Abstract
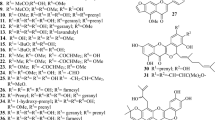
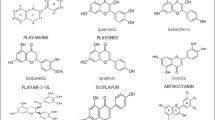
Flavonoids exist extensively in the human diet, and a variety of health effects have been ascribed to them. The cytotoxic effects of 23 flavonoids on breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7), colorectal carcinoma cells (LoVo and DLD-1) and prostatic cancer cells (PC3) were investigated. By comparing the cytotoxicity (EC50) of selected molecules that differ in only one structure element, we identified several structural properties associated with enhanced cytotoxicity, including the presence of the 2,3-double bond, appropriate hydroxyl numbers, 3-OH, 6-OH and ortho-hydroxylation in ring B. Flavonoids with a 5-OH exhibited lower cytotoxicity than their non-hydroxylated counterparts. Results indicated that 3,6-dihydroxylflavone showed the most potent cytotoxic effect on these cancer cells. The appearance of apoptotic cells with DAPI staining was observed in cancer cells under 3,6-dihydroxylflavone treatment, and the apoptosis analysis by flow cytometry also showed that 3,6-dihydroxylflavone induced apoptotic cell death in these cancer cells. These results revealed the structurally related toxicity of flavonoids on human cancer cells, and indicates that 3,6-dihydroxylflavone is an active compound worthy of development for cancer chemotherapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, M., Crepin, C., Savin, C., and Israel, L., Sodium phenylacetate induces growth inhibition and Bcl-2 down-regulation and apoptosis in MCF7 ras cells in vitro and in nude mice. Cancer. Res., 55, 5156–5160 (1995).
Bast, A., Haenen, G. R., Bruynzeel, A. M., and Van-der-Vijgh, W. J., Protection by flavonoids against anthracycline cardiotoxicity: from chemistry to clinical trials. Cardiovasc. Toxicol., 7, 154–159 (2007).
Booth, N. L., Overk, C. R., Yao, P., Burdette, J. E., Nikolic, D., and Chen, S. N., The chemical and biologic profile of a red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) phase II clinical extract. J. Altern. Complement. Med., 12, 133–139 (2006).
Bosetti, C., Bravi, F., Talamini, R., Parpinel, M., Gnagnarella, P., Negri, E., Montella, M., Lagiou, P., Franceschi, S., and La-Vecchia, C., Flavonoids and prostate cancer risk: a study in Italy. Nutr. Cancer., 56, 123–127 (2006).
Brusselmans, K., Vrolix, R., Verhoeven, G., and Swinnen, J. V., Induction of cancer cell apoptosis by flavonoids is associated with their ability to inhibit fatty acid synthase activity. J. Biol. Chem., 280, 5636–5645 (2005).
Chen, D., Daniel, K. G., Chen, M. S., Kuhn, D. J., Landis-Piwowar, K. R., and Dou, Q. P., Dietary flavonoids as proteasome inhibitors and apoptosis inducers in human leukemia cells. Biochem. Pharmacol., 69, 1421–1432 (2005).
Choi, S. I., Jeong, C. S., Cho, S. Y., and Lee, Y. S., Mechanism of apoptosis induced by apigenin in HepG2 human hepatoma cells: involvement of reactive oxygen species generated by NADPH oxidase. Arch. Pharm. Res., 30, 1328–1335 (2007).
Chun, O. K., Chung, S. J., and Song, W. O., Estimated dietary flavonoid intake and major food sources of U.S. adults. J. Nutr., 137, 1244–1252 (2007).
Ganguly, C., Saha, P., Panda, C. K., and Das, S., Inhibition of growth, induction of apoptosis and alteration of gene expression by tea polyphenols in the highly metastatic human lung cancer cell line NCI-H460. Asian. Pac. J. Cancer. Prev., 6, 326–331 (2005).
Haddad, A. Q., Venkateswaran, V., Viswanathan, L., Teahan, S. J., Fleshner, N. E., and Klotz, L. H., Novel antiproliferative flavonoids induce cell cycle arrest in human prostate cancer cell lines. Prostate. Cancer. Prostatic. Dis., 9, 68–76 (2006).
Jeune, M. A., Kumi, J. D., and Brown, J., Anticancer activities of pomegranate extracts and genistein in human breast cancer cells. J. Med. Food., 8, 469–475 (2005).
Jin, F., Jin, X. Y., Jin, Y. L., Sohn, D. W., Kim, S. A., Sohn, D. H., Kim, Y. C., and Kim, H. S., Structural requirements of 2′,4′,6′-tris(methoxymethoxy) chalcone derivatives for anti-inflammatory activity: the importance of a 2′-hydroxy moiety. Arch. Pharm. Res., 30, 1359–1367 (2007).
Johannot, L. and Somerset, S. M., Age-related variations in flavonoid intake and sources in the Australian population. Public. Health. Nutr., 9, 1045–1054 (2006).
Kumagai, T., Muller, C. I., Desmond, J. C., Imai, Y., Heber, D., and Koeffler, H. P., Scutellaria baicalensis, a herbal medicine: anti-proliferative and apoptotic activity against acute lymphocytic leukemia, lymphoma and myeloma cell lines. Leuk. Res., 31, 523–530 (2007).
Lim do, Y., Jeong, Y., Tyner, A. L., and Park, J. H., Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HT-29 human colon cancer cells by the dietary compound luteolin. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver. Physiol., 292, G66–G75 (2007).
Mosmann, T., Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods., 65, 55–63 (1983).
Rossi, M., Garavello, W., Talamini, R., La-Vecchia, C., Franceschi, S., Lagiou, P., Zambon, P., Dal-Maso, L., Bosetti, C., and Negri, E., Flavonoids and risk of squamous cell esophageal cancer. Int. J. Cancer., 120, 1560–1564 (2007).
Shen, S. C., Ko, C. H., Tseng, S. W., Tsai, S. H., and Chen, Y. C., Structurally related anti-cancer effects of flavanones in vitro and in vivo: involvement of caspase 3 activation, p21 gene expression, and reactive oxygen species production. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 197, 84–95 (2004).
Singh, R. P. and Agarwal, R., Natural flavonoids targeting deregulated cell cycle progression in cancer cells. Curr. Drug. Targets., 7, 345–354 (2006).
Song, W. O., Chun, O. K., and Chung, S. C., Tea Consumption is a determinant of flavonoid intake among US adults. J. Am. Diet. Assoc., 106, A80 (2006).
Theodoratou, E., Kyle, J., Cetnarskyj, R., Farrington, S. M., Tenesa, A., Barnetson, R., Porteous, M., Dunlop, M., and Campbell, H., Dietary flavonoids and the risk of colorectal cancer. Cancer. Epidemiol. Biomarkers. Prev., 16, 684–693 (2007).
Thomasset, S. C., Berry, D. P., Garcea, G., Marczylo, T., Steward, W. P., and Gescher, A. J., Dietary polyphenolic phytochemicals-promising cancer chemopreventive agents in humans? A review of their clinical properties. Int. J. Cancer., 120, 451–458 (2007).
Vijayababu, M. R., Kanagaraj, P., Arunkumar, A., Ilangovan, R., Dharmarajan, A., and Arunakaran, J., Quercetin induces p53-independent apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells by modulating Bcl-2-related proteins: a possible mediation by IGFBP-3. Oncol. Res., 16, 67–74 (2006).
Yang, H. M., Shin, H. R., Cho, S. H., Song, G. Y., Lee, I. J., Kim, M. K., Lee, S. H., Ryu, J. C., Kim, Y., and Jung, S. H., The role of the hydrophobic group on ring A of chalcones in the inhibition of interleukin-5. Arch. Pharm. Res., 29, 969–976 (2006).
Yoon, G., Kang, B. Y., and Cheon, S. H., Topisomerase I inhibition and cytotoxicity of licochalcones A and E from Glycyrrhiza inflata. Arch. Pharm. Res., 30, 313–316 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, H., Mi, M., Ling, W. et al. Structurally related cytotoxic effects of flavonoids on human cancer cells in vitro . Arch. Pharm. Res. 31, 1137–1144 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1280-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1280-8