Abstract
Objective
To explore the role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) pathway in the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) that may be implicated in pain-related negative emotion.
Methods
LTP of field potential was recorded in ACC slice and the expressions of phospho-ERK (pERK) and phospho-CREB (pCREB) were examined using immunohistochemistry method.
Results
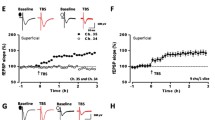
LTP could be induced stably in ACC slice by high frequency stimulation (2-train, 100 Hz, 1 s), while APv (an antagonist of NMDA receptor) could block the induction of LTP in the ACC, indicating that LTP in this experiment was NMDA receptor-dependent. Bath application of PD98059 (50 μmol/L), a selective MEK inhibitor, at 30 min before tetanic stimulation could completely block the induction of LTP. Moreover, the protein level of pERK in the ACC was transiently increased after LTP induction, starting at 5 min and returning to basal at 1 h after tetanic stimulation. The protein level of pCREB was also increased after LTP induction. The up-regulation in pERK and pCREB expressions could be blocked by pretreatment of PD98059. Double immunostaining showed that after LTP induction, most pERK was co-localized with pCREB.
Conclusion
NMDA receptor and ERK-CREB pathway are necessary for the induction of LTP in rat ACC and may play important roles in pain emotion.
摘要
目的
探讨细胞外信号激酶(ERK)/cAMP 反应原件蛋白 (CREB) 信号通路对大鼠前扣带皮层神经元长时程增强(LTP) 诱导的影响。
方法
采用离体脑片场电位记录方法观察ERK激酶抑制剂对大鼠前扣带皮层 (ACC) LTP诱导的影响, 采用免疫组织化学方法观察ACC脑片在强直刺激后不同时间点磷酸化ERK (pERK)和磷酸化CREB (pCREB)的表达情况。
结果
在大鼠ACC脑薄片上, 高频刺激 (2-train, 100 Hz, 1 s) 能诱导出稳定的场电位 (fEPSP) 长时程增强。 预先给予NMDA 受体竞争性拮抗剂APv (50 µmol/L)可完全阻断LTP 的产生, 提示本实验中ACC 神经元LTP是NMDA受体依赖性的。 灌流液中预先给予MEK抑制剂PD98059 (50 µmol/L)能完全阻断LTP 的产生。 取高频刺激后不同时间点的脑片进行免疫组化检测, 结果显示, 高频刺激后 5 min 时, pERK 表达显著升高, 在10 min 达到最高峰, 1 h 后回复到基础表达水平。 同样, 高频刺激后ACC 脑片中pCREB 的表达也显著增加。 预先灌流液中给予MEK抑制剂PD98059能够阻断高频刺激引起的pERK和pCREB表达上调。 免疫双标结果显示几乎所有的pERK都能与pCREB共定位于同一个神经细胞。
结论
大鼠前扣带皮层中NMDA受体和ERK/CREB信号通路是长时程增强诱导所必需的。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bliss TV, Lomo T. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anaesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J Physiol 1973, 232: 331–356.
Bliss TV, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 1993, 361: 31–39.
Kandel ER. The molecular biology of memory storage: A dialogue between genes and synapses. Science 2001, 294: 1030–1038.
Merzenich M. Long-term change of mind. Science 1998, 282: 1062–1063.
Ji RR, Kohno T, Moore KA, Woolf CJ. Central sensitization and LTP: do pain and memory share similar mechanisms? Trends Neurosci 2003, 26: 696–705.
Foltz E, White L. The role of rostral cingulumotomy in “pain” relief. Int J Neurol 1968, 6: 353–373.
Sikes RW, Vogt BA. Nociceptive neurons in area 24 of rabbit cingulate cortex. J Neurophysiol 1992, 68: 1720–1732.
Koyama T, Tanaka YZ, Mikami A. Nociceptive neurons in the macaque anterior cingulate activate during anticipation of pain. Neuro Report 1998, 9: 2663–2667.
Rainville P, Duncan GH, Price DD, Carrier B, Bushnell MC. Pain affect encoded in human anterior cingulate but not somatosensory cortex. Science 1997, 277: 968–971.
Johansen JP, Fields HL, Manning BH. The affective component of pain in rodents: Direct evidence for a contribution of the anterior cingulate cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98: 8077–8082.
Gao YJ, Ren WH, Zhang YQ, Zhao ZQ. Contributions of the anterior cingulate cortex and amygdala to pain- and fear-conditioned place avoidance in rats. Pain 2004, 110: 343–353.
Sweatt JD. The neuronal MAP kinase cascade: a biochemical signal integration system subserving synaptic plasticity and memory. J Neurochem 2001, 76: 1–10.
Sweatt JD. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in synaptic plasticity and memory. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2004, 14: 311–317.
Kawasaki Y, Kohno T, Zhuang ZY, Brenner GJ, Wang HB, VanderMeer C, et al. Ionotropic and metabotropic receptors, protein kinase A, protein kinase C, and Src contribute to C-fiber-induced ERK activation and cAMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation in dorsal horn neurons, leading to central sensitization. J Neuroscience 2004, 24: 8310–8321.
Krapivinsky G, Krapivinsky L, Manasian Y, Ivanov A, Tyzio R, Pellegrino C, et al. The NMDA receptor is coupled to the ERK pathway by a direct interaction between NR2B and RasGRF1. Neuron 2003, 40: 775–784.
Bozon B, Kelly A, Josselyn SA, Silva AJ, Davis S, Laroche S. MAPK, CREB and zif268 are all required for the consolidation of recognition memory. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2003, 358: 805–814.
Impey S, Obrietan K, Storm DR. Making new connections: Role of ERK MAP kinase signaling in neuronal plasticity. Neuron 1999, 23: 11–14.
Impey S, Obrietan K, Wong ST, Poser S, Yano S, Wayman G, et al. Cross talk between ERK and PKA is required for Ca2+ stimulation of CREB-dependent transcription and ERK nuclear translocation. Neuron 1998, 21: 869–883.
Obrietan K, Impey S, Smith D, Athos J, Storm DR. Circadian regulation of cAMP response element-mediated gene expression in the Suprachiasmatic nuclei. J Biol Chem 1999, 274: 17748–17756.
Treisman R. Regulation of transcription by MAP kinase cascades. Curr Opin in Cell Biol 1996, 8: 205–215.
Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci 1998, 1: 602–609.
English JD, Sweatt JD. Activation of p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase in hippocampal long term potentiation. J Biol Chem 1996, 271: 24329–24332.
Kida S, Josselyn SA, de Ortiz SP, Kogan JH, Chevere I, Masushige S, et al. CREB required for the stability of new and reactivated fear memories. Nat Neurosci 2002, 5: 348–355.
Ji RR, Baba H, Brenner GJ, Woolf CJ. Nociceptive-specific activation of ERK in spinal neurons contributes to pain hypersensitivity. Nat Neurosci 1999, 2: 1114–1119.
Ji RR, Rupp F. Phosphorylation of transcription factor CREB in rat spinal cord after formalin-induced hyperalgesia: Relationship to c-fos induction. J Neurosci 1997, 17: 1776–1785.
Karim F, Wang CC, Gereau RW. Metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes 1 and 5 are activators of extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling required for inflammatory pain in mice. J Neurosci 2001, 21: 3771–3779.
Bourtchuladze R, Frenguelli B, Blendy J, Cioffi D, Schutz G, Silva AJ. Deficient long-term-memory in mice with a targeted mutation of the camp-responsive element-binding protein. Cell 1994, 79: 59–68.
English JD, Sweatt JD. A requirement for the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in hippocampal long term potentiation. J Biol Chem 1997, 272: 19103–19106.
Patterson SL, Pittenger C, Morozov A, Martin KC, Scanlin H, Drake C, et al. Some forms of cAMP-mediated long-lasting potentiation are associated with release of BDNF and nuclear translocation of phospho-MAP kinase. Neuron 2001, 32(1): 123–140.
Wei F, Vadakkan KI, Toyoda H, Wu LJ, Zhao MG, Xu H, et al. Calcium calmodulin-stimulated adenylyl cyclases contribute to activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in spinal dorsal horn neurons in adult rats and mice. J Neurosci 2006, 26: 851–861.
Cao H, Gao YJ, Ren WH, Li TT, Duan KZ, Cui YH, et al. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in the anterior cingulate cortex contributes to the induction and expression of affective pain. J Neurosci 2009, 29: 3307–3321.
Lu YF, Kandel ER, Hawkins RD. Nitric oxide signaling contributes to late-phase LTP and CREB phosphorylation in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 1999, 19: 10250–10261.
Zhao MG, Toyoda H, Lee YS, Wu LJ, Ko SW, Zhang XH, et al. Roles of NMDA NR2B subtype receptor in prefrontal long-term potentiation and contextual fear memory. Neuron 2005, 47: 859–872.
Di Cristo G, Berardi N, Cancedda L, Pizzorusso T, Putignano E, Ratto GM, et al. Requirement of ERK activation for visual cortical plasticity. Science 2001, 292: 2337–2340.
Toyoda H, Wu LJ, Zhao MG, Xu H, Zhuo M. Time-dependent postsynaptic AMPA GluR1 receptor recruitment in the cingulate synaptic potentiation. Dev Neurobiol 2007, 67: 498–509.
Ji RR, Befort K, Brenner GJ, Woolf CJ. ERK MAP kinase activation in superficial spinal cord neurons induces prodynorphin and NK-1 upregulation and contributes to persistent inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. J Neurosci 2002, 22: 478–485.
Vanhoutte P, Barnier JV, Guibert B, Pages C, Besson MJ, Hipskind RA, et al. Glutamate induces phosphorylation of Elk-1 and CREB, along with c-fos activation, via an extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent pathway in brain slices. Mol Cell Biol 1999, 19: 136–146.
Lonze BE, Ginty DD. Function and regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous system. Neuron 2002, 35: 605–623.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, H., Cui, YH., Zhao, ZQ. et al. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in the anterior cingulate cortex contributes to the induction of long-term potentiation in rats. Neurosci. Bull. 25, 301–308 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-009-0904-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-009-0904-5
Keywords
- long-term potentiation
- extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- cAMP response element binding protein
- anterior cingulate cortex
- rat