Abstract
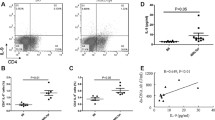
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is characterized by inflammatory and dysregulatory immune responses including overactive B cells, overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines, and T cell hyperactivity. PGE2 modulates a variety of immune processes at sites of inflammation, including production of inflammatory cytokines. However, the role of PGE2 in dysregulatory inflammatory and immune responses in lupus remains unclear. We investigated whether PGE2 mediates production of inflammatory cytokines in pristane-induced lupus BALB/c mice. Our results showed that levels of serum and BAL PGE2 and LPS-stimulated production of PGE2 by peritoneal macrophages were remarkably increased in pristane-induced lupus mice compared to healthy controls. Exogenous PGE2 enhanced production of IL-6, IL-10, and NO but decreased TNF-α by macrophages and augmented IFN-γ, IL-6, and IL-10 by splenocytes from pristane-induced lupus mice compared to healthy controls. Exogenous PGE2 also enhanced production of IFN-γ, IL-6, and IL-10 by thymocytes from pristane-induced lupus mice. Indomethacin (Indo), a PGE2 synthesis inhibitor, greatly inhibited LPS-induced production of IL-6 and IL-10 by macrophages from pristane-induced lupus mice, while enhanced TNF-α. Indo remarkably inhibited Con A-increased production of IFN-γ, IL-6, and IL-10 by splenocytes and thymocytes from pristane-induced lupus mice. Therefore, our findings suggest that endogenous PGE2 may mediate dysregulation of production of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-10, and IFN-γ, and NO in pristane-induced lupus mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akahoshi, M., Nakashima, H., Tanaka, Y., Kohsaka, T., Nagano, S., Ohgami, E., Arinobu, Y., Yamaoka, K., Niiro, H., Shinozaki, M., Hirakata, H., Horiuchi, T., Otsuka, T., and Niho, Y., Th1/Th2 balance of peripheral T helper cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum., 42, 1644–1648 (1999).
Akaogi, J., Nozaki, T., Satoh, M., and Yamada, H., Role of PGE2 and EP receptors in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and as a novel therapeutic strategy. Endocr. Metab. Immune. Disord. Drug Targets., 6, 383–394 (2006).
Aringer, M. and Smolen, J. S., SLE — Complex cytokine effects in a complex autoimmune disease: tumor necrosis factor in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther., 5, 172–177 (2003).
Betz, M. and Fox, B. S., Prostaglandin E2 inhibits production of Th1 lymphokines but not of Th2 lymphokines. J. Immunol., 146, 108–113 (1991).
Chae, B. S. and Shin, T. Y., Immunoregulatory abnormalities of T cells and hyperreactivity of B cells in the in vitro immune response in pristane-induced lupus mice. Arch. Pharm. Res., 30, 191–198 (2007).
Chen, S., Hu, D., Shi, X., Shen, N., Gu, Y., and Bao, C., The relationship between Th1/Th2-type cells and disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Chin. Med. J. (Engl), 113, 877–880 (2000).
Gerez, L., Shkolnik, T., Hirschmann, O., Lorber, M., Arad, G., and Kaempfer, R., Hyperinducible expression of the interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) gene and its suppression in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Clin. Exp. Immunol., 109, 296–303 (1997).
Haas, C., Ryffel, B., and Le Hir, M., IFN-gamma receptor deletion prevents autoantibody production and glomerulone-phritis in lupus-prone (NZB x NZW)F1 mice. J. Immunol., 160, 3713–3718 (1998).
Harizi, H., Juzan, M., Pitard, V., Moreau, J. F., and Gualde, N., Cyclooxygenase-2-issued prostaglandin E2 enhances the production of endogenous IL-10, which down-regulates dendritic cell functions. J. Immunol., 168, 2255–2263 (2002).
Hinson, R. M., Williams, J. A., and Shacter, E., Elevated interleukin 6 is induced by prostaglandin E2 in a murine model of inflammation: possible role of cyclooxygenase-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 93, 4885–4890 (1996).
Hoffman, R. W., T cells in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol., 113, 4–13 (2004).
Ishihara, K. and Hirano, T., IL-6 in autoimmune disease and chronic inflammatory proliferative disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev., 13, 357–368 (2002).
Jozefowski, S., Bobek, M., and Marcinkiewicz, J., Exogenous but not endogenous prostanoids regulate cytokine secretion from murine bone marrow dendritic cells: EP2, DP, and IP but not EP1, EP3, and FP prostanoid receptors are involved. Int. Immunopharmacol., 3, 865–878 (2003).
Kyttaris, V. C., Juang, Y. T., and Tsokos, G. C., Immune cells and cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus: an update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol., 17, 518–522 (2005).
Liang, B., Gardner, D. B., Griswold, D. E., Bugelski, P. J., and Song, X. Y., Anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody inhibits autoimmune responses in a murine model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology, 119, 296–305 (2006).
Llorente, L., Zou, W., Levy, Y., Richaud-Patin, J., Wijdenes, J., Alcocer-Varela, J., Morel-Fourrier, B., Brouet, J. C., Alarcon-Segovia, D., Galanaud, P., and Emilie, D., Role of interleukin 10 in the B lymphocyte hyperactivity and autoantibody production of human systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Exp. Med., 181, 839–844 (1995).
Murphy, K. M., Ouyang, W., Farrar, J. D., Yang, J., Ranganath, S., Asnagli, H., Afkarian, M., and Murphy, T. L., Signaling and transcription in T helper development. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 18, 451–494 (2000).
Oates, J. C. and Gilkeson, G. S., The biology of nitric oxide and other reactive intermediates in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol., 121, 243–250 (2006).
Reininger, L., Santiago, M. L., Takahashi, S., Fossati, L., and Izui, S., T helper cell subsets in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Med. Interne. (Paris), 147, 467–471 (1996).
Richards, H. B., Satoh, M., Shaw, M., Libert, C., Poli, V., and Reeves, W. H., Interleukin 6 dependence of anti-DNA antibody production: evidence for two pathways of autoantibody formation in pristane-induced lupus. J. Exp. Med., 188, 985–990 (1998).
Samoilova, E. B., Horton, J. L., Hilliard, B., Liu, T. S., and Chen, Y., IL-6-deficient mice are resistant to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: roles of IL-6 in the activation and differentiation of autoreactive T cells. J. Immunol., 161, 6480–6486 (1998).
Seery, J. P., IFN-gamma transgenic mice: clues to the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus? Arthritis Res., 2, 437–440 (2000).
Takeuchi, T., Tsuzaka, K., Abe, T., Yoshimoto, K., Shiraishi, K., Kameda, H., and Amano, K., T cell abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity, 38, 339–346 (2005).
Theofilopoulos, A. N., Koundouris, S., Kono, D. H., and Lawson, B. R., The role of IFN-gamma in systemic lupus erythematosus: a challenge to the Th1/Th2 paradigm in autoimmunity. Arthritis Res., 3, 136–141 (2001).
Theofilopoulos, A. N. and Lawson, B. R., Tumour necrosis factor and other cytokines in murine lupus. Ann. Rheum. Dis., 58(Suppl 1), 149–155 (1999).
Tsai, C. Y., Wu, T. H., Tsai, S. T., Chen, K. H., Thajeb, P., Lin, W. M., Yu, H. S., and Yu, C. L., Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-6, prostaglandin E2 and autoantibodies in patients with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus and central nervous system infections. Scand. J. Rheumatol., 23, 57–63 (1994).
Vassiliou, E., Jing, H., and Ganea, D., Prostaglandin E2 inhibits TNF production in murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Cell. Immunol., 223, 120–132 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chae, B.S., Shin, T.Y., Kim, D.K. et al. Prostaglandin E2-mediated dysregulation of proinflammatory cytokine production in pristane-induced lupus mice. Arch. Pharm. Res. 31, 503–510 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1185-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1185-6