Abstract
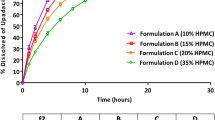
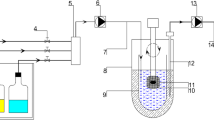
This study was to evaluate the pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence of two tacrolimus formulations which had different in vitro drug release profiles. Dynamic solubility, in vitro dissolution profiles of the two formulations, and their influence on pharmacokinetics were examined. The male volunteers were randomly assigned to receive a single 1-mg capsule of the test or reference formulation and pharmacokinetic parameters were determined using a noncompartmental method. The two formulations released >85 % of tacrolimus in water within 30 min, which passed the criterion of evaluating the test formulation. However, the test formulation produced a faster initial release rate and plateaued in about 15 min, while the reference showed almost zero order initial release profiles. The AUC0−∞ values were 145.92 (reference) and 140.49 ng h/mL (test). The mean Cmax was 15.70 (reference) and 16.08 ng/mL (test) with Tmax values of 1.63 and 1.60 h, respectively. The t1/2 for the reference and test formulations was 29.12 and 27.85 h, respectively. Relative bioavailability was calculated to be 96.28 %. The point estimates for the mean ratio of the test to reference for the AUC0−t and Cmax were 0.969 and 1.026, respectively, satisfying the criterion for bioequivalence. The results suggest that the test formulation is pharmacokinetically equivalent to the reference in terms of both rate and extent of absorption. Even though the in vitro dissolution profiles of the formulations might not be equivalent, the pharmacokinetics indicated bioequivalence. Therefore, when developing poorly soluble drugs, it might be beneficial to pay attention to the dynamic solubility as well as dissolution profiles.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arima, H., K. Yunomae, K. Miyake, T. Irie, F. Hirayama, and K. Uekama. 2001. Comparative studies of the enhancing effects of cyclodextrins on the solubility and oral bioavailability of tacrolimus in rats. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 90: 690–701.
Gao, S., J. Sun, D. Fu, H. Zhao, M. Lan, and F. Gao. 2012. Preparation, characterization and pharmacokinetic studies of tacrolimus-dimethyl-beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complex-loaded albumin nanoparticles. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 427: 410–416.
Hata, T., F. Shimojo, Y. Tokunaga, T. Hirose, S. Kimura, and S. Ueda. 1999. Medicinal composition. Korea Patent 1019997004614.
Honbo, T., M. Kobayashi, K. Hane, T. Hata, and Y. Ueda. 1987. The oral dosage form of FK-506. Transplantation Proceedings 19: 17–22.
Joe, J.H., W.M. Lee, Y.J. Park, K.H. Joe, D.H. Oh, Y.G. Seo, J.S. Woo, C.S. Yong, and H.G. Choi. 2010. Effect of the solid-dispersion method on the solubility and crystalline property of tacrolimus. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 395: 161–166.
Kagayama, A., S. Tanimoto, J. Fujisaki, A. Kaibara, K. Ohara, K. Iwasaki, Y. Hirano, and T. Hata. 1993. Oral absorption of FK506 in rats. Pharmaceutical Research 10: 1446–1450.
Korea Food and Drug Administration (KFDA). 2002. Guideline for bioequivalence test.
Kino, T., H. Hatanaka, M. Hashimoto, M. Nishiyama, T. Goto, M. Okuhara, M. Kohsaka, H. Aoki, and H. Imanaka. 1987. FK-506, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from a Streptomyces. I. Fermentation, isolation, and physico-chemical and biological characteristics. Journal of Antibiotics 40: 1249–1255.
Liu, J., J.D. Farmer Jr, W.S. Lane, J. Friedman, I. Weissman, and S.L. Schreiber. 1991. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell 66: 807–815.
Park, M.S., I.H. Lim, G.Y. Jung, J.K. Kim, and U.K. Jee. 2005. Pharmaceutical composition comprising macrolide-based antibiotic having improved solubility and release properties as active ingredient, preparation method thereof, and sustained release compositions having enhanced durability comprising the same. Korea Patent 1020050069855.
Ramakrishna, N.V., K.N. Vishwottam, S. Puran, S. Manoj, M. Santosh, S. Wishu, M. Koteshwara, J. Chidambara, B. Gopinadh, and B. Sumatha. 2004. Liquid chromatography-negative ion electrospray tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of tacrolimus in human plasma and its bioanalytical applications. Journal of Chromatography B 805: 13–20.
Shargel, L., B. Andrew, and S. Wu-Pong. 2005. Applied biopharmaceutics and pharmacokinetics, Appleton & Lange Reviews/McGraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division.
Streit, F., V.W. Armstrong, and M. Oellerich. 2002. Rapid liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry routine method for simultaneous determination of sirolimus, everolimus, tacrolimus, and cyclosporin A in whole blood. Clinical Chemistry 48: 955–958.
Yamashita, K., T. Nakate, K. Okimoto, A. Ohike, Y. Tokunaga, R. Ibuki, K. Higaki, and T. Kimura. 2003. Establishment of new preparation method for solid dispersion formulation of tacrolimus. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 267: 79–91.
Yoshida, T., I. Kurimoto, K. Yoshihara, H. Umejima, N. Ito, S. Watanabe, K. Sako, and A. Kikuchi. 2012. Aminoalkyl methacrylate copolymers for improving the solubility of tacrolimus. I: evaluation of solid dispersion formulations. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 428: 18–24.
Zidan, A.S., Z. Rahman, V. Sayeed, A. Raw, L. Yu, and M.A. Khan. 2012. Crystallinity evaluation of tacrolimus solid dispersions by chemometric analysis. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 423: 341–350.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Bio-Scientific Research Grant funded by the Pusan National University (PNU, Bio-Scientific Research Grant) (PNU-2010-101-240).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, M., Yeom, D., Kim, N.A. et al. Bioequivalence of tacrolimus formulations with different dynamic solubility and in-vitro dissolution profiles. Arch. Pharm. Res. 38, 73–80 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0343-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0343-3