Abstract
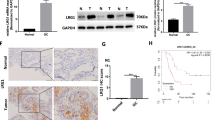
Our study aimed to identify key genes involved in the use of fluvastatin and zoledronate against breast cancer, as well as to investigate the roles of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) in the malignant behaviors of breast cancer cells. The expression data GSE33552 was downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus database, including mocked-, fluvastatin- and zoledronate-treated MDA-MB-231 cells. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified in fluvastatin- and zoledronate-treated cells using limma package, respectively. Pathway enrichment analysis and protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis were then performed. Then we used shRNA specifically targeting VEGFA (shVEGFA) to knock down the expression of VEGFA in MDA-MB-231 cells. Cell viability assay, scratch wound healing assay, Transwell invasion assay and flow cytometry were performed to explore the effects of VEGFA knockdown on the malignant behaviors of breast cancer cells. VEGFA was up-regulated in both fluvastatin- and zoledronate-treated breast cancer cells. Moreover, VEGFA was a hub node in PPI network. In addition, VEGFA was successfully knocked down in MDA-MB-231 cells by shVEGFA. Suppression of VEGFA promoted the migration and invasion of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Suppression of VEGFA inhibited the apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 cells. Our results indicate that up-regulation of VEGFA may prevent the progression of breast cancer after fluvastatin and zoledronate treatment via inducing cell apoptosis and inhibiting migration and invasion. VEGFA may serve as a potential prognostic indicator for clinical outcome in the management of breast cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stebbing J, Slater S, Slevin M (2006) Breast cancer (metastatic). Clin Evid 15:2331–2359
Group EBCTC (2015) Adjuvant bisphosphonate treatment in early breast cancer: meta-analyses of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet 386(10001):1353–1361
Garwood ER, Kumar AS, Baehner FL, Moore DH, Au A, Hylton N, Flowers CI, Garber J, Lesnikoski B-A, Hwang ES (2010) Fluvastatin reduces proliferation and increases apoptosis in women with high grade breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 119(1):137–144
Kotamraju S, Willams CL, Kalyanaraman B (2007) Statin-induced breast cancer cell death: role of inducible nitric oxide and arginase-dependent pathways. Cancer Res 67(15):7386–7394
Kanugula AK, Gollavilli PN, Vasamsetti SB, Karnewar S, Gopoju R, Ummanni R, Kotamraju S (2014) Statin-induced inhibition of breast cancer proliferation and invasion involves attenuation of iron transport: intermediacy of nitric oxide and antioxidant defence mechanisms. FEBS J 281(16):3719–3738
Senaratne S, Pirianov G, Mansi J, Arnett T, Colston K (2000) Bisphosphonates induce apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer 82(8):1459
Dedes P, Gialeli C, Tsonis A, Kanakis I, Theocharis A, Kletsas D, Tzanakakis G, Karamanos N (2012) Expression of matrix macromolecules and functional properties of breast cancer cells are modulated by the bisphosphonate zoledronic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820(12):1926–1939
Furriol J, Puntervoll HE, Knutsvik G, Mannelqvist M, Aziz S, Wik E, Akslen LA (2015) Associations between VEGF polymorphisms and clinical outcome in breast cancer. Cancer Res 75(15 Supplement):135–135
Croset M, Goehrig D, Frackowiak A, Bonnelye E, Ansieau S, Puisieux A, Clézardin P (2014) TWIST1 expression in breast cancer cells facilitates bone metastasis formation. J Bone Miner Res 29(8):1886–1899
Vintonenko N, Jais J-P, Kassis N, Abdelkarim M, Perret G-Y, Lecouvey M, Crepin M, Di Benedetto M (2012) Transcriptome analysis and in vivo activity of fluvastatin versus zoledronic acid in a murine breast cancer metastasis model. Mol Pharmacol 82(3):521–528
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA (2004) Affy—analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics 20(3):307–315
Smyth GK (2005) Limma: linear models for microarray data. In: Bioinformatics and computational biology solutions using R and Bioconductor. Springer, pp 397–420
Li C, Li X, Miao Y, Wang Q, Jiang W, Xu C, Li J, Han J, Zhang F, Gong B (2009) SubpathwayMiner: a software package for flexible identification of pathways. Nucleic Acids Res 37(19):e131–e131
Kanehisa M (2002) The KEGG database. Novartis Found Symp 247:91–101 discussion 101–103, 119–128, 244–152
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S, Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C (2013) STRING v9. 1: protein-protein interaction networks, with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res 41(D1):D808–D815
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504
Cory G (2011) Scratch-wound assay. Cell Migration. Springer, In, pp 25–30
Rydén L, Linderholm B, Nielsen NH, Emdin S, Jönsson P-E, Landberg G (2003) Tumor specific VEGF-A and VEGFR2/KDR protein are co-expressed in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 82(3):147–154
Oommen S, Gupta SK, Vlahakis NE (2011) Vascular endothelial growth factor a (VEGF-A) induces endothelial and cancer cell migration through direct binding to integrin α9β1 identification of a specific α9β1 binding site. J Biol Chem 286(2):1083–1092
Yin YP, Wei WH, Wang HC, Zhu BY, Yu YH, Chen XS, Peeling RW, Cohen MS (2009) Performance of serological tests for syphilis in sexually transmitted diseases clinics in Guangxi Autonomous Region, China: implications for syphilis surveillance and control. Sex Health 6(1):5–9
Eun YG, Lee YC, Lee J-W (2015) A polymorphism of VEGFA is associated with susceptibility to extrathyroidal invasion of papillary thyroid cancer. Cancer Res 75(15 Supplement):5280–5280
Gong J, Zhu S, Zhang Y, Wang J (2014) Interplay of VEGFa and MMP2 regulates invasion of glioblastoma. Tumor Biol 35(12):11879–11885
Chen L, Xiao H, Wang Z-H, Huang Y, Liu Z-P, Ren H, Song H (2014) miR-29a suppresses growth and invasion of gastric cancer cells in vitro by targeting VEGF-A. BMB Rep 47(1):39–44
Gu A, Lu J, Wang W, Shi C, Han B, Yao M (2016) Role of miR-497 in VEGF-A-mediated cancer cell growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 70:118–125
Whitehurst B, Flister MJ, Bagaitkar J, Volk L, Bivens CM, Pickett B, Castro-Rivera E, Brekken RA, Gerard RD, Ran S (2007) Anti-VEGF-A therapy reduces lymphatic vessel density and expression of VEGFR-3 in an orthotopic breast tumor model. Int J Cancer 121(10):2181–2191
Rydén L, Stendahl M, Jonsson H, Emdin S, Bengtsson NO, Landberg G (2005) Tumor-specific VEGF-A and VEGFR2 in postmenopausal breast cancer patients with long-term follow-up. Implication of a link between VEGF pathway and tamoxifen response. Breast Cancer Res Treat 89(2):135–143
Bai X, Geng J, Li X, Yang F, Tian J (2015) VEGF-A inhibition ameliorates podocyte apoptosis via repression of activating protein 1 in diabetes. Am J Nephrol 40(6):523–534. doi:10.1159/000369942
Zelzer E, Mamluk R, Ferrara N, Johnson RS, Schipani E, Olsen BR (2004) VEGFA is necessary for chondrocyte survival during bone development. Development 131(9):2161–2171
Balasubramanian SP, Cox A, Cross SS, Higham SE, Brown NJ, Reed MW (2007) Influence of VEGF-A gene variation and protein levels in breast cancer susceptibility and severity. Int J Cancer 121(5):1009–1016
Ma X, Shen D, Li H, Zhang Y, Lv X, Huang Q, Gao Y, Li X, Gu L, Xiu S (2015) MicroRNA-185 inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis by targeting VEGFA directly in von Hippel-Lindau–inactivated clear cell renal cell carcinoma. In: Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations. Elsevier, pp 169. e161–169. e111
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, H., Zhang, Q., Zhao, C. et al. VEGFA Involves in the Use of Fluvastatin and Zoledronate Against Breast Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 24, 557–565 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0277-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0277-4