Abstract
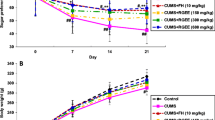
Magnolia bark combined with ginger rhizome is a common drug pair in traditional Chinese prescriptions for the treatment of depression. In the present study, we examined antidepressant-like effects of the mixture of honokiol and magnolol (HMM) from magnolia bark and essential oil from ginger rhizome (OGR) alone and in combination in chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) of rats. Behavioral (sucrose intake, immobility time of forced swimming test) and biochemical parameters [serotonin (5-HT) in prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and striatum, gastric mucosa cholecystokinin (CCK) and serum gastrin (GAS) levels] were simultaneously examined in the CUMS rats. 20 mg/kg HMM alone, but not OGR, significantly increased sucrose intake and reduced immobility time in the CUMS rats. Moreover, 20 mg/kg HMM and 14 mg/kg OGR in combination exhibited significant synergistic effects on sucrose intake increase and immobility time reduction in the CUMS rats. HMM elevated 5-HT levels in various brain regions, and OGR reduced gastric mucosa CCK and serum GAS levels in the CUMS rats. These results suggested that the synergistic antidepressant-like effects of compatibility of HMM with OGR might be mediated simultaneously by regulation of the serotonergic and gastroenteric system functions. These findings also provided a pharmacological basis for the clinical application of this drug pair of magnolia bark and ginger rhizome in traditional Chinese medicine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aly, A., Shulkes, A., and Baldwin, G. S., Gastrins, cholecystokinins and gastrointestinal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1704, 1–10 (2004).
Banerjee, S., Sharma, R., Kale, R. K., and Rao, A. R., Influence of certain essential oils on carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes and acid-soluble sulfhydryls in mouse liver. Nutr. Cancer., 21, 263–269 (1994).
Bekris, S., Antoniou, K., Daskas, S., and Papadopoulou, D. Z., Behavioural and neurochemical effects induced by chronic mild stress applied to rat strains. Behav. Brain Res., 161, 45–59 (2005).
Claghorn, J., A double-blind comparison of paroxetine and placebo in the treatment of depressed outpatients. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol., 6, 25–30 (1992).
Curzon, G. and Green, A. R., Rapid method for the determination of 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in small regions of rat brain. Br. J. Pharmacol., 39, 653–655 (1970).
Dockray, G. J., Clinical endocrinology and metabolism. Gastrin. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 18, 555–568 (2004).
D’Aquila, P. S., Newton, J., and Willner, P., Durnal variation in the effect of chronic mild stress on sucrose intake and preference. Physiol. Behav., 62, 421–426 (1997).
Delgado, P. and Moreno, F., Antidepressants and the brain. Int. Clin. Psychopharm., 14, 9–16 (1999).
Dumitriu, D., Collins, K., Alterman, R., and Mathew, S. J., Neurostimulatory therapeutics in management of treatment-resistant depression with focus on deep brain stimulation. Mt. Sinai. J. Med., 75, 263–275 (2008).
Edkins, J. S., The chemical mechanism of gastric secretion. J. Physiol., 34, 133–144 (1906).
Fossey, M. D. and Lydiard, R. B., Anxiety and the gastrointestinal system. Psychiatr. Med., 8, 175–186 (1990).
Goodwin, F. R. and Jamison, K. R., Manic-depressive illness. New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1990:416–441.
Gronli, J., Fiske, E., Murison, R., Bjorvatn, B., Sorensen, E., Ursin, R., and Portas, C. M., Extracellular levels of serotonin and GABA in the hippocampus after chronic mild stress in rats. A microdialysis study in an animal model of depression. Behav. Brain Res., 181, 42–51 (2007).
Guo, Y. S., Kong, L. D., Wang, Y. M., and Huang, Z. Q., Antidepressant evaluation of polysaccharides from a Chinese herbal medicine Banxia-houpu decoction. Phytother. Res., 18, 204–207 (2004).
Harro, J., Haidkind, R., Harro, M., Modiri, A. R., Gillberg, P. G., Pahkla, R., Matto, V., and Oreland, L., Chronic mild unpredictable stress after noradrenergic denervation: attenuation of behavioural and biochemical effects of DSP-4 treatment. Eur. Neuropsychopharm., 10, 5–16 (1999).
Hsieh, M. T., Chueh, F. Y., and Lin, M. T., Magnolol decreases body temperature by reducing 5-hydroxytryptamine release in the rat hypothalamus. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol., 25, 813–817 (1998).
Itoh, H., Katagiri, F., Ikawa, K., and Takeyama, M., Effects of domperidone on human plasma levels of motilin, somatostatin, gastrin, adrenocorticotropic hormone and cortisol. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 28, 1752–1756 (2005).
Kabuto, H., Nishizawa, M., Tada, M., Higashio, C., Shishibori, T., and Kohno, M., Zingerone [4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-butanone] prevents 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopamine depression in mouse striatum and increases superoxide scavenging activity in serum. Neurochem. Res., 30, 325–332 (2005).
Katagiri, F., Inoue, S., Itoh, H., and Takeyama, M., Clinical application of an enzyme immunoassay for cholecystokininlike immunoreactive substance for determination of the human plasma levels: the effect of metoclopramide on gastrointestinal peptides and stress-related hormones. J. Pept. Sci., 12, 311–320 (2006).
Kim, H., Whang, W. W., Kim, H. T., Pyun, K. H., Cho, S. Y., Hahm, D. H., Lee, H. J., and Shim, I., Expression of neuropeptide Y and cholecystokinin in the rat brain by chronic mild stress. Brain Res., 983, 201–208 (2003).
Kitanaka, N., Kitanaka, J., and Takemura, M., Inhibition of methamphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion in mice by clorgyline, a monoamine oxidase-a inhibitor, through alteration of the 5-hydroxytriptamine turnover in the striatum. Neuroscience, 130, 295–308 (2005).
Koh, K. B. and Park, J. K., The relation between anger management style and organ system-related somatic symptoms in patients with depressive disorders and somatoform disorders. Yonsei. Med. J., 49, 46–52 (2008).
Kuribara, H., Stavinoha, W. B., and Maruyama, Y., Behavioural pharmacological characteristics of honokiol, an anxiolytic agent present in extracts of Magnolia bark, evaluated by an elevated plus-maze test in mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 50, 819–826 (1998).
Kyung, K. S., Gon, J. H., Geun, K. Y., Sup, J. J., Suk, W. J., and Ho, K. J., 6-Shogaol, a natural product, reduces cell death and restores motor function in rat spinal cord injury. Eur. J. Neurosci., 24, 1042–1052 (2006).
Lei, Z. J., Zhang, Z. Y., Wang, P., Yao, Y. F., and Wu, H. Q., Studies on constituents of the extracts of Magnoliae officinalis using supercritical fluid extraction with carbon dioxide. Chinese J. Mod. Appl. Pharm., 17, 13–14 (2000).
Li, J. M., Kong, L. D., Wang, Y. M., Cheng, C. H. K., Zhang, W. Y., and Tan, W. Z., Behavioral and biochemical studies on chronic mild stress models in rats treated with a Chinese traditional prescription Banxia-houpu decoction. Life Sci., 74, 55–73 (2003a).
Li, J. M., Yang, C., Zhang, W. Y., and Kong, L. D., The effects of banxia houpu decoction on a chronic mild stress model of depression. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi, 28, 55–59 (2003b).
Li, Y. C., Wang, F. M., Pan, Y., Qiang, L. Q., Cheng, G., Zhang, W. Y., and Kong, L. D., Antidepressant-like effects of curcumin on serotonergic receptor-coupled AC-cAMP pathway in chronic unpredictable mild stress of rats. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 33: 435–449 (2009).
Liang, M.H., From America: cookbook medicine or food for thought: practice guidelines development in USA. Ann. Rheum. Dis., 51, 1257–1258 (1992).
Lim, W. C., Seo, J. M., Lee, C. I., Pyo, H. B., and Lee, B. C., Stimulative and sedative effects of essential oils upon inhalation in mice. Arch. Pharm. Res., 28, 770–4 (2005).
Lofberg, C., Agren, H., Harro, J., and Oreland, L., Cholecystokinin in CSF from depressed patients: possible relations to severity of depression and suicidal behaviour. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol., 8, 153–157 (1998).
Maruyama, Y., Kuribara, H., Morita, M., Yuzurihara, M., and Weintraub, S. T., Identification of magnolol and honokiol as anxiolytic agents in extracts of saiboku-to, an oriental herbal medicine. J. Nat. Prod., 61, 135–138 (1998).
Mei, S. L., Zheng, Q. X., and Zou, G. M., GC-MS analysis on essential oil of ginger. J. Jilin Inst. Chem. Technol., 22, 11–13 (2005).
Nakazawa, T., Yasuda, T., and Ohsawa, K., Metabolites of orally administered Magnolia officinalis extract in rats and man and its antidepressant-like effects in mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 55, 1583–1591 (2003).
Nakamura, Y., Yoshida, C., Murakami, A., Ohigashi, H., Osawa, T., and Uchida, K., Zerumbone, a tropical ginger sesquiterpene, activates phase II drug metabolizing enzymes. FEBS. Lett., 572, 245–250 (2004).
Nestler, E. J., Barrot, M., DiLeone, R. J., Eisch, A. J., Gold, S. J., and Monteggia, L. M., Neurobiology of depression. Neuron, 34, 13–25 (2002a).
Nestler, E. J., Gould, E., Manji, H., Buncan, M., Duman, R. S., and Greshenfeld, H., Preclinical models: status of basic research in depression. Biol. Psychiat., 52, 503–528 (2002b).
Nutt, D. J., Relationship of neurotransmitters to the symptoms of major depressive disorder. J. Clin. Psychiat., 69, 4–7 (2008).
Papakostas, G. I., Fava, M., and Thase, M. E., Treatment of SSRI-resistant depression: a meta-analysis comparing within-versus across-class switches. Biol. Psychiat., 63, 699–704 (2008).
Papp, M., Klimek, V., and Willner, P., Parallel changes in dopamine D2 receptor binding in limbic forebrain associated with chronic mild stress-induced anhedonia and its reversal by imipramine. Psycho-pharmacology, 115, 441–446 (1994).
Papp, M., Nalepa, I., Antkiewicz-Michaluk, L., and Sanchez, C., Behavioural and biochemical studies of citalopram and WAY 100635 in rat chronic mild stress model. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 72, 465–474 (2002).
Pimentel, L. and Trommer, L., Cyclic antidepressant overdoses. A review. Emerg. Med. Clin. North. Am., 12, 533–547 (1994).
Porsolt, R. D., Anton, G., Blavet, N., and Jalfre, M., Behavioural despair in rats: A new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 47, 379–391 (1978).
Porsolt, R. D., Le Pichon, M., and Jalfre, M., Depression: A new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature, 266, 730–732 (1977).
Rehfeld, J. F., Four basic characteristics of the gastrin-CCK system. Am. J. Physiol., 240, G255–G266 (1981).
Singh, V. K., Singh, S., and Singh, D. K., Effect of active molluscicidal component of spices on different enzyme activities and biogenic amine levels in the nervous tissue of Lymnaea acuminata. Phytother. Res., 13, 649–654 (1999).
Tanum, L. and Malt, U. F., Personality traits predict treatment outcome with an antidepressant in patients with functional gastrointestinal disorder. Scand. J. Gastroenterol., 35, 935–41(2000).
Teng, C. M., Chen, C. C., Ko, F. N., Lee, L. G., Huang, T. F., Chen, Y. P., and Hsu, H. Y., Two antiplatelet agents from Magnolia officinalis. Thromb. Res., 50, 757–765 (1988).
Trivedi, M. H., Rush, A. J., Wisniewski, S. R., Nierenberg, A. A., Warden, D., Ritz, L., Norquist, G., Howland, R. H., Lebowitz, B., McGrath, P. J., Shores-Wilson, K., Biggs, M. M., Balasubramani, G. K., Fava, M., and STAR*D Study Team., Evaluation of outcomes with citalopram for depression using measurement-based care in STAR*D: implications for clinical practice. Am. J. Psychiat., 163, 28–40 (2006).
Tsai, T. H., Lee, T. F., Chen, C. F., and Wang, L. C., Modulatory effects of magnolol on potassium-stimulated 5-hydroxytryptamine 5-HT release from rat cortical and hippocampal slices. Neurosci. Lett., 186, 49–52 (1995).
Varghese, A. K., Verdú, E. F., Bercik, P., Khan, W. I., Blennerhassett, P. A., Szechtman, H., and Collins, S. M., Antidepressants attenuate increased susceptibility to colitis in a murine model of depression. Gastroenterology, 130, 143–153 (2006).
Wang, Y., Kong, L. D., and Chen, Y. M., Behavioural and biochemical effects of fractions prepared from Banxia Houpu decoction in depression models in mice. Phytother. Res., 19, 526–529 (2005).
Wank, S. A., G protein-coupled receptors in gastrointestinal physiology I. CCK receptors: an exemplary family. Am. J. Physiol., 274, G607–613 (1998).
Watanabe, K., Watanabe, H., Goto, Y., Yamaguchi, M., Yamamoto, N., and Hagino, K., Pharmacological properties of magnolol and honokiol extracted from Magnolia officinalis: central depressant effects. Planta Med., 49, 103–108 (1983).
Wei, F. X., Han, J., Wang, Q. L., Wang, J. M., Cheng, Y. H., and Shi, Y. H., Technique of supercritical fluid extraction-fractionation for gingerol. Fine Chem., 21, 269–272 (2004)
Welch, A. S. and Welch, B. L., Solvent extraction method for simultaneous determination of norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in a single mouse brain. Anal. Biochem., 30, 161–179 (1969).
Willner, P., Chronic mild stress (CMS) revisited: consistency and behavioural-neurobiological concordance in the effects of CMS. Neuropsychobiology, 52, 90–110 (2005).
Willner, P., Towell, A., Sampson, D., Sophokleous, S., and Muscat, R., Reduction of sucrose preference by chronic unpredictable mild stress, and its restoration by a tricyclic antidepressant. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 93, 358–364 (1987).
Xu, Q., Yi, L. T., Pan, Y., Wang, X., Li, Y. C., Li, J. M., Wang, C. P., and Kong, L. D., Antidepressant-like effects of the mixture of honokiol and magnolol from the barks of Magnolia officinalis in stressed rodents. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 32, 715–725 (2008).
Yamahara, J., Huang, Q. R., Li, Y. H., Xu, L., and Fujimura, H., Gastrointestinal motility enhancing effect of ginger and its active constituents. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 38, 430–431 (1990)
Yi, L. T., Li, J. M., Li, Y. C., Pan, Y., Xu, Q., and Kong, L. D., Antidepressant-like behavioral and neurochemical effects of the citrus-associated chemical apigenin. Life Sci., 82, 741–751 (2008)
Yi, L. T., Xu, Q., Li, Y. C., Yang, L., and Kong, L. D., Antidepressant-like synergism of extracts from magnolia bark and ginger rhizome alone and in combination in mice. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2009.03.001.
Yuan, C. L., Liang, A. J., Zeng, L., Jia, N., and Feng, L., Pharmacokinetics Profile of Magnolol and Honokiol in Wistar Rats. Pharm. J. Chin. PIA., 19, 258–261 (2003)..
Zhang, W. W., Li, J. M., Zhu, J. X., Shi, Z. Q., Wang, Y., and Kong, L. D., Chinese medicine Banxia-houpu decoction regulates c-fos expression in the brain regions in chronic mild stress model in rats. Phytother. Res., 18, 200–203 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiang, LQ., Wang, CP., Wang, FM. et al. Combined administration of the mixture of honokiol and magnolol and ginger oil evokes antidepressant-like synergism in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 32, 1281–1292 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1914-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1914-6