Abstract
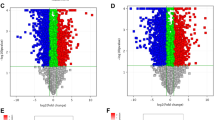
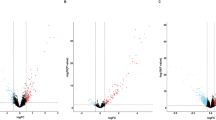
Integrative central axis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA plays pivotal roles in tumor development and progression. However, the regulatory role of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA in esophageal cancer remains elusive. TCGA database was utilized to investigate the differential expression of lncRNA, miRNA and mRNA in esophageal cancer (ESCA) and normal esophageal tissues, and GEO database was used to further validate the expression profile of key genes. Differential lncRNAs in TCGA database were submitted to Starbase, and lncRNAs related to overall survival were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier and log-rank test. We found 145 lncRNAs, 112 miRNAs and 2000 protein coding mRNAs were differentially expressed in ESCA samples, which were tightly involved in chromosome segregation, extracellular matrix assembly by GO assay, and KEGG assay revealed the correlation of differentially expressed genes with cell cycle, apoptosis and cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. Furthermore, there were 291 nodes in ceRNA network, which consisted of 40 lncRNAs, 28 miRNAs and 233 mRNAs, and formed 677 relations. Furthermore, 6 of 10 lncRNAs in TCGA database were consistent with GEO database, and expressions of 10 mRNAs in TCGA database all exhibited the same tendency with GEO database. Notably, we found 8 lncRNAs (WDFY3-AS2, CASC8, UGDH-AS1, RAP2C-AS1, AC007128.1, AC016205.1, AC092803.2 and AC079949.2) were correlated with overall survival of the patients with ESCA. The key differentially expressed genes participate in the development and progression of ESCA, and thus the elucidation of functions of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA will provide new novel therapeutic target for the patients with ESCA.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90
Abnet CC, Arnold M, Wei WQ (2018) Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology 154(2):360–373
Arnold M, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J, Forman D (2015) Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological subtype in 2012. Gut 64(3):381–387
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65(2):87–108
Ohashi S, Miyamoto S, Kikuchi O, Goto T, Amanuma Y, Muto M (2015) Recent advances from basic and clinical studies of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology 149(7):1700–1715
Song G, Shen Y, Ruan Z, Li X, Chen Y, Yuan W, Ding X, Zhu L, Qian L (2016) LncRNA-uc.167 influences cell proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation of P19 cells by regulating Mef2c. Gene 590(1):97–108
Zhao J, Liu Y, Zhang W, Zhou Z, Wu J, Cui P, Zhang Y, Huang G (2015) Long non-coding RNA Linc00152 is involved in cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, epithelial to mesenchymal transition, cell migration and invasion in gastric cancer. Cell Cycle 14(19):3112–3123
Song R, Hou G, Yang J, Yuan J, Wang C, Chai T, Liu Z (2018) Effects of PLK1 on proliferation, invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Lett 16(5):5739–5744
Morris KV, Mattick JS (2014) The rise of regulatory RNA. Nat Rev Genet 15(6):423–437
Garzon R, Calin GA, Croce CM (2009) MicroRNAs in Cancer. Annu Rev Med 60:167–179
Huarte M (2015) The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer. Nat Med 21(11):1253–1261
Schmitt AM, Chang HY (2016) Long noncoding RNAs in Cancer pathways. Cancer Cell 29(4):452–463
Evans JR, Feng FY, Chinnaiyan AM (2016) The bright side of dark matter: lncRNAs in cancer. J Clin Invest 126(8):2775–2782
Li DY, Chen WJ, Luo L, Wang YK, Shang J, Zhang Y, Chen G, Li SK (2017) Prospective lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network of long non-coding RNA LINC00968 in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells: a miRNA microarray and bioinformatics investigation. Int J Mol Med 40(6):1895–1906
Yao K, Wang Q, Jia J, Zhao H (2017) A competing endogenous RNA network identifies novel mRNA, miRNA and lncRNA markers for the prognosis of diabetic pancreatic cancer. Tumour Biol 39(6):1010428317707882
Ye S, Yang L, Zhao X, Song W, Wang W, Zheng S (2014) Bioinformatics method to predict two regulation mechanism: TF-miRNA-mRNA and lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA in pancreatic cancer. Cell Biochem Biophys 70(3):1849–1858
Liu Y, Zhu J, Ma X, Han S, Xiao D, Jia Y, Wang Y (2018) ceRNA network construction and comparison of gastric cancer with or without Helicobacter pylori infection. J Cell Physiol
Li R, Qu H, Wang S, Wei J, Zhang L, Ma R, Lu J, Zhu J, Zhong WD, Jia Z (2018) GDCRNATools: an R/Bioconductor package for integrative analysis of lncRNA, miRNA and mRNA data in GDC. Bioinformatics 34(14):2515–2517
Anders S, Pyl PT, Huber W (2015) HTSeq--a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 31(2):166–169
Lun AT, Chen Y, Smyth GK (2016) It's DE-licious: a recipe for differential expression analyses of RNA-seq experiments using quasi-likelihood methods in edgeR. Methods Mol Biol 1418:391–416
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH, Yang JH (2014) starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Database issue):D92–D97
Jeggari A, Marks DS, Larsson E (2012) miRcode: a map of putative microRNA target sites in the long non-coding transcriptome. Bioinformatics 28(15):2062–2063
Chou CH, Shrestha S, Yang CD, Chang NW, Lin YL, Liao KW, Huang WC, Sun TH, Tu SJ, Lee WH et al (2018) miRTarBase update 2018: a resource for experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D296–D302
Furio-Tari P, Tarazona S, Gabaldon T, Enright AJ, Conesa A (2016) spongeScan: a web for detecting microRNA binding elements in lncRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 44(W1):W176–W180
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, He QY (2012) Clusterprofiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 16(5):284–287
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, Smyth GK (2015) Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43(7):e47
Zhu H, Lu J, Zhao H, Chen Z, Cui Q, Lin Z, Wang X, Wang J, Dong H, Wang S et al (2018) Functional long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in clear cell kidney carcinoma revealed by reconstruction and comprehensive analysis of the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network. Med Sci Monit 24:8250–8263
Fan CN, Ma L, Liu N (2018) Systematic analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA network identifies four-lncRNA signature as a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer. J Transl Med 16(1):264
Lin P, Wen DY, Li Q, He Y, Yang H, Chen G (2018) Genome-wide analysis of prognostic lncRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs forming a competing endogenous RNA network in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem 48(5):1953–1967
Zhao J, Cheng W, He X, Liu Y, Li J, Sun J, Li J, Wang F, Gao Y (2018) Construction of a specific SVM classifier and identification of molecular markers for lung adenocarcinoma based on lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network. Onco Targets Ther 11:3129–3140
Chen X, Han H, Li Y, Zhang Q, Mo K, Chen S (2016) Upregulation of long noncoding RNA HOTTIP promotes metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via induction of EMT. Oncotarget 7(51):84480–84485
Song W, Zou SB (2016) Prognostic role of lncRNA HOTAIR in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Chim Acta 463:169–173
Liu B, Pan CF, Yao GL, Wei K, Xia Y, Chen YJ (2018) The long non-coding RNA AK001796 contributes to tumor growth via regulating expression of p53 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int 18:38
Wang W, Zhu Y, Li S, Chen X, Jiang G, Shen Z, Qiao Y, Wang L, Zheng P, Zhang Y (2016) Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes malignant development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting beta-catenin via Ezh2. Oncotarget 7(18):25668–25682
Yao J, Huang JX, Lin M, Wu ZD, Yu H, Wang PC, Ye J, Chen P, Wu J, Zhao GJ (2016) Microarray expression profile analysis of aberrant long non-coding RNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 48(6):2543–2557
Cao W, Wu W, Shi F, Chen X, Wu L, Yang K, Tian F, Zhu M, Chen G, Wang W et al (2013) Integrated analysis of long noncoding RNA and coding RNA expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Genomics 2013:480534
Wang W, Wei C, Li P, Wang L, Li W, Chen K, Zhang J, Zhang W, Jiang G (2018) Integrative analysis of mRNA and lncRNA profiles identified pathogenetic lncRNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gene 661:169–175
Dong X, Kong C, Liu X, Bi J, Li Z, Li Z, Zhu Y, Zhang Z (2018) GAS5 functions as a ceRNA to regulate hZIP1 expression by sponging miR-223 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res 8(8):1414–1426
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146(3):353–358
Chi H, Yang R, Zheng X, Zhang L, Jiang R, Chen J (2018) LncRNA RP11-79H23.3 Functions as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Regulate PTEN Expression through Sponging hsa-miR-107 in the Development of Bladder Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 19(9)
Wang P, Li J, Zhao W, Shang C, Jiang X, Wang Y, Zhou B, Bao F, Qiao H (2018) A novel LncRNA-miRNA-mRNA triple network identifies LncRNA RP11-363E7.4 as an important regulator of miRNA and gene expression in gastric Cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem 47(3):1025–1041
Botti G, Marra L, Malzone MG, Anniciello A, Botti C, Franco R, Cantile M (2017) LncRNA HOTAIR as prognostic circulating marker and potential therapeutic target in patients with tumor diseases. Curr Drug Targets 18(1):27–34
Wang Y, Li Y, Song HQ, Sun GW (2018) Long non-coding RNA LINC00899 as a novel serum biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis prediction of acute myeloid leukemia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22(21):7364–7370
Yang L, Zhou JD, Zhang TJ, Ma JC, Xiao GF, Chen Q, Deng ZQ, Lin J, Qian J, Yao DM (2018) Overexpression of lncRNA PANDAR predicts adverse prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Manag Res 10:4999–5007
Kiran M, Chatrath A, Tang X, Keenan DM, Dutta A (2018) A prognostic signature for lower grade gliomas based on expression of long non-coding RNAs. Mol Neurobiol
Mao Y, Fu Z, Zhang Y, Dong L, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Li X, Liu J (2018) A seven-lncRNA signature predicts overall survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Sci Rep 8(1):8823
Bao J, Zhou C, Zhang J, Mo J, Ye Q, He J, Diao J (2018) Upregulation of the long noncoding RNA FOXD2-AS1 predicts poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark 21(3):527–533
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (No. 182300410377), the Key scientific research projects of Henan higher education institutions (No.17A180016), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81272691, 30600006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure 1
Heatmap analysis for differential expressions of top 30 of lncRNA, miRNA and mRNA in ESCC and normal esophageal tissues. A: lncRNAs were displayed using heatmap in ESCC and normal esophageal tissues; B: miRNAs were displayed using heatmap in ESCC and normal esophageal tissues; C: protein coding mRNAs were displayed using heatmap in ESCC and normal esophageal tissues. X axis represents the samples, and Y axis denotes differential expressions of lncRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs. (JPG 3831 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
Prognostic investigation of a total of 15 of high nodes regarding lncRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs. LncRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs were submitted to Starbase online software as described in online manufacture’s instructions. (JPG 1280 kb)
Supplementary Figure 3
Prognostic assay of the 10 mRNAs in ESCA. The 10 mRNAs were submitted to Starbase online software as described in online manufacture’s instructions. (JPG 844 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 17 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
(DOCX 16 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
(DOCX 17 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
(DOCX 16 kb)
Supplementary Table 5
(DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Zhang, Q., Lou, Q. et al. Differential Analysis of lncRNA, miRNA and mRNA Expression Profiles and the Prognostic Value of lncRNA in Esophageal Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 26, 1029–1039 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-019-00655-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-019-00655-8