Abstract
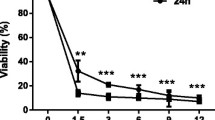
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) play a central role in liver fibrosis. Inhibition of HSC growth and induction of apoptosis have been proposed as therapeutic strategies for the treatment and prevention of liver fibrosis. Propyl gallate (PG) is an antioxidant widely used in processed foods, cosmetics and medicinal preparations. However, the anti-fibrotic effect of PG in liver injury is unclear. In this study, we investigated whether PG could induce apoptosis in activated HSCs. Treatment of activated HSCs with PG inhibited cell viability in a dose- and time-dependent manner. PG induced apoptosis as demonstrated by morphological changes, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage, caspase-3 cleavage, increased Bad expression, and decreased Bcl-2 protein expression. Through stimulation of the activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal protein kinase (JNK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) by PG treatment, we demonstrated that JNK and p38 MPAK are not involved in PG-induced apoptosis using their specific inhibitors. Taken together, these findings indicate that PG induces apoptosis in activated HSCs. The potential anti-fibrotic effect of PG warrants further evaluation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, J. M. and Cory, S., The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene, 26, 1324–1337 (2007).
Bataller, R. and Brenner, D. A., Liver fibrosis. J. Clin. Invest., 115, 209–218 (2005).
Canbay, A., Friedman, S., and Gores, G. J., Apoptosis: the nexus of liver injury and fibrosis. Hepatology, 39, 273–278 (2004).
Chen, C. H., Lin, W. C., Kuo, C. N., and Lu, F. J., Role of redox signaling regulation in propyl gallate-induced apoptosis of human leukemia cells. Food Chem. Toxicol., 49, 494–501 (2011).
Daniel, P. T., Schulze-Osthoff, K., Belka, C., and Güner, D., Guardians of cell death: the Bcl-2 family proteins. Essays Biochem., 39, 73–788 (2003).
Elsharkawy, A. M., Oakley, F., and Mann, D. A., The role and regulation of hepatic stellate cell apoptosis in reversal of liver fibrosis. Apoptosis, 10, 927–939 (2005).
Fallowfield, J. A., Therapeutic targets in liver fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol., 300, G709–G715 (2011).
Fan, M. and Chambers, T. C., Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in the response of tumor cells to chemotherapy. Drug Resist. Updat., 4, 253–267 (2001).
Friedman, S. L., Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 2247–250 (2000).
Friedman, S. L., Maher, J. J., and Bissell, D. M., Mechanisms and therapy of hepatic fibrosis: report of the AASLD Single Topic Basic Research Conference. Hepatology, 32, 1403–1408 (2000).
Friedman, S. L., Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology, 134, 1655–1669 (2008).
Han, Y. H. and Park, W. H., Propyl gallate inhibits the growth of HeLa cells via regulating intracellular GSH level. Food Chem. Toxicol., 47, 2531–2538 (2009).
Han, Y. H., Moon, H. J., You, B. R., Kim, S. Z., Kim, S. H., and Park, W. H., Propyl gallate inhibits the growth of HeLa cells via caspase-dependent apoptosis as well as a G1 phase arrest of the cell cycle. Oncol. Rep., 23, 1153–1158 (2010).
Herr, I. and Debatin, K. M., Cellular stress response and apoptosis in cancer therapy. Blood, 98, 2603–2614 (2001).
Kim, J. Y., Kim, K. M., Nan, J. X., Zhao, Y. Z., Park, P. H., Lee, S. J., and Sohn, D. H., Induction of apoptosis by tanshinone I via cytochrome c release in activated hepatic stellate cells. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 92, 195–200 (2003).
Li, J. T., Liao, Z. X., Ping, J., Xu, D., and Wang, H., Molecular mechanism of hepatic stellate cell activation and antifibrotic therapeutic strategies. J. Gastroenterol., 43, 419–428 (2008).
Lotersztajn, S., Julien, B., Teixeira-Clerc, F., Grenard, P., and Mallat, A., Hepatic fibrosis: molecular mechanisms and drug targets. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 45, 605–628 (2005).
Manning, D. S. and Afdhal, N. H., Diagnosis and quantitation of fibrosis. Gastroenterology, 134, 1670–1681 (2008).
Masters, S. C., Yang, H., Datta, S. R., Greenberg, M. E., and Fu, H., 14-3-3 inhibits Bad-induced cell death through interaction with serine-136. Mol. Pharmacol., 60, 1325–1331 (2001).
Park, E. J., Zhao, Y. Z., Kim, Y. C., and Sohn, D. H., Bakuchiol-induced caspase-3-dependent apoptosis occurs through c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated mitochondrial translocation of Bax in rat liver myofibroblasts. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 559, 115–123 (2007).
Reed, J. C. and Tomaselli, K. J., Drug discovery opportunities from apoptosis research. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 11, 586–592 (2000).
Subramanian, R. R., Masters, S. C., Zhang, H., and Fu, H., Functional conservation of 14-3-3 isoforms in inhibiting bad-induced apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res., 271, 142–151 (2001).
van Loo, G., Saelens, X., van Gurp, M., MacFarlane, M., Martin, S. J., and Vandenabeele, P., The role of mitochondrial factors in apoptosis: a Russian roulette with more than one bullet. Cell Death Differ., 9, 1031–1042 (2002).
Zhang, L., Yu, J., Park, B. H., Kinzler, K. W., and Vogelstein, B., Role of BAX in the apoptotic response to anticancer agents. Science, 290, 989–992 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Che, XH., Jiang, WY., Parajuli, D.R. et al. Apoptotic effect of propyl gallate in activated rat hepatic stellate cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 35, 2205–2210 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-1219-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-1219-z