Abstract
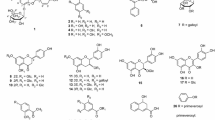
From the 70% ethanol extract of the rhizomes of Cyperus rotundus (CRE), several major constituents including the sesquiterpene derivatives (valencene, nootkatone, and caryophyllene α-oxide), monoterpenes (β-pinene, 1,8-cineole, and limonene) and 4-cymene were isolated and examined for their anti-allergic activity in vitro and in vivo. In rat basophilic leukemia (RBL)-1 cells, the sesquiterpenes strongly inhibited 5-lipoxygenase-catalyzed leukotrienes production. In addition, they inhibited β-hexosaminidase release by antigen-stimulated RBL-2H3 cells, with valencene having the highest inhibitory effect. CRE inhibited leukotrienes production and β-hexosaminidase release at 300 μg/mL. It was also found that the most active sesquiterpene (valencene) and CRE inhibited β-hexosaminidase degranulation by inhibiting the initial activation reaction, Lyn phosphorylation, in IgE-stimulated RBL-2H3 cells. Moreover, CRE, valencene and nootkatone significantly inhibited the delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction in mice when administered orally at 50–300 mg/kg. In conclusion, C. rotundus and its constituents, valencene, nootkatone, and caryophyllene α-oxide, exert anti-allergic activity in vitro and in vivo. These sesquiterpenes, but not monoterpenes, certainly contribute to the anti-allergic activity of the rhizomes of C. rotundus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae, K., The medicinal plants of Korea. Kyo-Hak Pub., Seoul, pp. 582, (2000).
Cheong, H., Choi, E. J., Yoo, G. S., Kim, K. M., and Ryu, S. Y., Desacetylmatricarin, an anti-allergic component from Taraxacum platycarpum. Planta Med., 64, 577–578 (1998).
Choi, O. H., Kim, J. H., and Kinet, J. P., Calcium mobilization via sphingosine kinase in signaling by the Fc epsilon RI antigen receptor. Nature, 380, 634–636 (1996).
Guerrini, A., Sacchetti, G., Muzzoli, M., Rueda, G. M., Medici, A., Besco, E., and Bruni, R., Composition of the volatile fraction of Ocotea bofo Kunth (Lauraceae) calyces by GC-MS and NMR fingerprinting and its antimicrobial and antioxidant activity. J. Agric. Food Chem., 54, 7778–7788 (2006).
Gupta, M. B., Palit, T. K., Signh, N., and Bhargava, K. P., Pharmacological studies to isolate the active constituents from Cyperus rotundus possessing anti-inflammatory, anti-pyretic and analgesic activities. Indian J. Med. Res., 59, 76–82 (1971).
Kawakami, Y., Kitaura, J., Satterthwaite, A. B., Kato, R. M., Asai, K., Hartman, S. E., Maeda-Tamamoto, M., Lowell, C. A., Rawlings, D. J., Witte, O. N., and Kawakami, T., Redundant and opposing functions of two tyrosine kinases, Btk and Lyn, in mast cell activation. J. Immunol., 165, 1210–1219 (2000).
Majetich, G., Behnke, M., and Hull, K. A., Stereoselective synthesis of (±)-nootkatone and (±)-valencene via an intramolecular Sakurai reaction. J. Org. Chem., 50, 3615–3618 (1985).
Marquardt, D. L. and Wasserman, S. I., Modulation of rat serosal mast cell biochemistry by in vivo dexamethasone administration. J. Immunol., 131, 934–939 (1983).
Minyard, P., Tumlinson, J. H., Hedin, P. A., and Thompson, A. C., Isolation and identification, constituents of cotton bud. terpene hydrocarbons. J. Agric. Food Chem., 13, 599–602 (1965).
Miyazawa, M., Kameoka, H., Morinaga, K., Negoro, K., and Mura, N., Hydroxycineole: four new metabolites of 1,8-cineole in rabbits. J. Agric. Food Chem., 37, 222–226 (1989).
Miyazawa, M., Nakamura, Y., and Ishikawa, Y., Insecticidal sesquiterpene from Alpinia oxyphylla against Drosophila melanogaster. J. Agric. Food Chem., 48, 3639–3641 (2000).
Morikawa, T., Matsuda, H., Sakamoto, Y., Ueda, K., and Yoshikawa, M., New farnesane-type sesquiterpenes, hedychiols A and B 8,9-diacetate, and inhibitors of degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells from the rhizome of Hedychium coronarium. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 50, 1045–1049 (2002).
Mossman, T., Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxic assays. J. Immunol. Methods, 65, 55–63 (1983).
Resch, M., Steigel, A., Chen, Z. L., and Bauer, R., 5-Lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase-1 inhibitory active compounds from Atractylodes lancea. J. Nat. Prod., 61, 347–350 (1998).
Rubin, P. and Mollison, K. W., Pharmacotherapy of diseases mediated by 5-lipoxygenase pathway eicosanoids. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat., 83, 188–197 (2007).
Ryu, S. Y., Oak, M. H., and Kim, K. M., Yomogin inhibits the degranulation of mast cells and the production of the nitric oxide in activated RAW 264.7 cells. Planta Med., 66, 171–173 (2000).
Schwartz, L. B., Lewis, R. A., Seldin, D., and Austen, F., Acid hydrolases and tryptase from secretory granules of disrupted human ling mast cells. J. Immunol., 126, 1290–1294 (1981).
Seo, W. -G., Pae, H. -O., Oh, G. -S., Chai, K. -Y., Kwon, T. -O., Yun, Y. -G., Kim, N. -Y., and Chung, H. -T., Inhibitory effects of methanol extract of Cyperus rotundus rhizomes on nitric oxide and superoxide production by murine macrophage cell line, RAW 264.7 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol., 76, 59–64 (2001).
Singh, N., Kulshrestha, V. K., Gupta, M. B., and Bhargava, K. P., A pharmacological study of Cyperus rotundus. Indian J. Med. Res., 58, 103–109 (1970).
Siraganian, R. P., Zhang, J., and Kimura, T., Regulation and function of protein tyrosine kinase Syk in FcɛRI-mediated signaling, In Razin, E. and Rivera, J. (Eds.). Signal transduction in mast cells and basophils. Springer, Germany, Berlin, pp. 115–133, (1999).
Thebtaranonth, C., Thebtaranonth, Y., Wanauppathamkul, S., and Yuthavong, Y., Antimalarial sesquiterpenes from tubers of Cyperus rotundus: structure of 10,12-peroxycalamenene, a sesquiterpene endoperoxide. Phytochemistry, 40, 125–128 (1995).
Thomet, O. A. R., Wiesmann, U. N., Blaser, K., and Simon, H. -U., Differential inhibition of inflammatory effector functions by petasin, isopetasin and neopetasin in human eosinophils. Clin. Exp. Allergy, 31, 1310–1320 (2001).
Tries, S., Neupert, W., and Laufer, S., The mechanism of action of the new anti-inflammatory compound ML3000: inhibition of 5-LOX and COX-1/2. Inflamm. Res., 51, 135–143 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, J.H., Lee, DU., Kim, Y.S. et al. Anti-allergic activity of sesquiterpenes from the rhizomes of Cyperus rotundus . Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 223–228 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0207-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0207-z