Abstract
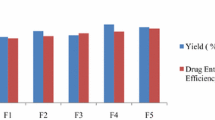
The purpose of the study was to formulate and evaluate controlled release chitosan microspheres of mirtazapine (MTZ) to improve the bioavailability by altering the pharmacokinetic profiles of the drug. Chitosan microspheres were prepared to prolong the release of the drug into the systemic circulation. Microspheres were prepared by a single water in oil (w/o) emulsion technique varying the chitosan/drug ratio, stirring speed and concentration of the crosslinking agent (glutaraldehyde). Drug-polymer compatibility studies were carried out using fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The microspheres were evaluated for encapsulation efficiency, particle size, surface morphology, swelling index, in vitro release, as well as erosion and in vivo studies in rats. The FT-IR and DSC studies revealed no interaction between drug and polymer. The encapsulation efficiency of different formulation varied from 53 ± 1.2% to 78 ± 1.5%. The mean particle size of the optimized formulation F-14 was 106.4 ± 0.5 μm. Surface morphology revealed that chitosan microspheres were discrete and spherical in shape with a porous surface. The release of MTZ from chitosan microspheres was rapid up to 4 h, and then it was continuously and slowly released up to 48 h. Optimized formulation (F-14) was found to be stable under accelerated storage conditions based on International Conference on Harmonisation guidelines. Pharmacokinetic studies revealed that the optimized formulation showed significant increases in systemic exposure (AUC = 177.70 ± 7.39 μg·h/mL), half-life (4.72 ± 0.46 h) and reduced clearance (0.009 ± 0.0001 L/h) compared to pure drug administration. Hence, the present study demonstrates that controlled release formulation of MTZ microspheres using chitosan can improve pharmacokinetic profiles of MTZ.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbuğa, J. and Bergişadi, N., 5-Fluorouracil-loaded chitosan microspheres: preparation and release characteristics. J. Microencapsul., 13, 161–168 (1996).
Akbuğa, J. and Bergişadi, N., Effect of formulation variables on cis-platin loaded chitosan microsphere properties. J. Microencapsul., 16, 697–703 (1999).
Berger, J., Reist, M., Mayer, J. M., Felt, O., Peppas, N. A., and Gurny, R., Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 57, 19–34 (2004).
Conner, R. E. O., Schwartz, J. B., and Felton, L. A., Powders. In Remington, The Science and Practice of Pharmacy, 21st Eds., vol. 1, Indian edition, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (Eds.). BI Publications Pvt Ltd, India, pp. 702–719, (2005).
Desai, K. G. and Park, H. J., Preparation of cross-linked chitosan microspheres by spray drying: effect of cross-linking agent on the properties of spray dried microspheres. J. Microencapsul., 22, 377–395 (2005).
Dhawan, S. and Singla, A. K., Nifedipine loaded chitosan microspheres prepared by emulsification phase-separation. Biotech. Histochem., 78, 243–254 (2003).
Genta, I., Perugini, P., and Pavanetto, F., Different molecular weight chitosan microspheres: influence on drug loading and drug release. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 24, 779–784 (1998).
Hamman, J. H., Stander, M., and Kotzé, A. F., Effect of the degree of quaternisation of N-trimethyl chitosan chloride on absorption enhancement: in vivo evaluation in rat nasal epithelia. Int. J. Pharm., 232, 235–242 (2002).
Jameela, S. R., Kumary, T. V., Lal, A. V., and Jayakrishnan, A., Progesterone-loaded chitosan microspheres: a long acting biodegradable controlled delivery system. J. Control. Release, 52, 17–24 (1998).
Morimoto, K., Katsumata, H., Yabuta, T., Iwanaga, K., Kakemi, M., Tabata, Y., and Ikada, Y., Evaluation of gelatin microspheres for nasal and intramuscular administrations of salmon calcitonin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 13, 179–185 (2001).
Muzzarelli, R. A. A., Jeuniauk, C., and Gooday, G. W., Chitin in Nature and Technology. Plenum, New York, (1986).
Nishioka, Y., Kyotani, S., Okamura, M., Miyazaki, M., Okazaki, K., Ohnishi, S., Yamamoto, Y., and Ito, K., Release characteristics of cisplatin chitosan microspheres and effect of containing chitin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo), 38, 2871–2873 (1990).
Nutt, D., Mirtazapine: pharmacology in relation to adverse effects. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. Suppl., 391, 31–37 (1997).
Okada, H., One- and three-month release injectable microspheres of the LH-RH superagonist leuprorelin acetate. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 28, 43–70 (1997).
Peppas, N. A., Analysis of Fickian and non-Fickian drug release from polymers. Pharm. Acta Helv., 60, 110–111 (1985).
Ramadas, M., Paul, W., Dileep, K. J., Anitha, Y., and Sharma, C. P., Lipoinsulin encapsulated alginate-chitosan capsules: intestinal delivery in diabetic rats. J. Microencapsul., 17, 405–411 (2000).
Ritger, P. L. and Peppas, N. A., A simple equation for description of solute release II. Fickian and anomalous release from swellable devices. J. Control. Release, 5, 37–42 (1987).
Shah, V. P., Midha, K. K., Findlay, J. W., Hill, H. M., Hulse, J. D., McGilveray, I. J., McKay, G., Miller, K. J., Patnaik, R. N., Powell, M. L., Tonelli, A., Viswanathan, C. T., and Yacobi, A., Bioanalytical method validation-a revisit with a decade of progress. Pharm. Res., 17, 1551–1557 (2000).
Sinha, V. R., Singla, A. K., Wadhawan, S., Kaushik, R., Kumria, R., Bansal, K., and Dhawan, S., Chitosan microspheres as a potential carrier for drugs. Int. J. Pharm., 274, 1–33 (2004).
Thanoo, B. C., Sunny, M. C., and Jayakrishnan, A., Crosslinked chitosan microspheres: preparation and evaluation as a matrix for the controlled release of pharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 44, 283–286 (1992).
Timmer, C. J., Sitsen, J. M., and Delbressine, L. P., Clinical pharmacokinetics of MTZ. Clin. Pharmacokinet., 38, 461–74 (2001).
Wang, Y. M., Sato, H., Adachi, I., and Horikoshi, I., Optimization of the formulation design of chitosan microspheres containing cisplatin. J. Pharm. Sci., 85, 1204–1210 (1996).
Yuan, Y., Chesnutt, B. M., Utturkar, G., Haggard, W. O., Yang, Y., Ong, J. L., and Bumgardner, J. D., The effect of cross-linking of chitosan microspheres with genipin on protein release. Carbohydr. Polym., 68, 561–567 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjan, O.P., Shavi, G.V., Nayak, U.Y. et al. Controlled release chitosan microspheres of mirtazapine: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 1919–1929 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-1112-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-1112-1