Abstract
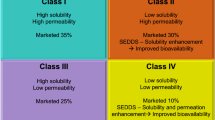
Dipyridamole shows poor and variable bioavailability after oral administration due to pHdependent solubility, low biomembrane permeability as well as being a substrate of P-glycoprotein. In order to improve the oral absorption of dipyridamole, a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) for dipyridamole was prepared and evaluated in vitro and in vivo. The optimum formulation was 18% oleic acid, 12% Labrafac lipophile WL 1349, 42% Solutol HS 15 and 28% isopropyl alcohol. It was found that the performance of self-microemulsification with the combination of oleic acid and Labrafac lipophile WL 1349 increased compared with just one oil. The results obtained from an in vitro dissolution assay indicated that dipyridamole in SMEDDS dissolved rapidly and completely in pH 6.8 aqueous media, while the commercial drug tablet was less soluble. An oral bioavailability study in rats showed that dipyridamole in the SMEDDS formulation had a 2.06-fold increased absorption compared with the simple drug suspension. It was evident that SMEDDS may be an effective approach to improve the oral absorption for drugs having pH-dependent solubility.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amidon, G. L., Lennernäs, H., Shah, V. P., and Crison, J. R., A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: the correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm. Res., 12, 413–420 (1995).
Balakrishnan, P., Lee, B. J., Oh, D. H., Kim, J. O., Lee, Y. I., Kim, D. D., Jee, J. P., Lee, Y. B., Woo, J. S., Yong, C. S., and Choi, H. G., Enhanced oral bioavailability of Coenzyme Q10 by self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm., 374, 66–72 (2009).
Balimane, P. V., Han, Y. H., and Chong, S., Current industrial practices of assessing permeability and Pglycoprotein interaction. AAPS J., 8, E1–E13 (2006).
Beten, D. B., Amighi, K., and Moës, A. J., Preparation of controlled-release coevaporates of dipyridamole by loading neutral pellets in a fluidized-bed coating system. Pharm. Res., 12, 1269–1272 (1995).
Bravo González, R. C., Huwyler, J., Walter, I., Mountfield, R., and Bittner, B., Improved oral bioavailability of cyclosporin A in male Wistar rats: comparison of a Solutol HS 15 containing self-dispersing formulation and a microsuspension. Int. J. Pharm., 245, 143–151 (2002).
Buckingham, L. E., Balasubramanian, M., Emanuele, R. M., Clodfelter, K. E., and Coon, J. S., Comparison of solutol HS 15, Cremophor EL and novel ethoxylated fatty acid surfactants as multidrug resistance modification agents. Int. J. Cancer, 62, 436–442 (1995).
Chen, Y., Li, G., Wu, X., Chen, Z., Hang, J., Qin, B., Chen, S., and Wang, R., Self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) of vinpocetine: formulation development and in vivo assessment. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 31, 118–125 (2008).
Cheng, J., Zhu, J. B., Wen, N., and Xiong, F., Stability and pharmacokinetic studies of O-palmitoyl amylopectin anchored dipyridamole liposomes. Int. J. Pharm., 313, 136–143 (2006).
Cornaire, G., Woodley, J., Hermann, P., Cloarec, A., Arellano, C., and Houin, G., Impact of excipients on the absorption of P-glycoprotein substrates in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Pharm., 278, 119–131 (2004).
Cui, J., Yu, B., Zhao, Y., Zhu, W., Li, H., Lou, H., and Zhai, G., Enhancement of oral absorption of curcumin by selfmicroemulsifying drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm., 371, 148–155 (2009).
Dahan, A. and Hoffman, A., The effect of different lipid based formulations on the oral absorption of lipophilic drugs: the ability of in vitro lipolysis and consecutive ex vivo intestinal permeability data to predict in vivo bioavailability in rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 67, 96–105 (2007).
Ghosh, P. K. and Murthy, R. S., Microemulsions: a potential drug delivery system. Curr. Drug Deliv., 3, 167–180 (2006).
Ghosh, P. K., Majithiya, R. J., Umrethia, M. L., and Murthy, R. S., Design and development of microemulsion drug delivery system of acyclovir for improvement of oral bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech, 7, 77 (2006).
Gursoy, R. N. and Benita, S., Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) for improved oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Biomed. Pharmacother., 58, 173–182 (2004).
Jadhav, K. R., Shaikh, I. M., Ambade, K. W., and Kadam, V. J., Applications of microemulsion based drug delivery system. Curr. Drug Deliv., 3, 267–273 (2006).
Jakobsson, B., el Hag, I. A., Erichsen, C., Christensson, P. I., Jönsson, P. E., and Stenram, U., Modulation of 5-fluorouracil and 5-fluorouridine toxicity by membrane transport inhibitors in normal tissues of rats with liver adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res., 9, 285–290 (1989).
Kale, A. A. and Patravale, V. B., Design and evaluation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) of nimodipine. AAPS PharmSciTech, 9, 191–196 (2008).
Khoo, S. M., Humberstone, A. J, Porter, C. J. H., Edwards, G. A., and Charman, W. N., Formulation design and bioavailability assessment of lipidic self-emulsifying formulations of halofantrine. Int. J. Pharm., 167, 155–164 (1998).
Kohri, N., Miyata, N., Takahashi, M., Endo, H., Iseki, K., Miyazaki, K., Takechi, S., and Nomura, A., Evaluation of pH-independent sustained-release granules of dipyridamole by using gastric-acidity-controlled rabbits and human subjects. Int. J. Pharm., 81, 49–58 (1992).
Liu, Y., Zhang, P., Feng, N., Zhang, X., Wu, S., and Zhao, J., Optimization and in situ intestinal absorption of selfmicroemulsifying drug delivery system of oridonin. Int. J. Pharm., 365, 136–142 (2009).
Mahmoud, E. A., Bendas, E. R., and Mohamed, M. I., Preparation and evaluation of self-nanoemulsifying tablets of carvedilol. AAPS PharmSciTech, 10, 183–192 (2009).
O’Driscoll, C. M., Lipid-based formulations for intestinal lymphatic delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 15, 405–415 (2002).
Patel, D. and Sawant, K. K., Oral bioavailability enhancement of acyclovir by self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDS). Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 33, 1318–1326 (2007).
Patel, D. and Sawant, K. K., Self micro-emulsifying drug delivery system: formulation development and biopharmaceutical evaluation of lipophilic drugs. Curr. Drug Deliv., 6, 419–424 (2009).
Patel, V. F. and Patel, N. M., Statistical evaluation of influence of xanthan gum and guar gum blends on dipyridamole release from floating matrix tablets. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 33, 327–334 (2007).
Rao, S. V. R. and Shao, J., Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) for oral delivery of protein drugs: I. Formulation development. Int. J. Pharm., 362, 2–9 (2008).
Sha, X., Yan, G., Wu, Y., Li, J., and Fang, X., Effect of selfmicroemulsifying drug delivery systems containing Labrasol on tight junctions in Caco-2 cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 24, 477–486 (2005).
Singh, A. K., Chaurasiya, A., Jain, G. K., Awasthi, A., Asati, D., Mishra, G., Khar, R. K., and Mukherjee, R., High performance liquid chromatography method for the pharmacokinetic study of bicalutamide SMEDDS and suspension formulations after oral administration to rats. Talanta, 78, 1310–1314 (2009).
Sugawara, M., Kadomura, S., He, X., Takekuma, Y., Kohri, N., and Miyazaki, K., The use of an in vitro dissolution and absorption system to evaluate oral absorption of two weak bases in pH-independent controlled-release formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 26, 1–8 (2005).
Terhaag, B., Donath, F., Le Petit, G., and Feller, K., The absolute and relative bioavailability of dipyridamole from different preparations and the in vitro-in vivo comparison. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol., 24, 298–302 (1986).
Varma, M. V., Perumal, O. P., and Panchagnula, R., Functional role of P-glycoprotein in limiting peroral drug absorption: optimizing drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 10, 367–373 (2006).
Verstuyft, C., Strabach, S., El-Morabet, H., Kerb, R., Brinkmann, U., Dubert, L., Jaillon, P., Funck-Brentano, C., Trugnan, G., and Becquemont, L., Dipyridamole enhances digoxin bioavailability via P-glycoprotein inhibition. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 73, 51–60 (2003).
Xi, J., Chang, Q., Chan, C. K., Meng, Z. Y., Wang, G. N., Sun, J. B., Wang, Y. T., Tong, H. H., and Zheng, Y., Formulation development and bioavailability evaluation of a self-nanoemulsified drug delivery system of oleanolic acid. AAPS PharmSciTech, 10, 172–182 (2009).
Yao, J., Lu, Y., and Zhou, J. P., Preparation of nobiletin in self-microemulsifying systems and its intestinal permeability in rats. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci., 11, 22–29 (2008).
Yin, Y. M., Cui, F. D., Mu, C. F., Choi, M. K., Kim, J. S., Chung, S. J., Shim, C. K., and Kim, D. D., Docetaxel microemulsion for enhanced oral bioavailability: preparation and in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Control. Release, 140, 86–94 (2009).
Zhang, Y., Gupta, A., Wang, H., Zhou, L., Vethanayagam, R. R., Unadkat, J. D., and Mao, Q., BCRP transports dipyridamole and is inhibited by calcium channel blockers. Pharm. Res., 22, 2023–2034 (2005).
Zhou, R., Moench, P., Heran, C., Lu, X., Mathias, N., Faria, T. N., Wall, D. A., Hussain, M. A., Smith, R. L., and Sun, D., pH-dependent dissolution in vitro and absorption in vivo of weakly basic drugs: development of a canine model. Pharm. Res., 22, 188–192 (2005).
Zvonar, A., Berginc, K., Kristl, A., and Gašperlin, M., Microencapsulation of self-microemulsifying system: improving solubility and permeability of furosemide. Int. J. Pharm., 388, 151–158 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, F., Zhong, H., He, J. et al. Self-microemulsifying drug delivery system for improved oral bioavailability of dipyridamole: Preparation and evaluation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 1113–1123 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0709-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0709-8