Abstract
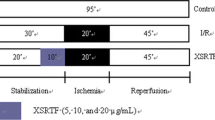
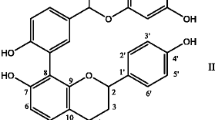
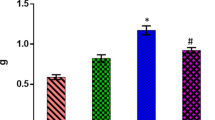
Reactive oxygen species exert toxic effects during ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury of various organs. This study was designed to evaluate the preventive effects of various isoflavonoids such as biochanin A, daidzein, genistein, rutin and quercetin. These compounds are wellknown naturally occurring compounds with beneficial health effects and antioxidant activity. Free radical scavenging activity was measured by 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay and superoxide dismutase (SOD) assay. Among the isoflavonoids tested, biochanine A, quercetin and rutin showed significant DPPH free radical scavenging activity. Similarly, treatment of biochanine A, genistein and rutin significantly increased SOD activity in neonant rat heart myocyte primary cells as well as in H9C2 cells. For ex vivo study, hearts from Sprague-Dawley rats were perfused in Langendorff apparatus with Krebs-Henseleit solution with a gas mixture of 95% O2 and 5% CO2. Hearts were subjected to 20 min of pre-ischemia followed by 20 min of global ischemia, and then 50 min of reperfusion at 37°C. The test compounds were perfused 10 min before ischemia and during the entire reperfusion period. Among the isoflavonoids tested, only rutin significantly increased left ventricular developed pressure (LVDP) and increased maximum positive and negative dP/dt (+/- dP/dtmax). In left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP) analysis, rutin, daidzein and biochanin A were effective. Among the isoflavonoids, rutin had consistent protective effects in I/R injury by affecting cardiac dynamic factors as well as by enhancing SOD and DPPH activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayako, O. M. and Irwin, F., Cellular distribution of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in rat liver. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 38388–38393 (2001).
Blois, M. S., Antioxidant determination by the use of a stable free radical. Nature, 181, 1199–2004 (1958).
Bonacasa, B., Siow, R. C., and Mann, G. E., Impact of dietary soy isoflavons in pregnancy on fetal programming of endothelial function in offspring. Microcirculation, 18, 270–285 (2011).
Buja, L. M., Myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Pathol., 14, 170–175 (2005).
Di, M. S., Venditti, P., and De, L. T., Tissue protection against oxidative stress. Experientia, 52, 768–794 (1996).
Kacmaz, A., User, E. Y., Sehirli, A. O., Tilki, M., Ozkan, S., and Sener, G., Protective effect of melatonin against ischemia/ reperfusion-induced oxidative remote organ injury in the rat. Surg. Today, 35, 744–750 (2005).
Kim, D. S., Kwon, D. Y., Kim, M. S., Kim, H. K., Lee, Y. C., Park, S. J., Yoo, W. H., Chae, S. W., Chung, M. J., Kim, H. R., and Chae, H. J., The involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress in flavonoid-induced protection on cardiac cell death caused by ischaemia/reperfusion. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 62, 197–204 (2010).
Kim, S. I., Sim, K. H., and Choi, H. Y., A comparative study of antioxidant activity in some Korean medicinal plant used as food materials. Mol. Cell. Toxicol., 6, 279–285 (2010).
Ko, W. C., Shih, C. M., Lai, Y. H., Chen, J. H., and Huang, H. L., Inhibitory effects of flavonoids on phosphodiesterase isoenzymes from guinea pig and their structure activity relationships. Biochem. Pharmacol. 68, 2087–2094 (2004).
Molavi, B. and Mehta, J. L., Oxidative stress in cardiovascular disease; molecular basis of its deleterious effects, its detection and its therapeutic considerations. Curr. Opin. Cardiol., 19, 499–493 (2004).
Mukherjee, S., Gangopadhya, H., and Das, D. K., Brocolli: a unique vegetable that protects mammalian hearts through the redox cycling of the thioredoxin super family. J. Agric. Food Chem., 56, 609–617 (2008).
Murphy, E. and Steenbergen, C., Mechanism underlying acute protection from cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. Physiol. Rev., 88, 581–609 (2008).
Ostadal, B., The past, the present and the future of experimental research on myocardial ischemia and protection. Pharmacol. Rep., 61, 3–12 (2009).
Piper, H. M., Garcia, D. D., and Ovize, M., A fresh look at reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Res., 38, 291–300 (1998).
Piper, H. M., Abdallah, Y., and Schafer. C., The first minutes of reperfusion: a window of opportunity for cardioprotection. Cardiovasc. Res., 61, 365–371 (2004).
Soiw, R. C. and Mann, G. E., Dietary isoflavons and vascular protection: activation of cellular antioxidant defences by SERMs or hormesis? Mol. Aspects. Med., 31, 468–477 (2010).
Wattanapitayakul, S. K. and Bauer, J. A., Oxidative pathways in cardiovascular disease: roles, mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Ther., 89, 187–206 (2001).
Yamamoto, S., Yamane, M., Yoshida, O., Okazaki, M., Waki, N., Toyooka, S., Oto, T., and Miyoshi, S., Activation of mitogenactivated protein kinases and regulation of their downstream molecules after rat lung transplantation from donors after cardiac death. Transplant. Proc., 43, 3628–3633 (2011).
Zweier, J. L. and Talukder, M. A., The role of antioxidants and free radicals in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Res., 70, 181–190 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhandary, B., Piao, C.S., Kim, DS. et al. The protective effect of rutin against ischemia/reperfusion-associated hemodynamic alteration through antioxidant activity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 35, 1091–1097 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-0617-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-0617-6