Abstract
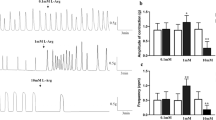
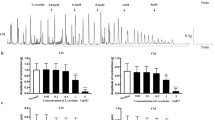
The effects of trimebutine maleate (TM) on spontaneous contractions of colonic longitudinal muscle were investigated in guinea pigs. The contractile responses of smooth muscle strips were recorded by an isometric force transducer. Membrane and action potentials were detected by an intracellular microelectrode technique. The whole-cell patch clamp recording technique was used to record the changes in large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKca) and L-type Ca2+ currents in colonic smooth muscle cells. At high concentrations (30, 100, and 300 μM), TM inhibited the amplitude of spontaneous contractions. At low concentrations (1 and 10 μM), TM attenuated the frequency and tone of smooth muscle strips, whereas TM had no influence on the amplitude of spontaneous contractions. TM depolarized the membrane potentials, but decreased the amplitude and frequency of action potentials at high concentrations. TM inhibited BKca and L-type Ca2+ currents in a dose-dependent manner. In the presence of the BKca channel opener, NS1619, TM also inhibited BKca currents. Bayk8644, a L-type Ca2+ channel opener, increased L-type Ca2+ currents. This augmentation was also attenuated by TM. These results suggest that TM attenuates intestinal motility through inhibition of L-type Ca2+ currents, and depolarizes membrane potentials by reducing BKca currents. Thus, TM may be a multiple-ion channel regulator in the gastrointestinal tract.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delvaux, M. and Wingate, D., Trimebutine: mechanism of action, effects on gastrointestinal function and clinical results. J. Int. Med. Res., 25, 225–246 (1997).
Dumitraşcu, D. L. and Stǎanculete, M., The effect of trimebutine on the psychosocial adjustment to illness in the irritable bowel syndrome. Rom. J. Intern. Med., 44, 273–280 (2006).
Frexinos, J., Fioramonti, J., and Bueno, L., Effect of trimebutine on colonic myoelectrical activity in IBS patients. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 28, 181–185 (1985).
Hennig, G. W., Smith, C. B., O’shea, D. M., and Smith, T. K., Patterns of intracellular and intercellular Ca2+ waves in the longitudinal muscle layer of the murine large intestine in vitro. J. Physiol., 543, 233–253 (2002).
Hiyama, T., Yoshihara, M., Matsuo, K., Kusunoki, H., Kamada, T., Ito, M., Tanaka, S., Nishi, N., Chayama, K., and Haruma, K., Meta-analysis of the effects of prokinetic agents in patients with functional dyspepsia. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 22, 304–310 (2007).
Kaneto, H., Takahashi, M., and Watanabe, J., The opioid receptor selectivity for trimebutine in isolated tissues experiments and receptor binding studies. J. Pharmacobiodyn., 13, 448–453 (1990).
Kountouras, J., Chatzopoulos, D., Zavos, C., Boura, P., Venizelos, J., and Kalis, A., Efficacy of trimebutine therapy in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease and irritable bowel syndrome. Hepatogastroenterology, 49, 193–197 (2002).
Li, J. X., Liu, X. G., Xie, P. Y., and Li, J., Regulation of activities of colonic smooth muscle in wrap restraint stress rats by trimebutine mealate. Zhonghua Xiao Hua Za Zhi, 23, 655–658 (2003).
Nagasaki, M., Yamada, K., Ikezawa, K., and Tamaki, H., Contribution of peripheral opioid receptors to the trimebutineinduced contractions of the proximal colon in anesthetized rats. Nippon Heikatsukin Gakkai Zasshi, 25, 27–30 (1989).
Nagasaki, M., Kurosawa, H., Naito, K., and Tamaki, H., Allosteric interaction of trimebutine maleate with dihydropyridine binding sites. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 189, 71–76 (1990).
Nagasaki, M., Kobayashi, T., and Tamaki, H., Effects of trimebutine on cytosolic Ca2+ and force transitions in intestinal smooth muscle. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 195, 317–321 (1991).
Nagasaki, M., Komori, S., and Ohashi, H., Effect of trimebutine on voltage-activated calcium current in rabbit ileal smooth muscle cells. Br. J. Pharmacol., 110, 399–403 (1993a).
Nagasaki, M., Komori, S., Tamaki, H., and Ohashi, H., Effect of trimebutine on K+ current in rabbit ileal smooth muscle cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 235, 197–203 (1993b).
Nagasaki, M., Itagaki, M., Komori, S., and Ohashi, H., Effect of trimebutine on contractile responses in skinned ileal smooth muscle. Jpn. J. Pharmacol., 65, 249–255 (1994).
Sanders, K. M., Regulation of smooth muscle excitation and contraction. Neurogastroenterol. Motil., 20Suppl 1, 39–53 (2008).
Shimada, T., Kurachi, Y., Terano, A., Hamada, E., and Sugimoto, T., Trimebutine maleate has inhibitory effects on the voltage-dependent Ca2+ inward current and other membrane currents in intestinal smooth muscle cells. Gastroenterol. Jpn., 25, 175–179 (1990).
Takenaga, H., Magaribuchi, T., and Tamaki, H., Effects of trimebutine maleate (TM-906) on the spontaneous contraction of isolated guinea pig colon. Jpn. J. Pharmacol., 34, 177–181 (1984).
Takenaga, H., Magaribuchi, T., and Tamaki, H., Effects of trimebutine maleate (TM-906) on the spontaneous contraction of isolated duodenum and ileum in both guinea pigs and rabbits. Jpn. J. Pharmacol., 40, 13–20 (1986).
Taniyama, K., Sano, I., Nakayama, S., Matsuyama, S., Takeda, K., Yoshihara, C., and Tanaka, C., Dual effect of trimebutine on contractility of the guinea pig ileum via the opioid receptors. Gastroenterology, 101, 1579–1587 (1991).
Xu, L., Chen, J., Yu, B., Dong, W., Chen, K., Luo, H., and Zhu, Y., Effect of progesterone on calcium activated potassium currents and intracellular calcium in guinea pig colon myocytes. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol., 27, 475–482 (2005).
Xu, L., Yu, B. P., Chen, J. G., and Luo, H. S., Mechanisms mediating serotonin-induced contraction of colonic myocytes. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol., 34, 120–128 (2007).
Xue, L., Fukuta, H., Yamamoto, Y., and Suzuki, H., Dual effects of trimebutine on electrical responses of gastric smooth muscles in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 294, 75–81 (1995).
Yamasato, T., Takaki, M., and Nakayama, S., Opiate-like inhibitory effect of trimebutine on the twitch response of the isolated guinea pig ileum. Acta Med. Okayama, 41, 33–35 (1987).
Zahradníková, A., Minarovic, I., and Zahradník, I., Competitive and cooperative effects of Bay K8644 on the L-type calcium channel current inhibition by calcium channel antagonists. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 322, 638–645 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, W., Zhang, H., Luo, HS. et al. Effects of trimebutine maleate on colonic motility through Ca2+-activated K+ channels and L-type Ca2+ channels. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 979–985 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0615-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0615-0