Abstract
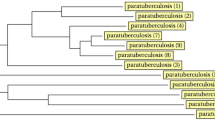
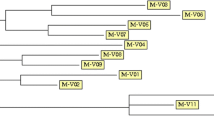
The aim of the present study is to evaluate the efficiency of three methods to determine the molecular diversity of 34 Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP) strains isolated from 17 cattle herds. The applied methods included the analysis of sequence polymorphism of the mononucleotide (G1 and G2) and trinucleotide sequences (GGT) of the Short Sequence Repeats (SSR) and the determination of size polymorphism of 9 different Mycobacterial Interspersed Repetitive Units (MIRU) and 6 Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTR). Sequence analysis of SSR of 34 isolates showed 4, 6, and 2 alleles of G1, G2, and GGT repeats, respectively. The amplification of the investigated 9 MIRU units revealed only two discriminatory genotyping systems (MIRU2 and MIRU3). Out of 6 VNTR PCR differentiation methods, only one method could be recommended for genotyping purposes. The profile 7g-12g-4ggt-II-b-2 of the combination systems G1-G2-GGT-MIRU2-MIRU3-VNTR1658 dominates among the examined isolates and was detected in 14.7% of the isolates. The use of certain repetitive loci of SSR, MIRU, and VNTR techniques in this study showed greater potential than others for the characterization of MAP isolates. The recommended loci can be used for the epidemiological tracing of MAP field strains and to determine the relationships between isolates in different herds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez, J., L. De Juan, A. Aranaz, B. Romero, J. Bezos, A. Mateos, and L. Domínguez. 2005. A survey on paratuberculosis in wildlife in Spain. Proceedings of the 8th International Colloquium on paratuberculosis, p. 690. Copenhagen, Denmark. August 14–18.
Amonsin, A., L.L. Li, Q. Zhang, J.P. Bannantine, A.S. Motiwala, S. Sreevatsan, and V. Kapur. 2004. Multilocus short sequencerepeat sequencing approach for differentiating among Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42, 1694–1702.
AVID (Arbeitskreis Veterinärmedizinische Infektionsdiagnostik). 1996. AVID-Methoden-sammlung. Mycobacterium paratubercolosis, p. 1–19. (www.dvg.net/index.php?id=234).
Bull, T.J., K. Sidi-Boumedine, E.J. McMinn, K. Stevenson, R. Pickup, and J. Hermon-Taylor. 2003. Mycobacterial interspaced repetitive units (MIRU) differentiate Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis from other species of the Mycobacterium avium complex. Mol. Cell. Probes 17, 157–164.
Collins, M.T. 1997. Mycobacterium paratuberculosis: a potential food-borne pathogen?. J. Dairy Sci. 80, 3445–3448.
Collins, M.T. 2003. Update on paratuberculosis: 1. Epidemiology of Johne’s disease and the biology of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Ir. Vet. J. 56, 565–574.
Corn, J.L., E.J.B. Manning, S. Sreevatsan, and J.R. Fischer. 2005. Isolation of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis from free-ranging birds and mammals on livestock premises. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 6963–6967.
Crossley, B.M., F.J. Zagmutt-Vergara, T.L. Fyock, R.H. Whitlock, and I.A. Gardner. 2005. Fecal shedding of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis by dairy cows. Vet. Microbiol. 107, 257–263.
Ghadiali, A.H., M. Strother, S.A. Naser, E.J. Manning, and S. Sreevatsan. 2004. Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains isolated from Crohn’s disease patients and animal species exhibit similar polymorphic locus patterns. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42, 5345–5348.
Harris, N.B., J.B. Payeur, V. Kapur, and S. Sreevatsan. 2006. Short-sequence-repeat analysis of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium subsp. avium isolates collected from animals throughout the United States reveals both stability of loci and extensive diversity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 44, 2970–2973.
Hunter, P.R. and M.A. Gaston. 1988. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: an application of Simpson’s index of diversity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 26, 2465–2466.
Kremer, K., D. Van Soolingen, R. Frothingham, W.H. Haa, P.W.M. Hermans, C. Martíon, P. Palittapongarnpim, B.B. Plikaytis, L.W. Riley, M.A. Yakrus, J.M. Musser, and J.D.A. Van Embden. 1999. Comparison of methods based on different molecular epidemiological markers for typing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains: Interlaboratory study of discriminatory power and reproducibility. J. Clin. Microbiol. 37, 2607–2618.
Möbius, P., G. Luyven, H. Hotzel, and H. Köhler. 2008. High genetic diversity among Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains from german cattle herds shown by combination of IS900 restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis and mycobacterial interspersed repetitive unit-variable-number tandem-repeat typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 46, 972–981.
Motiwala, A.S., L. Li, V. Kapur, and S. Sreevatsan. 2006. Current understanding of the genetic diversity of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. Microbes Infect. 8, 1406–1418.
Motiwala, A.S., M. Strother, N.E. Theus, R.W. Stich, B. Byrum, W.P. Shulaw, V. Kapur, and S. Sreevatsan. 2005. Rapid detection and typing of strains of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis from broth cultures. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43, 2111–2117.
Overduin, P., L. Schouls, P. Roholl, A. Van Der Zander, N. Mahmmod, A. Herrewegh, and D. Van Soolingen. 2004. Use of multilocus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis for typing Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42, 5022–5028.
Rideout, B., S. Brown, W. Davis, J. Gay, R. Gianella, M. Hines, W. Heuston, L. Hutchinson, and T. Rouse. 2003. The diagnosis and control of Johne’s disease. National Research Council report, National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., USA.
Romano, M.I., A. Amadio, F. Bigi, L. Klepp, I. Ethechoury, M.N. Llana, C. Morsella, F. Paolicchi, I. Pavlik, M. Bartos, S.C. Leao, and A. Cataldi. 2005. Further analysis of VNTR and MIRU in the genome of Mycobacterium avium complex, and application to molecular epidemiology of isolates from South America. Vet. Microbiol. 110, 221–237.
Pavlik, I., A. Horvathova, L. Dvorska, J. Bartl, P. Svastova, R. Du Marie, and I. Rychlik. 1999. Standardisation of restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis for Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. J. Microbiol. Methods 38, 155–167.
Pavlik, I., P. Svastova, J. Bartl, L. Dvorska, and I. Rychlik. 2000. Relationship between IS901 in the Mycobacterium avium complex strains isolated from birds, animals, humans, and the environment and virulence for poultry. Clin. Diag. Lab. Immunol. 7, 212–217.
Stratmann, J., M. Homuth, and G.F. Gerlach. 2005. Observations on the control and eradication of paratuberculosis in dairy herds. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 112, 304–306.
Supply, P., J. Magdalena, S. Himpens, and C. Locht. 1997. Identification of novel intergenic repetitive units in a mycobacterial two-component system operon. Mol. Microbiol. 26, 991–1003.
Sweeney, R.W. 1996. Transmission of paratuberculosis. Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 12, 305–312.
Thibault, V.C., M. Grayon, M.L. Boschiroli, C. Hubbans, P. Overduin, K. Stevenson, M.C. Gutierrez, P. Supply, and F. Biet. 2007. New variable-number tandem-repeat markers for typing Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis and M. avium strains: Comparison with IS900 and IS1245 restriction fragment length polymorphism typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 45, 2404–2410.
Thibault, V.C., M. Grayon, M.L. Boschiroli, E. Willery, C. Allix-Beguec, K. Stevenson, F. Biet, and P. Supply. 2008. Combined multilocus short-sequence-repeat and mycobacterial interspersed repetitive unit-variable-number tandem-repeat typing of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 46, 4091–4094.
Van Belkum, A., S. Scherer, L. Van Alphen, and H. Verbrugh. 1998. Short-sequence DNA repeats in prokaryotic genomes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 62, 275–293.
Vansnick, E., P. De Rijk, F. Vercammen, D. Geysen, L. Rigouts, and F. Portaels. 2004. Newly developed primers for the detection of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. Vet. Microbiol. 100, 197–204.
Whitlock, R. 1996. Johne’s disease, p. 899–904. In B.P. Simith (ed.) Large animal internal medicine. 2nd ed. Mosby, St. Louis, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Sayed, A., Hassan, A.A., Natour, S. et al. Evaluation of three molecular methods of repetitive element loci for differentiation of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP). J Microbiol. 47, 253–259 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-008-0257-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-008-0257-1