Abstract
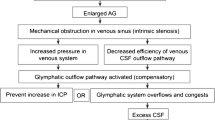
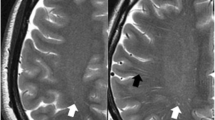
Perivascular space (PVS) is a crevice between two slices of cerebral pia maters, filled with tissue fluid, which be formed by pia mater emboling in the surrounding of cerebral perforating branch (excluding micrangium). Normal PVS (diameter < 2 mm) can be found in almost all healthy adults; however enlarged PVS (diameter > 2 mm) has correlation with neurological disorders probably. The article reviews the formation mechanism, imageology characteristics and the relation with neurological disorders of PVS, which is beneficial to the research of some neurological disorders etiopathogenesis and treatment.
摘要
血맜周围间隙(Perivascular space, PVS)是软脑膜内陷在脑穿支小血맜周围(不包括毛细血맜)而形成的介于两层软脑膜之间的间隙, 其间充满组织液。正常PVS 的直径一般小于2 mm, 存在于几乎所有健康成年人, 而PVS 的直径增大超过2 mm, 则与多种神经系统疾病相关。本文就PVS 的形成机制、影像学特点及其与神经系统疾病的关系作了阐述, 这将对研究一系列神经系统疾病的发病机制和治疗方法有所助益。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heier LA, Bauer CJ, Schwartz L, Zimmerman RD, Morgello S, Deck MD. Large Virchow-Robin spaces: MR-clinical correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1989, 10: 929–936.
Elster AD, Richardson DN. Focal high signal on MR scans of the midbrain caused by enlarged perivascular spaces: MR-pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1991, 156: 157–160.
Zhang ET, Inman CB, Weller RO. Interrelationships of the pia mater and the perivascular (Virchow-Robin) spaces in the human cerebrum. J Anat 1990, 170: 111–123.
Groeschel S, Chong WK, Surtees R, Hanefeld F. Virchow-Robin spaces on magnetic resonance images: normative data, their dilatation, and a review of the literature. Neuroradiology 2006, 48: 745–754.
Braffman BH, Zimmerman RA, Trojanowski JQ, Gonatas NK, Hickey WF, Schlaepfer WW. Brain MR: pathologic correlation with gross and histopathology. 1. Lacunar infarction and Virchow- Robin spaces. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1988, 151: 551–558.
Braffman BH, Zimmerman RA, Trojanowski JQ, Gonatas NK, Hickey WF, Schlaepfer WW. Brain MR: pathologic correlation with gross and histopathology. 2. Hyperintense white matter foci in the elderly. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1988, 151: 559–566.
Papayannis CE, Saidon P, Rugilo CA, Hess D, Rodriguez G, Sica RE, et al. Expanding Virchow-Robin spaces in the midbrain causing hydrocephalus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003, 24: 1399–1403.
Ogawa T, Okudera T, Fukasawa H, Hashimoto M, Inugami A, Fujita H, et al. Unusual widening of Virchow-Robin spaces: MR appearance. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1995, 16: 1238–1242.
Fazekas F, Kleinert R, Offenbacher H, Payer F, Schmidt R, Kleinert G, et al. The morphologic correlate of incidental punctate white matter hyperintensities on MR images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1991, 12: 915–921.
Sze G, De Armond SJ, Brant-Zawadzki M, Davis RL, Norman D, Newton TH. Foci of MRI signal (Pseudo Lesions) anterior to the frontal horns: histologic correlations of a normal finding. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1986, 147: 331–337.
Barkhof F. Enlarged Virchow-Robin spaces: do they matter? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2004, 75: 1516–1517.
Taber KH, Shaw JB, Loveland KA, Pearson DA, Lane DM, Hayman LA. Accentuated Virchow-Robin spaces in the centrum semiovale in children with autistic disorder. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2004, 28: 263–268.
Song CJ, Kim JH, Kier EL, Bronen RA. MR imaging and histologic features of subinsular bright spots on T2 weighted MR images: Virchow-Robin spaces of the extreme capsule and insular cortex. Radiology 2000, 214: 671–677.
Derouesné C, Gray F, Escourolle R, Castaigne P. Expanding cerebral lacunae in a hypertensive patient with normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 1987, 13: 309–320.
Papayannis CE, Saidon P, Rugilo CA, Hess D, Rodriguez G, Sica RE, et al. Expanding Virchow Robin spaces in the midbrain causing Hydrocephalus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003, 24: 1399–1403.
Weller RO. Pathology of cerebrospinal fluid and interstitial fluid of the CNS: significance for Alzheimer disease, prion disorders and multiple sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1998, 57: 885–894.
Weller RO, Massey A, Newman TA, Hutchings M, Kuo YM, Roher AE. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: amyloid beta accumulates in putative interstitial fluid drainage pathways in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 1998, 153: 725–733.
Preston SD, Steart PV, Wilkinson A, Nicoll JA, Weller RO. Capillary and arterial cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer’s disease: defining the perivascular route for the elimination of amyloid beta from the human brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2003, 29: 106–117.
Roher AE, Kuo YM, Esh C, Knebel C, Weiss N, Kalback W, et al. Cortical and leptomeningeal cerebrovascular amyloid and white matter pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Med 2003, 9:112–122.
Poirier J, Derouesne C. Cerebral lacunae: A proposed new classification. Clin Neuropathol 1984, 3: 266.
Heier LA, Bauer CJ, Schwartz L, Zimmerman RD, Morgello S, Deck MD. Large Virchow-Robin spaces: MR-clinical correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1989, 10: 929–936.
Cumurciuc R, Guichard JP, Reizine D, Gray F, Bousser MG, Chabriat H. Dilation of Virchow-Robin spaces in CADASIL. Eur J Neurol 2006, 13: 187–190.
Marnet D, Noudel R, Peruzzi P, Bazin A, Bernard MH, Scherpereel B, et al. Dilatation of Virchow-Robin perivascular spaces (types III cerebral lacunae): radio-clinical correlations. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2007, 163: 561–571.
Aachiron A, Faibel M. Sandlike appearance of Virchow-Robin spaces in early multiple sclerosis: a novel neuroradiologic marker. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002, 23: 376–380.
Ugawa Y, Shirouzu I, Terao Y, Hanajima R, Machii K, Mochizuki H, et al. Physiological analyses of a patient with extreme widening of Virchow-Robin spaces. J Neurol Sci 1998, 159: 25–27.
Benhaïem-Sigaux N, Gray F, Gherardi R, Roucayrol AM, Poirier J. Expanding cerebellar lacunae due to dilatation of the perivascular space associated with Binswanger’s subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy. Stroke 1987, 18: 1087–1092.
Demaerel P, Wilms G, Baert AL, Van den Bergh V, Sainte T. Widening of Virchow-Robin spaces. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1996, 17: 800–801.
Shiratori K, Mrowka M, Toussaint A, Spalke G, Bien S. Extreme, unilateral widening of Virchow-Robin spaces: case report. Neuroradiology 2002, 44: 990–992.
Bokura H, Kobayashi S, Yamaguchi S. Distinguishing silent lacunar infarction from enlarged Virchow-Robin spaces: a magnetic resonance imaging and pathological study. J Neurol 1998, 245:116–122.
Campi A, Benndorf G, Filippi M, Reganati P, Martinelli V, Terreni MR. Primary angiitis of the central nervous system: series MRI of brain and spinal cord. Neuroradiology 2001, 43:599–607.
House P, Salzman KL, Osborn AG, MacDonald JD, Jensen RL, Couldwell WT. Surgical considerations regarding giant dilations of the perivascular spaces. J Neurosurg 2004, 100: 820–824.
Kanamalla US, Calabro F, Jinkins JR. Cavernous dilatation of mesencephalic Virchow-Robin spaces with obstructive hydrocephalus. Neuroradiology 2000, 42: 881–884.
Achiron A, Faibel M. Sandlike appearance of Virchow-Robin spaces in early multiple sclerosis: a novel neuroradiologic marker. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002, 23: 376–380.
Di Costanzo A, Di Salle F, Santoro L, Bonavita V, Tedeschi G. Dilated Virchow-Robin spaces in myotonic dystrophy: frequency, extent and significance. Eur Neurol 2001, 46: 131–139.
Cheng YC, Ling JF, Chang FC, Wang SJ, Fuh JL, Chen SS, et al. Radiological manifestations of cryptococcal infection in central nervous system. J Chin Med Assoc 2003, 66: 19–26.
Soto-Ares G, Joyes B, Lemaître MP, Vallée L, Pruvo JP. MRI in children with mental retardation. Pediatr Radiol 2003, 33: 334–345.
Artigas J, Poo P, Rovira A, Cardo E. Macrocephaly and dilated Virchow-Robin spaces in childhood. Pediatr Radiol 1999, 29:188–190.
Härtel C, Bachmann S, Bönnemann C, Meinecke P, Sperner J. Familial megalencephaly with dilated Virchow-Robin spaces in meganetic resonance imaging: an autosomal recessive trait? Clin Dysmorphol 2005, 14: 31–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G. Perivascular space and neurological disorders. Neurosci. Bull. 25, 33–37 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-009-1103-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-009-1103-0