Abstract
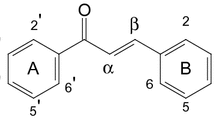
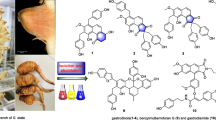
The purification of a MeOH extract from the rhizome of Acorus gramineus (Araceae) using column chromatography furnished two new stereoisomers of phenylpropanoid, acoraminol A (1) and acoraimol B (2). It also furnished 17 known phenolic compounds, β-asarone (3), asaraldehyde (4), isoacoramone (5), propioveratrone (6), (1′R,2′S)-1′,2′-dihydroxyasarone (7), (1′S,2′S)-1′,2′-dihydroxyasarone (8), 3′,4′-dimethoxycinnamyl alcohol (9), 3′,4′,5′-trimethoxycinnamyl alcohol (10), kaempferol 3-methyl ether (11), 2-[4-(3-hydroxypropyl)-2-methoxyphenoxy]-1,3-propanediol (12), hydroxytyrosol (13), tyrosol (14), (2S,5S)-diveratryl-(3R,4S)-dimethyltetrahydrofuran (15), (7S,8R)-dihydrodehydrodiconiferyl alcohol (16), 7S,8S-threo-4,7,9,9′-tetrahydroxy-3,3′-dimethoxy-8-O-4′-neolignan (17), 7S,8R-erythro-4,7,9,9′-tetrahydroxy-3,3′-dimethoxy-8-O-4′-neolignan (18), and dihydroyashsbushiketol (19). The structures of the new compounds were elucidated by analysis of spectroscopic data including 1D and 2D NMR data. The absolute configurations of 1 and 2 were determined using the convenient Mosher ester procedure. Compounds 5–19 were isolated for the first time from this plant source. The isolated compounds were tested for cytotoxicity against four human tumor cell lines in vitro using a Sulforhodamine B (SRB) bioassay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asakawa, Y., Chemical constituents of Alnus firma. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 43, 2223–2229 (1970).
Capasso, R., Cristinzio, G., Evidente, A., and Scognamiglio, F., Isolation, spectroscopy and selective phytotoxic effects of polyphenols from vegetable waste waters. Phytochemistry, 31, 4125–4128 (1992).
Chun, H. S., Kim, J. M., Choi, E. H., and Chang, N., Neuroprotective effects of several korean medicinal plants traditionally used for stroke remedy. J. Med. Food, 11, 246–251 (2008).
de Silva Filho, A. A., Albuquerque, S., Silva, M. L., Eberlin, M. N., Tomazela, D. M., and Bastos, J. K., Tetrahydrofuran lignans from Nectandra megapotamica with trypanocidal activity. J. Nat. Prod., 67, 42–45 (2004).
Feliciano, A. S., Medarde, M., Lopez, J. L., and Miguel del Corral, J. K., Two new cinnamyl isovalerate derivatives from Juniperus thurifera leaves. J. Nat. Prod., 49, 677–679 (1986).
Freire, F., Seco, J. M., Quinoa, E., and Riguera, R., Determining the absolute stereochemistry of secondary/secondary diols by 1H NMR: basis and applications. J. Org. Chem., 70, 3778–3790 (2005).
Greca, M. D., Monaco, P., Previtera, L., Aliotta, G., Pinto, G., and Pollio, A., Allelochemical activity of phenylpropanes from Acorus gramineus. Phytochemistry, 28, 2319–2321 (1989).
Herrera Braga, A. C., Zacchino, S., Badano, H., González Sierra, M., and Rúveda, E. A., 13C NMR spectral and conformational analysis of 8-O-4′ neolignans. Phytochemistry, 23, 2025–2028 (1984).
Joshi, B. P., Sharma, A., and Sinha, A. K., Microwave- and ultrasound-assisted semisynthesis of natural methoxylated propiophenones from isomeric mixture of phenylpropenes in minutes. Can. J. Chem., 83, 1826–1832 (2005).
Kouno, I., Yanagida, Y., Shimono, S., Shintomi, M., and Yang, C.-S., Phenylpropanoids from the barks of Illicium difengpi. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 40, 2461–2464 (1992).
Kuang, H. X., Xia, Y. G., Yang, B. Y., Wang, Q. H., and Lü, S. W., Lignan constituents from Chloranthus japonicus sieb. Arch. Pharm. Res., 32, 329–334 (2009).
Lee, J. Y., Lee, J. Y., Yun, B. S., and Hwang, B. K., Antifungal activity of β-asarone from rhizomes of Acorus gramineus. J. Agric. Food Chem., 52, 776–780 (2004).
Liao, J. F., Huang, S. Y., Jan, Y. M., Yu, L. L., and Chen, C. F., Central inhibitory effects of water extract of Acori graminei rhizoma in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol., 61, 185–193 (1998).
Matsuda, N. and Kikuchi, M., Studies on the constituents of Lonicera Species. X. Neolignan glycosides from the leaves of Lonicera gracilipes var. glandulosa MAXIM. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 44, 1676–1679 (1996).
Nawamaki, K. and Kuroyanagi, M., Sesquiterpenoids from Acorus calamus as germination inhibitors. Phytochemistry, 43, 1175–1182 (1996).
Prasad, A. K., Tyagi, O. D., Wengel, J., Boll, P. M., Olsen, C. E., Bisht, K. S., Singh, A., Sarangi, A., Kumar, R., Jain, S. C., and Parmar, V. S., Neolignans and a lignan from Piper clarkii. Phytochemistry, 39, 655–658 (1995).
Patra, A. and Mitra, A. K., Constituents of Acorus calamus. J. Nat. Prod., 44, 668–669 (1981).
Santos, B. V. O. and Chaves, M. C. O., 2,4,5-trimetoxypropiophenone from Piper marginatum. Biochem. Sys. Ecol., 27, 539–541 (1999).
Skehan, P., Storeng, R., Scudiero, D., Monks, A., McMahon, J., Vistica, D., Warren, J. T., Bokesch, H., Kenney, S., and Boyd, M. R., New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 82, 1107–1112 (1990).
Su, B. N., Park, E. J., Mbwambo, Z. H., Santarsiero, B. D., Mesecar, A. D., Fong, H. H., Pezzuto, J. M., and Kinghorn, A. D., New chemical constituents of Euphorbia quinquecostata and absolute configuration assignment by a convenient Mosher ester procedure carried out in NMR tubes. J. Nat. Prod., 65, 1278–1282 (2002).
Tang, W. and Eisenbrand, G., Chinese Drugs of Plant Origin. Springer, New York, pp. 45–46, (1992).
Valesi, A. G., Methylated flavonols in Larrea cuneifolia. Phytochemistry, 11, 2821–2826 (1972).
Wang, H. Z., Cheng, Y. G., and Fan C. S., Review of studies on chemical constituents and pharmacology of genus Acorus. Acta Bot. Yunnanica, 5, 96–100 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, C.H., Kim, K.H., Lee, I.K. et al. Phenolic constituents of Acorus gramineus . Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 1289–1296 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0808-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0808-6