Abstract
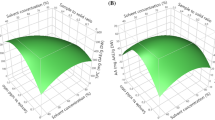
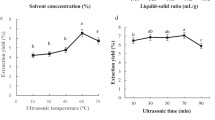
Response surface methodology (RSM) using a Box-Behnken design was used to optimize the extraction conditions for obtaining pancreatic lipase inhibitory and antioxidant principles from Ilex paraguariensis leaves. Three influencing factors: extraction time (min), the liquid–solid ratio, and ethanol concentration (%, v/v) were investigated in the ultrasonic extraction process. Optimization of the extraction conditions to obtain a product with minimum PL activity, maximum antioxidant activity, and maximum yield was performed using RSM by focusing on the three target influencing factors. The optimum conditions were established as the ethanol concentration (54.8 %), liquid–solid ratio (35.4), and extraction time (70.0 min). Under these conditions, the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl scavenging activity, PL activity, extraction yield were 59.3 ± 3.5, 35.3 ± 3.0, and 34.4 ± 0.4 %, respectively, similar to the theoretical predicted values of 59.7, 35.2, and 34.3 %, respectively.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn JH, Liu Q, Lee C, Ahn MJ, Yoo HS, Hwang BY, Lee MK (2012) A new pancreatic lipase inhibitor from Broussonetia kanzinoki. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:2760–2763
Arcari DP et al (2009) Antiobesity effects of yerba mate extract (Ilex paraguariensis) in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Obesity 17:2127–2133
Arcari DP et al (2011) Anti-inflammatory effects of yerba mate extract (Ilex paraguariensis) ameliorate insulin resistance in mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity. Mol Cell Endocrinol 335:110–115
Bae IK, Ham HM, Jeong MH, Kim DH, Kim HJ (2015) Simultaneous determination of 15 phenolic compounds and caffeine in teas and mate using RP-HPLC/UV detection: method development and optimization of extraction process. Food Chem 172:469–475
Bastos DHM, De Oliveira DM, Matsumoto RLT, Carvalho PO, Ribeiro ML (2007) Yerba mate: pharmacological properties, research and biotechnology. Med Aromat Plant Sci Biotechnol 1:37–46
Bhutani KK, Birari R, Kapat K (2007) Potential antiobesity and lipid lowering natural products: a review. Nat Product Commun 2:331–348
Birari RB, Bhutani KK (2007) Pancreatic lipase inhibitors from natural sources: unexplored potential. Drug Discov Today 12:879–889
Boaventura BC et al (2012) Association of mate tea (Ilex paraguariensis) intake and dietary intervention and effects on oxidative stress biomarkers of dyslipidemic subjects. Nutrition 28:657–664
Bracesco N, Sanchez AG, Contreras V, Menini T, Gugliucci A (2011) Recent advances on Ilex paraguariensis research: minireview. J Ethnopharmacol 136:378–384
Dai J, Mumper RJ (2010) Plant phenolics: extraction, analysis and their antioxidant and anticancer properties. Molecules 15:7313–7352
Grujic N, Lepojevic Z, Srdjenovic B, Vladic J, Sudji J (2012) Effects of different extraction methods and conditions on the phenolic composition of mate tea extracts. Molecules 17:2518–2528
Heck CI, de Mejia EG (2007) Yerba Mate Tea (Ilex paraguariensis): a comprehensive review on chemistry, health implications, and technological considerations. J Food Sci 72:R138–R151
Herzi N, Bouajila J, Camy S, Romdhane M, Condoret JS (2013) Comparison of different methods for extraction from Tetraclinis articulata: yield, chemical composition and antioxidant activity. Food Chem 141:3537–3545
Hilde HW, Nigel B (2010) The optimization of solid-liquid extraction of antioxidants from apple pomace by response surface methodology. J Food Eng 96:134–140
Kang YR et al (2012) Anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects of Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) in C57BL/6 J mice fed a high-fat diet. Lab Anim Res 28:23–29
Liu C, Jia S, Xu J (2012) Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis for protein from Actinidia arguta Sieb. et Zucc by response surface methodology and antioxidant activity of polypeptides. Food Sci 33:33–38
Martins F et al (2010) Mate tea inhibits in vitro pancreatic lipase activity and has hypolipidemic effect on high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Obesity 18:42–47
Miranda DD, Arcari DP, Pedrazzoli J Jr, Carvalho Pde O, Cerutti SM, Bastos DH, Ribeiro ML (2008) Protective effects of mate tea (Ilex paraguariensis) on H2O2-induced DNA damage and DNA repair in mice. Mutagenesis 23:261–265
Nabavi SF, Russo GL, Daglia M, Nabavi SM (2015) Role of quercetin as an alternative for obesity treatment: You are what you eat! Food Chem 179C:305–310
Pang J, Choi Y, Park T (2008) Ilex paraguariensis extract ameliorates obesity induced by high-fat diet: potential role of AMPK in the visceral adipose tissue. Arch Biochem Biophys 476:178–185
Peres RG, Tonin FG, Tavares MF, Rodriguez-Amaya DB (2013) HPLC-DAD-ESI/MS identification and quantification of phenolic compounds in Ilex paraguariensis beverages and on-line evaluation of individual antioxidant activity. Molecules 18:3859–3871
Shi Y, Burn P (2004) Lipid metabolic enzymes: emerging drug targets for the treatment of obesity. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:695–710
Strader CD, Hwa JJ, Van Heek M, Parker EM (1998) Novel molecular targets for the treatment of obesity. Drug Discov Today 3:250–256
Thaipong K, Boonprakob U, Crosby K, Cisneros-Zevallos L, Byrne DH (2006) Comparison of ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, and ORAC assays for estimating antioxidant activity from guava fruit extracts. J Food Compos Anal 19:669–675
Wang Y, Wang T, Ding L (2012) Optimization of polysaccharide extraction from Angelica sinensis using response surface methodology. Food Sci 33:146–149
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Grants (NRF-2014R1A1A1003605 and NRF-2014R1A4A1007304) from the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korean Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, KE., Shin, H., Jeon, Y.H. et al. Optimization of pancreatic lipase inhibitory and antioxidant activities of Ilex paraguariensis by using response surface methodology. Arch. Pharm. Res. 39, 946–952 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0768-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0768-y