Abstract
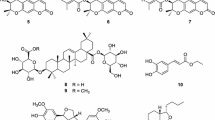
Belamcanda chinensis (L.) DC., which belongs to the family of Iridaceae, has been used as a folk medicine for the treatment of inflammation, asthma, tonsillitis, and many other throat disorders. Bioactivity-guided purification of the methylene chloride-soluble fraction of the rhizomes of B. chinensis based on the inhibition of nitric oxide production led to the identification of seventeen known compounds. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of extensive spectroscopic measurement such as NMR and ESI–MS. All of the isolated compounds were evaluated for their inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophage cells.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adegawa, S., T. Miyase, and A. Ueno. 1987. Sesquiterpene lactones from Diaspananthus uniflorus (SCH. BIP.) KITAM. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 35: 1479–1485.
Ahn, K.S., E.J. Noh, K.H. Cha, Y.S. Kim, S.S. Lim, K.H. Shin, and S.H. Jung. 2006. Inhibitory effects of irigenin from the rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis on nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 production in murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Life Sciences 78: 2336–2342.
Awale, S., S.P. Shrestha, Y. Tezuka, J.Y. Ueda, K. Matsushige, and S. Kadota. 2005. Neoflavonoids and related constituents from Nepalese propolis and their nitric oxide production inhibitory activity. Journal of Natural Products 68: 858–864.
Bas, E., M.C. Recio, R.M. Giner, S. Manez, C. Lopez-Gines, R. Gil-Benso, and J.L. Rios. 2007. Demethylnobiletin inhibits delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions, human lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine production. British Journal of Pharmacology 152: 1272–1282.
Chan, S.C., Y.S. Chang, J.P. Wang, S.C. Chen, and S.C. Kuo. 1998. Three new flavonoids and anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory constituents from the heartwood of Dalbergia odorifera. Planta Medica 64: 153–158.
Deesamer, S., U. Kokpol, W. Chavasiri, S. Douillard, V. Peyrot, N. Vidal, S. Combesc, and J. Finetc. 2007. Synthesis and biological evaluation of isoflavone analogues from Dalbergia oliveri. Tetrahedron 63: 12986–12993.
Eu, G.H., W.S. Woo, H.S. Chung, and E.H. Woo. 1991. Isoflavonoids of Belamcanda chinensis (II). Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy 22: 13–17.
Gao, Y., L. Fang, F. Liu, C. Zong, R. Cai, X. Chen, and Y. Qi. 2014. Suppressive effects of irisflorentin on LPS-induced inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Experimental Biology and Medicine 239: 1018–1024.
Hsieh, Y.H., P.M. Kuo, S.C. Chien, L.F. Shyur, and S.Y. Wang. 2007. Effects of Chamaecyparis formosensis Matasumura extractives on lipopolysaccharide-induced release of nitric oxide. Phytomedicine 14: 675–680.
Ito, H., S. Onoue, and T. Yoshida. 2001. Isoflavonoids from Belamcanda chinensis. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 49: 1229–1231.
Jin, Q., C. Lee, J.W. Lee, E.T. Yeon, D. Lee, S.B. Han, J.T. Hong, Y. Kim, M.K. Lee, and B.Y. Hwang. 2014. 2-Phenoxychromones and prenylflavonoids from Epimedium koreanum and their inhibitory effects on LPS-induced nitric oxide and interleukin-1β production. Journal of Natural Products 77: 1724–1728.
Jun, H.J., M.H. Hoang, J.W. Lee, J. Yaoyao, J.H. Lee, D.H. Lee, H.J. Lee, W.D. Seo, B.Y. Hwang, and S.J. Lee. 2012. Iristectorigenin B isolated from Belamcanda chinensis is a liver X receptor modulator that increases ABCA1 and ABCG1 expression in macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Biotechnology Letters 34: 2213–2221.
Jung, S.H., Y.S. Lee, S. Lee, S.S. Lim, Y.S. Kim, K. Ohuchi, and K.H. Shin. 2003. Anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activities of isoflavonoids from the rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis. Planta Medica 69: 617–622.
Jung, S.H., Y.S. Lee, S.S. Lim, S. Lee, K.H. Shin, and Y.S. Kim. 2004. Antioxidant activities of isoflavones from the rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis on carbon tetrachloride.induced hepatic injury in rats. Archives of Pharmacal Research 27: 184–188.
Jung, S.H., Y.S. Lee, S.S. Lim, Y.S. Kim, and K.H. Shin. 2002. Isoflavonoids from the rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis and their effects on aldose reductase and sorbitol accumulation in streptozotocin induced diabetic rat tissues. Archives of Pharmacal Research 25: 306–312.
Kondo, Y., K. Sugiyama, and S. Nozoe. 1986. Studies on the constituents of Vitex rotundifolia. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 34: 4829–4832.
Lee, C.K., C.K. Lu, Y.H. Kuo, J.Z. Chen, and G.Z. Sun. 2004. New prenylated flavones from the roots of Ficus beecheyana. Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society 51: 437–442.
Lee, D.S., K.S. Kim, W. Ko, B. Li, S. Keo, G.S. Jeong, H. Oh, and Y.C. Kim. 2014. The neoflavonoid latifolin isolated from MeOH extract of Dalbergia odorifera attenuates inflammatory responses by inhibiting NF-κB activation via Nrf2-mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression. Phytotherapy Research 28: 1216–1223.
Lee, Y.S., S.H. Kim, J.K. Kim, S. Lee, S.H. Jung, and S.S. Lim. 2011. Preparative isolation and purification of seven isoflavones from Belamcanda chinensis. Phytochemical Analysis 22: 468–473.
Liu, M., S. Yang, L. Jin, D. Hu, Z. Wu, and S. Yang. 2012. Chemical constituents of the ethyl acetate extract of Belamcanda chinensis (L.) DC roots and their antitumor activities. Molecules 17: 6156–6169.
Matsuda, H., T. Morikawa, F. Xu, K. Ninomiya, and M. Yoshikawa. 2004. New isoflavones and pterocarpane with hepatoprotective activity from the stems of Erycibe expansa. Planta Medica 70: 1201–1209.
Monthakantirat, O., W. De-Eknamkul, K. Umehara, Y. Yoshinaga, T. Miyase, T. Warashina, and H. Noguchi. 2005. Phenolic constituents of the rhizomes of the Thai medicinal plant Belamcanda chinensis with proliferative activity for two breast cancer cell lines. Journal of Natural Products 68: 361–364.
Muangnoicharoen, N., and A.W. Frahm. 1982. Neoflavanoids of Dalbergia parviflora. Phytochemistry 20: 291–293.
Muijsers, R.B., E. van Den Worm, G. Folkerts, C.J. Beukelman, A.S. Koster, D.S. Postma, and F.P. Nijkamp. 2000. Apocynin inhibits peroxynitrite formation by murine macrophages. British Journal of Pharmacology 130: 932–936.
Nagase, H., N. Omae, A. Omori, O. Nakagawasai, T. Tadano, A. Yokosuka, Y. Sashida, Y. Mimaki, T. Yamakuni, and Y. Ohizumi. 2005. Nobiletin and its related flavonoids with CRE-dependent transcription-stimulating and neuritegenic activities. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 337: 1330–1336.
Pan, C.H., E.S. Kim, S.H. Jung, C.W. Nho, and J.K. Lee. 2008. Tectorigenin inhibits IFN-gamma/LPS-induced inflammatory responses in murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Archives of Pharmacal Research 31: 1447–1456.
Sekine, N., T. Ashitani, T. Murayama, S. Shibutani, S. Hattori, and K. Takahashi. 2009. Bioactivity of latifolin and its derivatives against termites and fungi. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 57: 5707–5712.
Song, Z.J., X.M. Xu, W.L. Deng, S.L. Peng, L.S. Ding, and H.H. Xu. 2011. A new dimeric iridal triterpenoid from Belamcanda chinensis with significant molluscicide activity. Organic Letters 13: 462–465.
Tang, W., and G. Eisenbrand. 2011. Handbook of Chinese medicinal plants: chemistry, pharmacology, toxicology, vol. 1, 246–249. Weinheim: Wiley.
Wozniak, D., B. Janda, I. Kapusta, W. Oleszek, and A. Matkowski. 2010. Antimutagenic and anti-oxidant activities of isoflavonoids from Belamcanda chinensis (L.) DC. Mutation Research: Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 696: 148–153.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported financially by the Medical Research Center Program (MRC, 2008-0062275) through the National Research Foundation of Korea. The authors thank the Center for Research Instruments and Experimental Facilities, Chungbuk National University for providing the NMR spectroscopic measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.W., Lee, C., Jin, Q. et al. Chemical constituents from Belamcanda chinensis and their inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 38, 991–997 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0529-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0529-8