Abstract
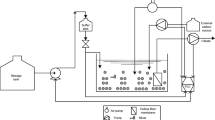
Anaerobic bioreactors supplemented with membrane technology have become quite popular, owing to their favorable energy recovery characteristics. In this study, a lab-scale anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor (AnMBR) was assessed in experimental treatments of pre-settled dilute municipal wastewater obtained from a full-scaled wastewater treatment plant. The MBR system was operated in continuous flow mode for 440 days. To evaluate the performance of the AnMBR under various loading rates, the hydraulic retention time (HRT) was reduced in a stepwise manner (from 2 to 0.5 days). Afterward, the mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) were reduced from 7,000 to 3,000 mg/L in increments of 1,000 mg/L, resulting in a decrease in solids retention time (SRT) at a constant HRT of 1.0 day. The soluble chemical oxygen demand (SCOD) concentration in the feed varied between 38 and 131 mg/L, whereas the average permeate SCOD ranged between 18 and 37 mg/L, reflecting excellent effluent quality. The AnMBR performance in terms of COD removal proved stable, despite variations in influent characteristics and HRT and SRT changes. The concentration of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) was reduced with decreases in HRT from 42 to 22 mg VS/mg of MLSS, thereby indicating that the increased biomass concentration biodegraded the EPS at lower HRTs. AnMBR is, therefore, demonstrably a feasible option for the treatment of dilute wastewater with separate stage nitrogen and phosphorus removal processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harada, H., K. Momonoi, S. Yamazaki, and S. Takizawa (1994) Application of anaerobic-UF membrane reactor for treatment of a wastewater containing high strength particulate organics. Water Sci. Technol. 30: 307–319.
Beaubien, A., M. Baty, F. Jeannot, E. Francoeur, and J. Manem (1996) Design and operation of anaerobic membrane bioreactors: Development of a filtration testing strategy J. Memb. Sci. 109: 173–184.
Cadi, Z., H. Huyard, J. Manem, and R. Moletta (1994) Anaerobic digestion of a synthetic wastewater containing starch by a membrane reactor. Environ. Technol. 15: 1029–1039.
Choo, K. H. and C. H. Lee (1998) Hydrodynamic behavior of anaerobic biosolids during crossflow filtration in the membrane anaerobic bioreactor. Wat. Res. 32: 3387–3397.
Ross, W. R., J. P. Barnard, J. Le Roux, and H. A. de Villiers (1990) Application of ultrafiltration membranes for solid-liquid separation in anaerobic digester systems: The ADUF process. Wat. SA. 16: 85–91.
Ince, B., O. Ince, P. J. Sallis, and G. K. Anderson (1998) Experimental determination of the inert soluble COD fraction of a brewery wastewater under anaerobic conditions. Environ. Technol. 19: 437–442.
Strohwald, N. K. H. and W. R. Ross (1992) Application of the ADUF process to brewery effluent on a laboratory scale. Wat. Sci. Technol. 25: 95–105.
Kim, H. and K. R. Pagilla (2002) Verification of enhanced phosphate removal capability in pure cultures of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus under anaerobic/aerobic conditions in a SBR. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 7: 335–339.
APHA (1992) Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater. 18th Edn. APHA, Washington DC, USA.
Choo, K. H. and C. H. Lee (1996) Membrane fouling mechanisms in the membrane-coupled anaerobic bioreactor, Wat. Res. 30: 1771–1780.
Kang, I. J., S. H. Yoon, and C. H. Lee (2002) Comparison of the filtration characteristics of organic and inorganic membranes in a membrane-coupled anaerobic bioreactor. Wat. Res. 36: 1803–1813.
Kim, J. S., C. H. Lee, and I. S. Chang (2001) Effect of pump shear on the performance of a crossflow membrane bioreactor. Wat. Res. 35: 2137–2144.
Chang, I. S. and C. H. Lee (1998) Membrane filtration characteristics in membrane coupled activated sludge system-the effect of physiological states of activated sludge on membrane fouling. Desali. 120: 221–233.
Nagaoka, H., S. Ueda, and A. Miya (1996) Influence of bacterial extracellular polymers on the membrane separation activated sludge process. Wat. Sci. Technol. 34: 165–172.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baek, S.H., Pagilla, K.R. & Kim, HJ. Lab-scale study of an anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) for dilute municipal wastewater treatment. Biotechnol Bioproc E 15, 704–708 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-0194-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-0194-9