Abstract
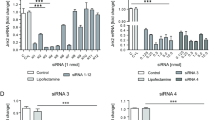
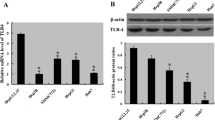
Hepatitis B virus triggers an increase of NF-κB inducing kinase (NIK)-dependent NF-κB activation, followed by the promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, we examined the inhibitory effect of NIK-specific siRNA on NF-κB signaling and HCC. The results of this study indicated that these siRNAs suppressed HBV-derived HCC by regulating NIK activation. To exert a protective effect from degradation enzyme, cationic liposomes were contrived and modified to contain β-sitosterol glucoside to target the asialoglycoprotein receptors in liver cancer cells. The cationic dimyristoyl diacyltrimethylammonium propane liposomes were prepared by a reverse-phase evaporation method with slight modification. β-Sitosterol glucoside was added to the lipid mixture at the beginning of the liposome preparation for the purpose of liver targeting. These liposomes assisted the delivery of the siRNA to specific cells and protected it from various lyases, followed by the ultimate suppression of HCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dykxhoorn, D. M., Novina, C. D., and Sharp, P. A., Killing the messenger: short RNAs that silence gene expression. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 4, 457–467 (2003).
Elbashir, S. M., Harborth, J., Lendeckel, W., Yalcin, A., Weber, K., and Tuschl, T., Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature, 411, 494–498 (2001).
Ghosh, S., and Karin, M., Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell, 109Suppl, S81–S96 (2002).
Hannon, G. J., RNA interference. Nature, 418, 244–251 (2002).
Kawano, K., Nakamura, K., Hayashi, K., Nagai, T., Takayama, K., and Maitani, Y., Liver targeting liposomes containing beta-sitosterol glucoside with regard to penetrationenhancing effect on HepG2 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 25, 766–770 (2002).
Kittler, R., and Buchholz, F., RNA interference: gene silencing in the fast lane. Semin. Cancer Biol., 13, 259–265 (2003).
Malinin, N. L., Boldin, M. P., Kovalenko, A. V., and Wallach, D., MAP3K-related kinase involved in NF-kappaB induction by TNF, CD95 and IL-1. Nature, 385, 540–544 (1997).
Mann, D. A., and Oakley, F., NF-kappaB: a signal for cancer. J. Hepatol., 42, 610–611 (2005).
Nakano, H., Shindo, M., Sakon, S., Nishinaka, S., Mihara, M., Yagita, H., and Okumura, K., Differential regulation of IkappaB kinase alpha and beta by two upstream kinases, NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase kinase-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 95, 3537–3542 (1998).
Okamoto, T., Sakurada, S., Yang, J. P., and Merin, J. P., Regulation of NF-kappa B and disease control: identification of a novel serine kinase and thioredoxin as effectors for signal transduction pathway for NF-kappa B activation. Curr. Top. Cell. Regul., 35, 149–161 (1997).
Qi, X. R., Yan, W. W., and Shi, J., Hepatocytes targeting of cationic liposomes modified with soybean sterylglucoside and polyethylene glycol. World J. Gastroenterol, 11, 4947–4952 (2005).
Rabe, C., Cheng, B., and Caselmann, W. H., Molecular mechanisms of hepatitis B virus-associated liver cancer. Dig. Dis., 19, 279–287 (2001).
Richmond, A., Nf-kappa B, chemokine gene transcription and tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2, 664–674 (2002).
Ryu, H. M., Park, S. G., Yea, S. S., Jang, W. H., Yang, Y. I., and Jung, G., Gene expression analysis of primary normal human hepatocytes infected with human hepatitis B virus. World J. Gastroenterol, 12, 4986–4995 (2006).
Sharp, P. A., RNA interference—2001. Genes Dev., 15, 485–490 (2001).
Sorensen, D. R., Leirdal, M., and Sioud, M., Gene silencing by systemic delivery of synthetic siRNAs in adult mice. J. Mol. Biol., 327, 761–766 (2003).
Stark, G. R., Kerr, I. M., Williams, B. R., Silverman, R. H., and Schreiber, R. D., How cells respond to interferons. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 67, 227–264 (1998).
Zandi, E., Rothwarf, D. M., Delhase, M., Hayakawa, M., and Karin, M., The IkappaB kinase complex (IKK) contains two kinase subunits, IKKalpha and IKKbeta, necessary for IkappaB phosphorylation and NF-kappaB activation. Cell, 91, 243–252 (1997).
Zhang, Y., Rong Qi, X., Gao, Y., Wei, L., Maitani, Y., and Nagai, T., Mechanisms of co-modified liver-targeting liposomes as gene delivery carriers based on cellular uptake and antigens inhibition effect. J. Control. Release., 117, 281–290 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, HA., Park, IS., Kim, TW. et al. Suppression of hepatitis B virus-derived human hepatocellular carcinoma by NF-κB-inducing kinase-specific siRNA using liver-targeting liposomes. Arch. Pharm. Res. 32, 1077–1086 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1714-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1714-z