Abstract
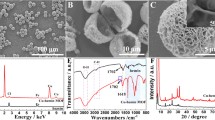
In the present study, an electrochemical glucose biosensor has been developed based on nano-copper oxide micro hollow spheres. The nano-copper oxide micro hollow spheres were synthesized via hydrothermal method using pluronic F-127 as a surfactant. For structural characterization of CuO hollow sphere structures, the scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction spectroscopy were applied. The performance parameters of the sensor were improved by optimizing the modification process. The electrochemical characteristics of the proposed glucose biosensor were investigated by using cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry techniques in both 0.1 M and 1 M NaOH solutions. The results revealed that the proposed electrode has a wide dynamic range from 1 µM to 11.50 mM for glucose detection at 0.1 M NaOH solution which covers two linear ranges from 1 µM to 3 mM and from 3 mM to 11.50 mM. The sensitivities of the two linear ranges were obtained as 25.0 ± 0.8 µA·mM−1·cm−2 and 13.6 ±0.3 µA·mM−1·cm−2, respectively. An extremely wide linear range from 1 µM to 16 mM with a sensitivity of 35.2 ± 0.4 µA·mM−1 cm−2 was achieved for the 1 M NaOH solution. The sensor achieved a 1 µM practical lowest limit of detection which is an excellent low limit of detection at both NaOH concentrations compared to some important previously reported works. In addition, the good tolerance toward the interfering species and the satisfactory behavior in real sample analysis verified the promising performance of the proposed sensor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laing, S. P., A. J. Swerdlow, S. D. Slater, J. L. Botha, A. C. Burden, N. R. Waugh, A. W. Smith, R. D. Hill, P. J. Bingley, C. C. Patterson, Z. Qiao, and H. Keen (1999) The British Diabetic Association Cohort Study, II: cause-specific mortality in patients with insulin-treated diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 16: 466–471.
Sreedevi, V. and P. R. A. V. Kumar (2017) A review on type 2 diabetes mellitus associated with cognitive disfunction and dementia and future perspective. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 6: 579–600
World Health Organization (2017) Global report on diabetes. https://www.who.int/diabetes/global-report/en/.
Brethauer, S. A., A. Aminian, H. Romero-Talamás, E. Batayyah, J. Mackey, L. Kennedy, S. R. Kashyap, J. P. Kirwan, T. Rogula, M. Kroh, B. Chand, and P. R. Schauer (2013) Can diabetes be surgically cured? Long-term metabolic effects of bariatric surgery in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann. Surg. 258: 628–636.
Buse, J. B., S. Caprio, W. T. Cefalu, A. Ceriello, S. Del Prato, S. E. Inzucchi, S. McLaughlin, G. L. Phillips, R. P. Robertson, F. Rubino, R. Kahn, and M. S. Kirkman (2009) How do we define cure of diabetes? Diabetes Care. 32: 2133–2135.
Bhalla, N., P. Jolly, N. Formisano, and P. Estrela (2016) Introduction to biosensors. Essays Biochem. 60: 1–8.
Yoo, E. H. and S. Y. Lee (2010) Glucose biosensors: an overview of use in clinical practice. Sensors. 10: 4558–4576.
Mastrototaro, J. J., K. W. Johnson, R. J. Morff, D. Lipson, C. C. Andrew, and D. J. Allen (1991) An electroenzymatic glucose sensor fabricated on a flexible substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 5: 139–144.
Reitz, E., W. Jia, M. Gentile, Y. Wang, and Y. Lei (2008) CuO nanospheres based nonenzymatic glucose sensor. Electroanalysis. 20: 2482–2486.
Shichiri, M., N. Asakawa, Y. Yamasaki, R. Kawamori, and H. Abe (1986) Telemetry glucose monitoring device with needle-type glucose sensor: a useful tool for blood glucose monitoring in diabetic individuals. Diabetes Care. 9: 298–301.
Wang, J., D. F. Thomas, and A. Chen (2008) Nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on nanoporous PtPb networks. Anal. Chem. 80: 997–1004.
Yang, H. and Y. Zhu (2005) A high performance glucose biosensor enhanced via nanosized SiO2. Anal. Chim. Acta. 554: 92–97.
Foroughi, F., M. Rahsepar, M. J. Hadianfard, and H. Kim (2018) Microwave-assisted synthesis of graphene modified CuO nanoparticles for voltammetric enzyme-free sensing of glucose at biological pH values. Microchim. Acta. 185: 57.
Espro, C., N. Donato, S. Galvagno, D. Aloisio, S. G. Leonardi, and G. Neri (2014) CuO nanowires-based electrodes for glucose sensors. Chem. Eng. Trans. 41: 415–420.
Chakraborty, P., S. Dhar, K. Debnath, and S. P. Mondal (2019) Glucose and hydrogen peroxide dual-mode electrochemical sensing using hydrothermally grown CuO nanorods. J. Electroanal. Chem. 833: 213–220.
Liu, Z., B. Yadian, H. Liu, C. Liu, B. Zhang, R. V. Ramanujan, and Y. Huang (2013) Fabrication of hybrid CuO/Pt/Si nanoarray for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Electrochem. Commun. 33: 138–141.
Rahman, M., A. J. S. Ahammad, J. H. Jin, S. J. Ahn, and J. J. Lee (2010) A comprehensive review of glucose biosensors based on nanostructured metal-oxides. Sensors. 10: 4855–4886.
Ahammad, A. J. S., A. Al Mamun, T. Akter, M. A. Mamun, S. Faraezi, and F. Z. Monira (2016) Enzyme-free impedimetric glucose sensor based on gold nanoparticles/polyaniline composite film. J. Solid State Electrochem. 20: 1933–1939.
Yan, X., J. Yang, L. Ma, X. Tong, Y. Wang, G. Jin, and X. Y. Guo (2015) Size-controlled synthesis of Cu2O nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide sheets and their application as non-enzymatic glucose sensor materials. J. Solid State Electrochem. 19: 3195–3199.
Yi, W., J. Liu, H. Chen, Y. Gao, and H. Li (2015) Copper/nickel nanoparticle decorated carbon nanotubes for nonenzymatic glucose biosensor. J. Solid State Electrochem. 19: 1511–1521.
Liu, L., Y. Chen, H. Lv, G. Wang, X. Hu, and C. Wang (2015) Construction of a non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on copper nanoparticles/poly(o-phenylenediamine) nanocomposites. J. Solid State Electrochem. 19: 731–738.
Qi, J., X. Lai, J. Wang, H. Tang, H. Ren, Y. Yang, Q. Jin, L. Zhang, R. Yu, G. Ma, Z. Su, H. Zhao, and D. Wang (2015) Multi-shelled hollow micro-/nanostructures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44: 6749–6773.
Wang, X., J. Feng, Y. Bai, Q. Zhang, and Y. Yin (2016) Synthesis, properties, and applications of hollow micro-/nanostructures. Chem. Rev. 116: 10983–11060.
Prasad, M. S., R. Chen, Y. Li, D. Rekha, D. Li, H. Ni, and N. Y. Sreedhar (2018) Polypyrrole supported with copper nanoparticles modified alkali anodized steel electrode for probing of glucose in real samples. IEEE Sens. J. 18: 5203–5212.
Li, R., X. Liu, H. Wang, Y. Wu, K. C. Chan, and Z. Lu (2019) Sandwich nanoporous framework decorated with vertical CuO nanowire arrays for electrochemical glucose sensing. Electrochim. Acta. 299: 470–478.
Kim, K., S. Kim, H. N. Lee, Y. M. Park, Y. S. Bae, and H. J. Kim (2019) Electrochemically derived CuO nanorod from copper-based metal-organic framework for non-enzymatic detection of glucose. Appl. Surf. Sci. 479: 720–726.
Chakraborty, P., S. Dhar, N. Deka, K. Debnath, and S. P. Mondal (2020) Non-enzymatic salivary glucose detection using porous CuO nanostructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 302: 127134.
Liu, B., X. Hu, Y. Deng, S. Yang, and C. Sun (2011) Electrocatalytic dechlorination of chloroacetic acids by silver nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Solid State Electrochem. 16: 927–930.
Zhang, L., Z. Shi, and Q. Lang (2011) Fabrication of poly(orthanilic acid)-multiwalled carbon nanotubes composite film-modified glassy carbon electrode and its use for the simultaneous determination of uric acid and dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid. J. Solid State Electrochem. 15: 801–809.
Wang, L., F. Yu, F. Wang, and Z. Chen (2016) Electrochemical detection of DNA methylation using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a composite made from carbon nanotubes and β-cyclodextrin. J. Solid State Electrochem. 20: 1263–1270.
Houshmand, M., A. Jabbari, H. Heli, M. Hajjizadeh, and A. A. Moosavi-Movahedi (2008) Electrocatalytic oxidation of aspirin and acetaminophen on a cobalt hydroxide nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Solid State Electrochem. 12: 1117–1128.
Yang, Z., Y. Tang, J. Li, Y. Zhang, and X. Hu (2014) Facile synthesis of tetragonal columnar-shaped TiO2 nanorods for the construction of sensitive electrochemical glucose biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 54: 528–533.
Du, G. H. and G. Van Tendeloo (2004) Cu(OH)2 nanowires, CuO nanowires and CuO nanobelts. Chem. Phys. Lett. 393: 64–69.
Barragan, J. T. C., S. Kogikoski, E. T. S. G. da Silva, and L. T. Kubota (2018) Insight into the electro-oxidation mechanism of glucose and other carbohydrates by CuO-based electrodes. Anal. Chem. 90: 3357–3365.
Esmaeeli, A., A. Ghaffarinejad, A. Zahedi, and O. Vahidi (2018) Copper oxide-polyaniline nanofiber modified fluorine doped tin oxide (FTO) electrode as non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 266: 294–301.
Ahmad, R., N. Tripathy, M. S. Ahn, K. S. Bhat, T. Mahmoudi, Y. Wang, J. Y. Yoo, D. W. Kwon, H. Y. Yang, and Y. B. Hahn (2017) Highly efficient non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on CuO modified vertically-grown ZnO nanorods on electrode. Sci. Rep. 7: 5715.
Karikalan, N., R. Karthik, S. M. Chen, C. Karuppiah, and A. Elangovan (2017) Sonochemical synthesis of sulfur doped reduced graphene oxide supported CuS nanoparticles for the non-enzymatic glucose sensor applications. Sci. Rep. 7: 2494.
Zhang, S., N. Wang, H. Yu, Y. Niu, and C. Sun (2005) Covalent attachment of glucose oxidase to an Au electrode modified with gold nanoparticles for use as glucose biosensor. Bioelectrochemistry. 67: 15–22.
Kaushik, A., R. Khan, P. R. Solanki, P. Pandey, J. Alam, S. Ahmad, and B. D. Malhotra (2008) Iron oxide nanoparticles-chitosan composite based glucose biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 24: 676–683.
Rakhi, R. B., P. Nayak, C. Xia, and H. N. Alshareef (2016) Novel amperometric glucose biosensor based on MXene nanocomposite. Sci. Rep. 6: 36422.
Shamsipur, M., Z. Karimi, M. A. Tabrizi, and S. Rostamnia (2017) Highly sensitive non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor by Nafion/SBA-15-Cu (II) modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 799: 406–412.
Zhang, L., C. Ye, X. Li, Y. Ding, H. Liang, G. Zhao, and Y. Wang (2018) A CuNi/C nanosheet array based on a metal-organic framework derivate as a supersensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Nano-Micro Lett. 10: 28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haghparas, Z., Kordrostami, Z., Sorouri, M. et al. Fabrication of Non-enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensor Based on Nano-copper Oxide Micro Hollow-spheres. Biotechnol Bioproc E 25, 528–535 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-020-0058-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-020-0058-x