Abstract
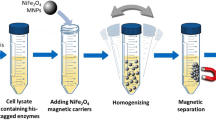
Ni2+-functionalized Fe3O4@polydopamine magnetic nanoparticles (Ni2+-PD-MNPs) were designed and synthesized by in situ coating of magnetic nanoparticles with polydopamine, followed by conjugation of Ni2+ to the polydopamine film. The Ni2+-PD-MNPs were used to purify His-tagged red fluorescent protein (His-RFP) via affinity interaction between Ni2+ and the His-tag. The results showed that the Ni2+-PD-MNPs had extraordinary selectivity for His-RFP purification. In addition, a Histagged transaminase (ω-transaminase BJ110) was selectively immobilized onto the Ni2+-PD-MNPs without purification, and the immobilized enzyme showed improved specific activity, as well as enhanced stability and reusability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Terpe, K. (2003) Overview of tag protein fusions: From molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 60: 523–533.
Cao, L. Q. (2005) Immobilised enzymes: Science or art? Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 9: 217–226.
Ghosh, R. (2002) Protein separation using membrane chromatography: Opportunities and challenges. J. Chromatogr A. 952: 13–27.
Palani, A., J. S. Lee, J. Huh, M. Kim, Y. J. Lee, J. H. Chang, K. Lee, and S. W. Lee (2008) Selective enrichment of cysteine-containing peptides using SPDP-functionalized superparamagnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles: Application to comprehensive proteomic profiling. J. Proteome Res. 7: 3591–3596.
Muir, T. W., D. Sondhi, and P. A. Cole (1998) Expressed protein ligation: A general method for protein engineering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 95: 6705–6710.
Lichty, J. J., J. L. Malecki, H. D. Agnew, D. J. Michelson-Horowitz, and S. Tan (2005) Comparison of affinity tags for protein purification. Protein Exp. Purif. 41: 98–105.
Scheich, C., V. Sievert, and K. Büssow (2003) An automated method for high-throughput protein purification applied to a comparison of His-tag and GST-tag affinity chromatography. BMC Biotechnol. 3: 1–8.
Porath, J., J. Carlsson, I. Olsson, and G. Belfrage (1975) Metal chelate affinity chromatography, a new approach to protein fractionation. Nature 258: 598–599.
Frenzel, A., C. Bergemann, G. Kohl, and T. Reinard (2003) Novel purification system for 6× His-tagged proteins by magnetic affinity separation. J. Chromatogr B. 793: 325–329.
Vinckier, N. K., A. Chworos, and S. M. Parsons (2011) Improved isolation of proteins tagged with glutathione S-transferase. Protein Express. Purif. 75: 161–164.
Tural, B., S. Tural, E. Erta, Yalnklç, and A. S. Demir (2013) Purification and covalent immobilization of benzaldehyde lyase with heterofunctional chelate-epoxy modified magnetic nanoparticles and its carboligation reactivity. J. Mol. Catal. B Enz. 95: 41–47.
Rossi, L. M., N. S. Costa, F. P. Silva, and R. Wojcieszak (2014) Magnetic nanomaterials in catalysis: Advanced catalysts for magnetic separation and beyond. Green Chem. 16: 2906–2933.
Engelmark, C. K., M. Kadow, Y. Wikmark, H. M. Svedendahl, M. L. Rothstein, D. M. Rothstein, and J. E. Bäckvall (2014) A general protein purification and immobilization method on controlled porosity glass: Biocatalytic applications. Chem. Commun. 50: 9134–9137.
Lin, Y. C., M. R. Liang, Y. C. Lin, and C. T. Chen (2011) Specifically and reversibly immobilizing proteins/enzymes to Nitriolotriacetic- acid-modified mesoporous silicas through Histidine tags for purification or catalysis. Chem-Eur J. 17: 13059–13067.
Xu, F., J. H. Geiger, G. L. Baker, and M. L. Bruening (2011) Polymer brush-modified magnetic nanoparticles for His-tagged protein purification. Langmuir. 27: 3106–3112.
Ho, L. F., S. Y. Li, S. C. Lin, and W. H. Hsu (2004) Integrated enzyme purification and immobilization processes with immobilized metal affinity adsorbents. Proc. Biochem. 39: 1573–1581.
Ball, V., D. D. Frari, V. Toniazzo, and D. Ruch (2012) Kinetics of polydopamine film deposition as a function of pH and dopamine concentration: Insights in the polydopamine deposition mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 386: 366–372.
Lee, H., S. M. Dellatore, W. M. Miller, and P. B. Messersmith (2007) Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Sci. 318: 426–430.
Yan, Y., Z. Zheng, C. Deng, X. Zhang, and P. Yang (2013) Facile synthesis of Ti4+-immobilized Fe3O4@polydopamine core-shell microspheres for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Chem. Commun. 49: 5055–5057.
Lin, Y. C., M. R. Liang, Y. C. Lin, and C. T. Chen (2011) Specifically and reversibly immobilizing proteins/enzymes to nitriolotriacetic-acid-modified mesoporous silicas through Histidine tags for purification or catalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 17: 13059–13067.
Liu, J., Z. K. Sun, Y. H. Deng, Y. Zou, C. Y. Li, X. H. Guo, L. Q. Xiong, Y. Gao, F. Y. Li, and D. Y. Zhao (2009) Highly water-dispersible biocompatible magnetite particles with low cytotoxicity stabilized by citrate groups. Angew Chem. 121: 5989–5993.
Aminiana, M., F. Nabatchian, A. V. Raygani, and M. Torabi (2013) Mechanism of Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 binding to cetyltrimethylammonium bromide: An interference with the Bradford assay. Anal. Biochem. 434: 287–291.
Lele, S. and T. R. Anantharaman (1966) Influence of crystallite shape on particle size broadening of Debye-Scherrer reflections. Proc. Math. Sci. 64: 261–274.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Ni, K., Wei, D. et al. One-step purification and immobilization of his-tagged protein via Ni2+-functionalized Fe3O4@polydopamine magnetic nanoparticles. Biotechnol Bioproc E 20, 901–907 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-015-0136-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-015-0136-7