Abstract
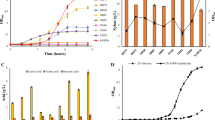
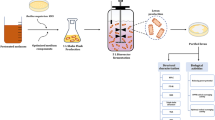
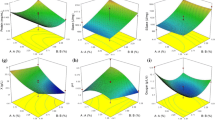
A bioflocculant produced by B. licheniformis was investigated with regard to a low-cost culture medium and its industrial application. Molasses replaced sucrose as the sole carbon source in bioflocculant fermentation. The optimum low-cost culture medium was determined to be composed of 20 g/L molasses, 0.4 g/L urea, 0.4 g/L NaCl, 0.2 g/L KH2PO4, 1.6 g/L K2HPO4, and 0.2 g/L MgSO4. The bioflocculant from B. licheniformis was then applied to treat sugarcane-neutralizing juice to remove colloids, suspended particles, and coloring matters in a sugar refinery factory. The optimal operation conditions were a bioflocculant dosage of 21 U/mL, pH 7.3 and a heating temperature of 100°C. The color and turbidity of the sugarcane juice reached IU 1267 and IU 206, respectively, after clarification with the bioflocculant; these values were almost the same as those acquired following treatment with polyacrylamide (PAM), the most widely applied flocculant in sugar industries. These results suggest the great potential for use of bioflocculants in the sugar refinery process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salehizadeh, H. and S. A. Shojaosadati (2001) Extracellular biopolymeric flocculants: Recent trends and biotechnological importance. Biotechnol. Adv. 19: 371–385.
He, N., Y. Li, J. Chen, and Q. B. Li (2005) Recent investigations and applications of bioflocculant. Microbiol. 32: 104–108.
He, J., Q. W. Zhen, N. Qiu, Z. D. Liu, B. J. Wang, Z. Z. Shao, and Z. N. Yu (2009) Medium optimization for the production of a novel bioflocculant from Halomonas sp. V3a using response surface methodology. Bioresour. Technol. 100: 5922–5927.
Joshi, A. A. and P. P. Kanekar (2011) Production of exopolysaccharide by Vagococcus carniphilus MCM B-1018 isolated from alkaline Lonar Lake, India. Ann. Microbiol. DOI 10.1007/s13213-010-0189-y.
Li, Z. and X. Y. Zhang (2010) Screening and identification of a bioflocculant-producing strain and its culture condition optimization. Chin. J. Env. Eng. 4: 2515–2518.
Feng, Y. L., H. J. Wang, H. R. Li, Z. W. Du, and X. B. Luo (2008) A bioflocculant-producing silicate bacteria screening and its flocculating activity. J. Central South University (Science and Technology) 39: 934–939.
Zhang, Z. Q., B. Lin, S.Q. Xia, X. J. Wang, and A. M. Yang (2007) Production and application of a novel bioflocculant by multiple-microorganism consortia using brewery wastewater as carbon source. J. Environ. Sci. 19: 667–673.
Wang, S. G., W. X. Gong, X. W Liu, L. Tian, Q. Y. Yue, and B. Y. Gao (2007) Production of a novel bioflocculant by culture of Klebsiella mobilis using dairy wastewater. Biochem. Eng. J. 36: 81–86.
Zhou, X., L. P. Huang, J. Wang, J. T. Zhou, and J. S. Zhang (2003) Production and properties of bioflocculant by pseudomonas sp. GX4-1 using fish meal wastewater. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 9: 436–438.
Kurane, R., K. Hatamochi, T. Kakuno, M. Kiyohara, M. Hirano, and Y. Taniguchi (1994) Production of a bioflocculant by Rhodococcus erythropolis S-1 grown on alcohols. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 58: 428–429.
Liu, L. F. and C. Q. Ruan (2009) Production and characteristics of a bioflocculant using molasses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32: 152–155.
Liu, L. F., S. Mei, J. Guo, and C. Q. Ruan (2008) On the production of a bioflocculant using molasses. J. Guangdong Univ. Technol. 25: 13–16.
Mao, Y. L., T. Zhu, Z. F. Pei, X. Z. Liu, L. H. Zhu, D. L. Guo, and K. Zhang (2010) Study on production of a novel bioflocculant using molasses wastewater and conditions optimization and effect experiments. Chin. J. Env. Eng. 4: 86–90.
Liu, L. F. and W. Cheng (2010) Characteristics and culture conditions of a bioflocculant produced by Penicillium sp. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 23: 213–218.
Zhu, Y. B., F. Ma, N. Q. Ren, J. L. Huang, and A. J. Wang (2005) Bioflocculant producing capability by two strains of Bacillus sp. on diversified carbon sources. Environ. Sci. 26: 152–155.
Mao, Y. L., Y. H. Wang, R. Q. Liu, X. Chen, and Y. S. Yan (2008) Production of bioflocculants from molasses wastewater and optimization of flocculation conditions. China water & wastewater 24: 20–23.
Yang, G., N. Wang, and C. Zhang (2011) Flocculating properties of the novel bioflocculant poly(γ-glutamic acid) and its use in jean dyeing wastewater treatment. Adv. Mat. Res. 183-185.
Yue, L. X., C. L. Ma, and M. Z (2006) Bioflocculant produced by Klebsiella sp. MYC and its application in the treatment of oilfield produced water. J. Ocean Univ. China 5: 333–338.
Li, Z., S. Zhong, H. Y. Lei, R. W. Chen, Q. Yu, and H. L. Li (2009) Production of a novel bioflocculant by Bacillus licheniformis X14 and its application to low temperature drinking water treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 100: 3650–3656.
Matthys, C., M. Bilau, Y. Govaert, E. Moons, S. De-Henauw, and J. L. Willems (2005) Risk assessment of dietary acrylamide intake in Flemish adolescents. Food Chem. Toxicol. 43: 271–278.
Li, N., Z. N. Deng, X. Z. Li, K. Y. Zhou, and Z. Q. Liang (2006) Research and application of microbial flocculation in sugarcane mill. Chin. J. Industrial Microbiol. 36: 43–46.
Kurane, R., K. Toeda, K. Takeda, and T. Suzuki (1986) Culture conditions for production of microbial flocculant by Rhodococcus erythropolis. Agric. Biol. Chem. 50: 2309–2313.
Li, Y. and C. G. Zhen (1995) Chemical analysis method in cane sugar manufacture. 3 rd ed., pp. 51–56. China Light Industry Association, Beijing, China.
Xiong, Y. Y., Y. P. Wang, Y. Yu, Q. B. Li, H. T. Wang, R. H. Chen, and N. He (2010) Production and characterization of a novel bioflocculant from Bacillus licheniformis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76: 2778–2782.
Feng, D. L. and S. H. Xu (2008) Characterization of bioflocculant MBF3-3 produced by an isolated Bacillus sp. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24: 1627–1632.
Yim, J. H., S. J. Kim, S. H. Ahn, and H. K. Lee (2007) Characterization of a novel bioflocculant, p-KG03, from a marine dinoflagellate, Gyrodinium impudicum KG03. Bioresour. Technol. 98: 361–367.
Zhang, Z. Q., S. Q. Xia, J. F. Zhao, and J. Zhang (2010) Characterization and flocculation mechanism of high efficiency microbial flocculant TJ-F1 from Proteus mirabilis. Colloids Surf. B 75: 247–251.
Nakamura, J., S. Miyashiro, and Y. Hirose (1976) Modes of flocculation of yeast cells with flocculant produced by Aspergillus sojae AJ7002. Agric. Biol. Chem. 40: 1565–1571.
Wu, J. Y. and H. F. Ye (2007) Characterization and flocculating properties of an extracellular biopolymer produced from a Bacillus subtilis DYU1 isolate. Proc. Biochem. 42: 1114–1123.
Ji, B., X. Y. Zhang, Z. Li, H.Q. Xie, X. M. Xiao, and G. J. Fan (2010) Flocculation properties of a bioflocculant produced by Bacillus licheniformis. Water Sci. Technol. 62: 1907–1913.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuang, X., Wang, Y., Li, Q. et al. The production of bioflocculants by Bacillus licheniformis using molasses and its application in the sugarcane industry. Biotechnol Bioproc E 17, 1041–1047 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0213-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0213-0