Abstract
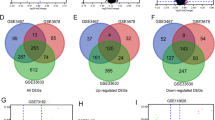
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have displayed dysregulated expression in several types of cancer. Nevertheless, their function and underlying mechanisms in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) remains largely unknown. This study aimed to describe the regulatory mechanisms in PTC. The expression profile of circRNA was download from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. The mRNA and miRNA data of PTC was downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. The circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network by Cytoscape. The interactions between proteins were analyzed using the STRING database and hubgenes were identified using MCODE plugin. Then, we conducted a circRNA-miRNA-hubgenes regulatory module. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Gene and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis were conducted using R packages “Clusterprofile”. We identified 14 differential expression circRNAs (DEcircRNA), 3106 differential expression mRNAs (DEmRNA), 142 differential expression miRNAs (DEmiRNA) and in PTC. Twelve circRNAs, 33 miRNAs, and 356 mRNAs were identified to construct the ceRNA network of PTC. PPI network and module analysis identified 5 hubgenes. Then, a circRNA-miRNA-hubgene subnetwork was constructed based on the 2 DEcircRNAs, 3 DEmiRNAs, and 4 DEmRNAs. GO and KEGG pathway analysis indicated DEmRNAs might be associated with PTC onset and progression. These ceRNAs are critical in the pathogenesis of PTC and may serve as future therapeutic biomarkers.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 68(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442
Mao Y, Xing M (2016) Recent incidences and differential trends of thyroid cancer in the USA. Endocr Relat Cancer 23(4):313–322. https://doi.org/10.1530/erc-15-0445
Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, Pacini F, Randolph GW, Sawka AM, Schlumberger M, Schuff KG, Sherman SI, Sosa JA, Steward DL, Tuttle RM, Wartofsky L (2016) 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid Cancer: the American Thyroid Association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid Cancer. Thyroid. 26(1):1–133. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2015.0020
Liu FH, Kuo SF, Hsueh C, Chao TC, Lin JD (2015) Postoperative recurrence of papillary thyroid carcinoma with lymph node metastasis. J Surg Oncol 112(2):149–154. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.23967
Grant CS (2015) Recurrence of papillary thyroid cancer after optimized surgery. Gland Surg 4(1):52–62. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2014.12.06
Qu S, Yang X, Li X, Wang J, Gao Y, Shang R, Sun W, Dou K, Li H (2015) Circular RNA: a new star of noncoding RNAs. Cancer Lett 365(2):141–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.06.003
Chen LL (2016) The biogenesis and emerging roles of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17(4):205–211. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2015.32
Wang F, Nazarali AJ, Ji S (2016) Circular RNAs as potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Am J Cancer Res 6(6):1167–1176
Li J, Yang J, Zhou P, le Y, Zhou C, Wang S, Xu D, Lin HK, Gong Z (2015) Circular RNAs in cancer: novel insights into origins, properties, functions and implications. Am J Cancer Res 5(2):472–480
Liu M, Liu KD, Zhang L et al (2018) Circ_0009910 regulates growth and metastasis and is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. J Cell Biochem 22(23):8248–8256. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201812_16519
Zhang X, Xu Y, Qian Z et al (2018) circRNA_104075 stimulates YAP-dependent tumorigenesis through the regulation of HNF4a and may serve as a diagnostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 9(11):1091. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1132-6
Zhang G, Sun W, Zhu L, Feng Y, Wu L, Li T (2018) Overexpressed circ_0029426 in glioblastoma forecasts unfavorable prognosis and promotes cell progression by sponging miR-197. J Cell Biochem 120:10295–10302. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28313
Liu G, Huang K, Jie Z, Wu Y, Chen J, Chen Z, Fang X, Shen S (2018) CircFAT1 sponges miR-375 to promote the expression of yes-associated protein 1 in osteosarcoma cells. Mol Cancer 17(1):170. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0917-7
Li X, Zhang Z, Jiang H, Li Q, Wang R, Pan H, Niu Y, Liu F, Gu H, Fan X, Gao J (2018) Circular RNA circPVT1 promotes proliferation and invasion through sponging miR-125b and activating E2F2 signaling in non-small cell lung Cancer. J Cell Biochem 51(5):2324–2340. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495876
Wang R, Zhang S, Chen X et al (2018) EIF4A3-induced circular RNA MMP9 (circMMP9) acts as a sponge of miR-124 and promotes glioblastoma multiforme cell tumorigenesis. 17(1):166. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0911-0
Wong N, Wang X (2015) miRDB: an online resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations. Nucleic Acids Res 43(Database issue):D146–D152. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1104
Fromm B, Billipp T, Peck LE, Johansen M, Tarver JE, King BL, Newcomb JM, Sempere LF, Flatmark K, Hovig E, Peterson KJ (2015) A uniform system for the annotation of vertebrate microRNA genes and the evolution of the human microRNAome. Annu Rev Genet 49:213–242. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-120213-092023
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, He QY (2012) clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 16(5):284–287. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2011.0118
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, Liu J, Marzluff WF, Sharpless NE (2013) Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA. 19(2):141–157. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.035667.112
Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glazar P et al (2015) Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant, conserved, and dynamically expressed. Mol Cell 58(5):870–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.03.027
Lux S, Bullinger L (2018) Circular RNAs in Cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 1087:215–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1426-1_17
Chen S, Zhao Y (2018) Circular RNAs: characteristics, function, and role in human cancer. Histol Histopathol 33(9):887–893. https://doi.org/10.14670/hh-11-969
Kristensen LS, Hansen TB, Veno MT, Kjems J (2018) Circular RNAs in cancer: opportunities and challenges in the field. Oncogene. 37(5):555–565. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.361
Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X et al (2018) Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol Cancer 17(1):79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0827-8
Chen F, Feng Z, Zhu J, Liu P, Yang C, Huang R, Deng Z (2018) Emerging roles of circRNA_NEK6 targeting miR-370-3p in the proliferation and invasion of thyroid cancer via Wnt signaling pathway. Cancer Biol Ther 19(12):1139–1152. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2018.1480888
Wei H, Pan L, Tao D, Li R (2018) Circular RNA circZFR contributes to papillary thyroid cancer cell proliferation and invasion by sponging miR-1261 and facilitating C8orf4 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503(1):56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.174
Liu F, Zhang J, Qin L et al (2018) Circular RNA EIF6 (Hsa_circ_0060060) sponges miR-144-3p to promote the cisplatin-resistance of human thyroid carcinoma cells by autophagy regulation. Aging (Albany NY) 10(12):3806–3820. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101674
Jin X, Wang Z, Pang W et al (2018) Upregulated hsa_circ_0004458 contributes to progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma by inhibition of miR-885-5p and activation of RAC1. Med Sci Monit 24:5488–5500. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.911095
Jiang W, Wen D, Gong L, Wang Y, Liu Z, Yin F (2018) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000673 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma malignance by decreasing miR-767-3p targeting SET. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 500(2):211–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.041
Chang P, Wang F, Li Y (2018) Hsa_circ_0000673 is down-regulated in gastric cancer and inhibits the proliferation and invasion of tumor cells by targetting miR-532-5p. Biosci Rep 38(5). https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20180538
Bartel DP (2018) Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell. 173(1):20–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.006
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 136(2):215–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
Liu C, Liu R, Zhang D, Deng Q, Liu B, Chao HP, Rycaj K, Takata Y, Lin K, Lu Y, Zhong Y, Krolewski J, Shen J, Tang DG (2017) MicroRNA-141 suppresses prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by targeting a cohort of pro-metastasis genes. Nat Commun 8:14270
Song HM, Luo Y, Li DF, Wei CK, Hua KY, Song JL, Xu H, Maskey N, Fang L (2015) MicroRNA-96 plays an oncogenic role by targeting FOXO1 and regulating AKT/FOXO1/Bim pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(9):9889–9900
Spitschak A, Meier C, Kowtharapu B, Engelmann D, Putzer BM (2017) MiR-182 promotes cancer invasion by linking RET oncogene activated NF-kappaB to loss of the HES1/Notch1 regulatory circuit. Mol Cancer 16(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-016-0563-x
Wu ZY, Wang SM, Chen ZH, Huv SX, Huang K, Huang BJ, du JL, Huang CM, Peng L, Jian ZX, Zhao G (2015) MiR-204 regulates HMGA2 expression and inhibits cell proliferation in human thyroid cancer. Cancer Biomark 15(5):535–542. https://doi.org/10.3233/cbm-150492
Li J, Zheng X, Gao M, Zhao J, Li Y, Meng X, Qian B, Li J (2017) Suberoyl bis-hydroxamic acid activates Notch1 signaling and induces apoptosis in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma through p53. Oncol Rep 37(1):458–464. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.5281
Kim YH, Choi YW, Lee J, Soh EY, Kim JH, Park TJ (2017) Senescent tumor cells lead the collective invasion in thyroid cancer. Nat Commun 8:15208. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15208
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: QL, LZP, and JYM. Performed the experiments: QL, LZP, and MH. Analyzed the data: QL, LZP, and JYM. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: QL, LZP, and MH. Wrote the paper: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
Ethical approval was not required in this study due to the public-available data.
Informed Consent
The data did not include the use of human subjects or personal identifying information. Thus, no informed consent was required for this part of the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Pan, Lz., Hu, M. et al. Molecular Network-Based Identification of Circular RNA-Associated ceRNA Network in Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 26, 1293–1299 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-019-00697-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-019-00697-y