Abstract
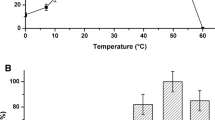
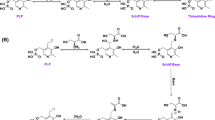
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) is an organic cofactor found in all transaminase enzymes. In this study PLP was used to replace the enzymatic deamination step in the Ehrlich pathway, for the oxidative conversion of amino acids into 2-keto acids. PLP functions in an enzymeindependent manner. It was further used in the synthesis of higher alcohols through a sequential enzymatic reduction in vitro and in vivo. PLP-dependent oxidation was investigated against five representative amino acids: valine, leucine, isoleucine, norvaline, and phenylalanine. In vitro amino acid oxidation resulted in approximately 45 ~ 75% [mole/mole] of each 2-keto acid conversion and in vitro ammonia formation was less than 2-keto acid formation, with 20% of conversion yields. Whole cell E. coli expressing reduction enzymes KivD/ADH with both single amino acid and amino acid mixture (4% yeast extract) gave the highest yield (30 ~ 55%) in the presence of the PLP-Cu complex and following enzymatic reactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, X., N. Li, and A. D. Ellington (2007) Ribozyme catalysis of metabolism in the RNA world. Chem. Biodivers. 4: 633–655.
Ouzounis, C. and N. Kyrpides (1996) The emergence of major cellular processes in evolution. FEBS Lett. 390: 119–123.
Schipp, C. J., E. Marco-Urrea, A. Kublik, J. Seifert, and L. Adrian (2013) Organic cofactors in the metabolism of Dehalococcoides mccartyi strains. Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. Lond. B, Biol. Sci. 368: 20120321.
Richter, M. (2013) Functional diversity of organic molecule enzyme cofactors. Nat. Prod. Rep. 30: 1324–1345.
Richard, J. P., T. L. Amyes, J. Crugeiras, and A. Rios (2011) The PLP cofactor: Lessons from studies on model reactions. Biochimica et Biophysica Act. 1814: 1419–1425.
Vanderlinde, R. E. (1986) Review of pyridoxal phosphate and the transaminases in liver disease. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 16: 79–93.
Eliot, A. C. and J. F. Kirsch (2004) Pyridoxal phosphate enzymes: Mechanistic, structural, and evolutionary considerations. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 73: 383–415.
Phillips, R. S. (2015) Chemistry and diversity of Pyridoxal-5'-phosphate dependent enzymes. Biochimica et Biophysica Act. 1854: 1167–1174.
Griswold, W. R. and M. D. Toney (2011) Role of the pyridine nitrogen in pyridoxal 5'-phosphate catalysis: Activity of three classes of PLP enzymes reconstituted with deazapyridoxal 5'-phosphate. J. Am. Chem.l Soc. 133: 14823–14830.
Shin, J. S. and B. G. Kim (2009) Transaminase-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis of L-2-aminobutyric acid from achiral reactants. Biotechnol. Lett. 31: 1595–1599.
Yun, H. and B. G. Kim (2008) Asymmetric synthesis of (S)-alpha-methylbenzylamine by recombinant Escherichia coli coexpressing omega-transaminase and acetolactate synthase. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 72: 3030–3033.
Yun, H., S. Lim, B. K. Cho, and B. G. Kim (2004) omega-Amino acid:pyruvate transaminase from Alcaligenes denitrificans Y2k-2: A new catalyst for kinetic resolution of beta-amino acids and amines. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70: 2529–2534.
Miyoshi Ikawa, E. E. S. (1954) Oxidative deamination of amino acids by pyridoxal and metal salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 76: 4900–4902.
Atsumi, S., T. Hanai, and J. C. Liao (2008) Non-fermentative pathways for synthesis of branched-chain higher alcohols as biofuels. Natur. 451: 86–89.
Huo, Y. X., K. M. Cho, J. G. Rivera, E. Monte, C. R. Shen, Y. Yan, and J. C. Liao (2011) Conversion of proteins into biofuels by engineering nitrogen flux. Nat. Biotechnol. 29: 346–351.
Choi, K. Y., D. G. Wernick, C. A. Tat, and J. C. Liao (2014) Consolidated conversion of protein waste into biofuels and ammonia using Bacillus subtilis. Metabol. Eng. 23: 53–61.
Hazelwood, L. A., J. M. Daran, A. J. van Maris, J. T. Pronk, and J. R. Dickinson (2008) The Ehrlich pathway for fusel alcohol production: A century of research on Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74: 2259–2266.
Li, S., J. Wen, and X. Jia (2011) Engineering Bacillus subtilis for isobutanol production by heterologous Ehrlich pathway construction and the biosynthetic 2-ketoisovalerate precursor pathway overexpression. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 91: 577–589.
Kim, B., B. R. Cho, and J. S. Hahn (2014) Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the production of 2-phenylethanol via Ehrlich pathway. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 111: 115–124.
Lan, E. I. and J. C. Liao (2013) Microbial synthesis of n-butanol, isobutanol, and other higher alcohols from diverse resources. Bioresour. Technol. 135: 339–349.
Koike, K. and M. Koike (1984) Fluorescent analysis of alphaketo acids in serum and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 141: 481–487.
Shanbhag, V. M. and A. E. Martell (1991) Oxidative deamination of amino acids by molecular oxygne with pyridoxal derivatives and metal ions as catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113: 6479–6487.
Cooper, A. J. (1985) Glutamate-branched-chain amino acid transaminase. Meth. Enzymol. 113: 71–73.
Goto, M., I. Miyahara, H. Hayashi, H. Kagamiyama, and K. Hirotsu (2003) Crystal structures of branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase complexed with glutamate and glutarate: True reaction intermediate and double substrate recognition of the enzyme. Biochem. 42: 3725–3733.
Viljoen, A. J., C. J. Kirsten, B. Baker, P. D. van Helden, and I. J. Wiid (2013) The role of glutamine oxoglutarate aminotransferase and glutamate dehydrogenase in nitrogen metabolism in Mycobacterium bovis BCG. PloS one. 8: e84452.
Gordon A. Hamilton, and A. Revesz (1966) Oxidation by molecular oxygen. IV. A possible model reaction for some amine oxidases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 88: 2069–2070.
Toohey, J. I. (2006) Vitamin B12 and methionine synthesis: A critical review. Is nature's most beautiful cofactor misunderstood? BioFactors. 26: 45–57.
Denessiouk, K. A., V. V. Rantanen, and M. S. Johnson (2001) Adenine recognition: A motif present in ATP-, CoA-, NAD-, NADP-, and FAD-dependent proteins. Protein. 44: 282–291.
Sniekers, M., V. Foulon, G. P. Mannaerts, L. Van Maldergem, H. Mandel, B. D. Gelb, M. Casteels, and P. P. Van Veldhoven (2006) Thiamine pyrophosphate: An essential cofactor for the alpha-oxidation in mammals—implications for thiamine deficiencies? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63: 1553–1563.
Foulon, V., M. Casteels, G. P. Mannaerts, B. D. Gelb, and P. P. Van Veldhoven (2003) Thiamine pyrophosphate: An essential cofactor in the mammalian metabolism of 3-methyl-branched fatty acids—implications for thiamine deficiencies? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 544: 305–306.
Frank, R. A., F. J. Leeper, and B. F. Luisi (2007) Structure, mechanism and catalytic duality of thiamine-dependent enzymes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 64: 892–905.
Bolander, F. F. (2006) Vitamins: Not just for enzymes. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drug. 7: 912–915.
Fischer, J. D., G. L. Holliday, S. A. Rahman, and J. M. Thornton (2010) The structures and physicochemical properties of organic cofactors in biocatalysis. J. Mol. Biol. 403: 803–824.
Rotello, V. M. and R. P. Swenson (2001) Organic redox cofactors. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 3: 721–722.
Fischer, J. D., G. L. Holliday, and J. M. Thornton (2010) The CoFactor database: Organic cofactors in enzyme catalysis. Bioinformat. 26: 2496–2497.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, KY. Non-enzymatic PLP-dependent oxidative deamination of amino acids induces higher alcohol synthesis. Biotechnol Bioproc E 20, 988–994 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-015-0434-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-015-0434-0