp. nov. and Halorubrum aidingense sp. nov., isolated from two salt lakes in Xin-Jiang, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 1631–1634.
Dussault, H.P. 1955. An improved technique for staining red halophilic bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 70, 484–485.
Euzeby, J.P. 1997. List of bacterial names with standing in nomenclature: a folder available on the Internet. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47, 590–592.
Ezaki, T., H. Hashimoto, and E. Yabuuchi. 1989. Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 39, 224–229.
Fan, H., Y. Xue, Y. Ma, A. Ventosa, and W.D. Grant. 2004. Halorubrum tibetense sp. nov., a novel haloalkaliphilic archaeon from Lake Zabuye in Tibet, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 54, 1213–1216.
Felsenstein, J. 1981. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 17, 368–376.
Felsenstein, J. 2005. PHYLIP — Phylogeny Inference Package, version 3.6. Distributed by the author. University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA.
Feng, J., P. Zhou, Y.G. Zhou, S.J. Liu, and K. Warren-Rhodes. 2005. Halorubrum alkaliphilum sp. nov., a novel haloalkaliphile isolated from a soda lake in Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55, 149–152.
Gerhardt, P., R.G.E. Murray, W.A. Wood, and N.R. Krieg. 1994. Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C., USA.
Gonzalez, C., C. Gutierrez, and C. Ramirez. 1978. Halobacterium vallismortis sp. nov. An amylolytic and carbohydrate-metabolizing, extremely halophilic bacterium. Can. J. Microbiol. 24, 710–715.
Gonzalez, J.M. and C. Saiz-Jimenez. 2002. A fluorimetric method for the estimation of G+C mol% content in microorganisms by thermal denaturation temperature. Environ. Microbiol. 4, 770–773.
Gutierrez, C. and C. Gonzalez. 1972. Method for simultaneous de tection of proteinase and esterase activities in extremely halophilic bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. 24, 516–517.
Hu, L., H. Pan, Y. Xue, A. Ventosa, D.A. Cowan, B.E. Jones, W.D. Grant, and Y. Ma. 2008. Halorubrum luteum sp. nov., isolated from Lake Chagannor, inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 58, 1705–1708.
Kimura, M. 1980. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 16, 111–120.
Kluge, A.G. and F.S. Farris. 1969. Quantitative phyletics and the evolution of anurans. Syst. Zool. 18, 1–32.
McGenity, T.J. and W.D. Grant. 1995. Transfer of Halobacterium saccharovorum, Halobacterium sodomense, Halobacterium trapanicum NRC 34021 and Halobacterium lacusprofundi to the genus Halorubrum gen. nov., as Halorubrum saccharovorum comb. nov., Halorubrum sodomense comb. nov., Halorubrum trapanicum comb. nov., and Halorubrum lacusprofundi comb. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 18, 237–243.
McGenity, T.J. and W.D. Grant. 2001. Genus VII. Halorubrum, p. 320–324. In D.R. Boone, R.W. Castenholz, and G.M. Garrity (eds.), Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Springer, New York, N.Y., USA.
Montalvo-Rodriguez, R., J. Lopez-Garriga, R.H. Vreeland, A. Oren, A. Ventosa, and M. Kamekura. 2000. Haloterrigena thermotolerans sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon from Puerto Rico. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50, 1065–1071.
Mwatha, W.E. and W.D. Grant. 1993. Natronobacterium vacuolata sp. nov., a haloalkaliphilic archaeon isolated from Lake Magadi, Kenya. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 43, 401–404.
Oren, A., A. Ventosa, and W.D. Grant. 1997. Proposed minimal standards for description of new taxa in the order Halobacteriales. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47, 233–238.
Purdy, K.J., T.D. Cresswell-Maynard, D.B. Nedwell, T.J. McGenity, W.D. Grant, K.N. Timmis, and T.M. Embley. 2004. Isolation of haloarchaea that grow at low salinities. Environ. Microbiol. 6, 591–595.
Roh, S.W., Y. Sung, Y.D. Nam, H.W. Chang, K.H. Kim, J.H. Yoon, C.O. Jeon, H.M. Oh, and J.W. Bae. 2008. Arthrobacter soli sp. nov., a novel bacterium isolated from wastewater reservoir sediment. J. Microbiol. 46, 40–44.
Saitou, N. and M. Nei. 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425.
Sambrook, J., E.F. Fritsch, and T. Maniatis. 1989. Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, N.Y., USA.
Sehgal, S.N. and N.E. Gibbons. 1960. Effect of some metal ions on the growth of Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can. J. Microbiol. 6, 165–169.
Suh, H.K. and S.S. Yoon. 1987. A study on the regional characteristics of Korean chotkal. Korean J. Dietary Culture 2, 45–54.
Tamura, K., J. Dudley, M. Nei, and S. Kumar. 2007. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 1596–1599.
Tindall, B.J. 1990. Lipid composition of Halobacterium lacusprofundi. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 66, 199–202.
Ventosa, A., J.J. Nieto, and A. Oren. 1998. Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 62, 504–544.
Wayne, L.G., D.J. Brenner, and R.R. Colwell. 1987. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 37, 463–464.
Xin, H., T. Itoh, P. Zhou, K. Suzuki, M. Kamekura, and T. Nakase. 2000. Natrinema versiforme sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from Aibi salt lake, Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50, 1297–1303.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roh, S.W., Bae, JW. Halorubrum cibi sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from salt-fermented seafood. J Microbiol. 47, 162–166 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-009-0016-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-009-0016-y