Abstract
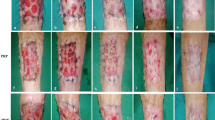
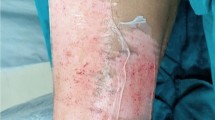
The management of the donor site after harvesting a skin graft is an important issue, as patients often report more discomfort at the donor site than at the recipient site. There is, however, a plethora of dressings available for the treatment and management of donor sites, yet, there is no widely accepted method established for these partial thickness wounds. Honey has been found to be useful in the treatment of burns and other wounds, split-thickness skin graft donor sites are like partial thickness burn wounds and honey’s healing effect on burn wound can also be expected on these types of wounds. Therefore, this study was undertaken to evaluate the effect of honey on skin graft donor sites. From 2002 to 2004, 100 patients who have undergone skin grafting for various reasons formed the material of the randomized study divided into two groups of 50 each in honey-treated group and Vaseline gauze-treated group. Graft donor site area ranged from 30 to 48 cm2, mean 32.6 cm2. In the group treated with honey, 90 % of the patients had nil or only moderate pain, whereas in the group treated with Vaseline gauze,88 % had nil or mild pain (p > 0.001, not significant). There were no allergic reactions in any of the patients in either group. On opening of the dressing on the 7th day, epithelialization has occurred in 48 patients as compared to 39 in group 2, i.e., donor sites treated with Vaseline gauze (p < 0.05, statistically significant). By the 10th day, all the wounds healed in honey-treated group, whereas 76 % of wounds healed in Vaseline gauze-treated group (p < 0.05). At 1 month follow-up, the results were comparable in both groups, with regard to patient satisfaction. In conclusion, honey-impregnated gauze causes less pain and heals donor sites wounds faster with good cosmetic result.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Winter GD (1963) A note on wound healing under dressings with special reference to perforated dressing. J Invest Dermatol 45:209
Baghel PS, Sukla S, Mathur RK, Rand RA (2009) A comparative study to evaluate the effect of honey dressing and silver sulfadiazine dressing on wound healing in burn patients. Indian J Plast Surg 42:176–181
Bangroo AK, Khatri R, Chauhan S (2005) Honey dressing in pediatric burns. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg 10:172–175
Subrahmanyam M (1991) Topical application of honey in treatment of burns. Br J Surg 78:497–498
Jull AB, Rodgers A, Walker N (2008) Honey as a topical treatment for wounds. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 4:CD005083
Wijesinghe M, Weatherall M, Perrin K, Beasley R (2009) Honey in the treatment of burns: a systematic review and meta-analysis of its efficacy. N Z Med J 122:47–60
Poulsen TD, Freund KG, Arendrup K et al (1991) Polyurethane film (Opsite) vs. impregnated gauze (Jelonet) in the treatment of outpatient burns: a prospective randomized study. Burns 17:59–61
Sallisbury RE, Wilmore DW, Silverstein P, Pruittt BA (1976) Biological dressings for skin graft donor sites. Arch Surg 106:705–706
Misirlioglu A, Eroglu S, Karacaoglan N et al (2003) Use of honey as an adjunct in the healing of split-thickness skin graft donor site. Dermatol Surg 29:168–172
Atiyeh BS, Ghanimeh G, Kaddoura IL, Ioannovich J (2001) Split-thickness skin graft donor site dressing: preliminary results of a controlled, clinical comparative study of MEBO and Sofra-Tulle. Ann Plast Surg 46:87–88
Acknowledgments
The author expresses his sincere thanks to B. V. Jagtap for his help in conducting the study. Thanks are also due to the Dean Government Medical College, Miraj and General Hospital, Sangli for permission to publish the paper.
Conflict of interest
None declared
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subrahmanyam, M. Honey Dressing Accelerates Split-Thickness Skin Graft Donor Site Healing. Indian J Surg 77 (Suppl 2), 261–263 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-012-0789-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-012-0789-9