Abstract
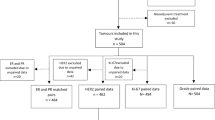
In this study, we compared the accuracy of marker evaluation in core needle biopsy (CNB) specimens versus excision specimens (ESs) from breast cancer patients. This retrospective study used data collected from the breast cancer database at the West China Hospital, China. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) results from CNB specimens and ESs were compared, using estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and Ki-67 as markers. Molecular subtyping and endocrine therapy usage correlations based on CNB samples and ESs were evaluated. The results obtained from CNB samples and ESs exhibited substantial agreement for the detection of ER (κ = 0.522), PR (κ = 0.441), and HER2 (κ = 0.451), and also influenced endocrine therapy usage. Fair and poor correlations were observed for Ki-67 staining and molecular subtyping (κ = 0.195), respectively. This disagreement might be attributable to a combination of heterogeneity and large tumor size. This study indicates that the discordance rate in molecular marker staining between CNB specimens and ESs is significant enough that results obtained with CNB specimens should be used cautiously or verified using ESs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Breast cancer (2015) www.NCCN.com.
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lønning PE, Børresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumors. Nature 406:747–752
Gonçalves AV, Thuler LC, Kestelman FP, Carmo PA, Lima CF, Cipolotti R (2011) Underestimation of malignancy of core needle biopsy for nonpalpable breast lesions. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 33:123–131
Dekker TJ, Smit VT, Hooijer GK, Van de Vijver MJ, Mesker WE, Tollenaar RA, Nortier JW, Kroep JR (2013) Reliability of core needle biopsy for determining ER and HER2 status in breast cancer. Ann Oncol 24:931–937. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds599
Chen X, Yuan Y, Gu Z, Shen K (2012) Accuracy of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2 status between core needle and open excision biopsy in breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 134:957–967. doi:10.1007/s10549-012-1990-z
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates A, Gelber RD, Thürlimann H, Senn HJ, Panel member (2011) Subtypes—dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2011. Ann Oncol 22:1736–1747
Harris L, Fritsche H, Mennel R, Norton L, Ravdin P, Taube S, Somerfield MR, Hayes DF, Bast RC Jr (2007) American Society of Clinical Oncology: American society of clinical oncology 2007 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:5287–5312
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Wolff AC, Mangu PB, Temin S (2010) American society of clinical oncology/college of American pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J Oncol Pract 6:195–197. doi:10.1200/JOP.777003
Usami S, Moriya T, Amari M, Suzuki A, Ishida T, Sasano H, Ohuchi N (2007) Reliability of prognostic factors in breast carcinoma determined by core needle biopsy. Jpn J Clin Oncol 37:250–255. doi:10.1093/jjco/hym021
Ricci MD, Calvano Filho CM, Oliveira Filho HR, Filassi JR, Pinotti JA, Baracat EC (2012) Analysis of the concordance rates between core needle biopsy and surgical excision in patients with breast cancer. Rev Assoc Med Bras 58:532–536. doi:10.1016/S0104-4230(12)70245-2
Petrau C, Clatot F, Cornic M, Berghian A, Veresezan L, Callonnec F, Baron M, Veyret C, Laberge S, Thery JC, Picquenot JM (2015) Reliability of prognostic and predictive factors evaluated by needle Core biopsies of large breast invasive tumors. Am J Clin Pathol 144:555–562. doi:10.1309/AJCP9KFVM2GZMNDV
Litherland JC, Evans AJ, Wilson AR, Kollias J, Pinder SE, Elston CW, Ellis IO, Yeoman LJ (1996) The impact of core-biopsy on pre-operative diagnosis rate of screen detected breast cancers. Clin Radiol 51:562–565. doi:10.1016/S0009-9260(96)80136-X
Youk JH, Kim EK, Kim MJ, Oh KK (2008) Sonographically guided 14-gauge core needle biopsy of breast masses: a review of 2,420 cases with long-term-follow-up. AJR Am J Roentgenol 190:202–207. doi:10.2214/AJR.07.2419
Collins LC, Connolly JL, Page DL, Goulart RA, Pisano ED, Fajardo LL, Berg WA, Caudry DJ, McNeil BJ, Schnitt SJ (2004) Diagnostic agreement in the evaluation of image-guided breast core needle biopsies: results from a randomized clinical trial. Am J Surg Pathol 28:126–123. doi:10.1097/00000478-200401000-00015
Crowe JP Jr, Rim A, Patrick RJ, Rybicki LA, Grundfest-Broniatowski SF, Kim JA, Lee KB (2003) Does core needle breast biopsy accurately reflect breast pathology? Surgery 134:523–526
Crowe JP Jr, Patrick RJ, Rybicki LA, Grundfest SF, Kim JA, Lee KB, Rim A (2003) Does ultrasound core breast biopsy predict histologic finding on excisional biopsy? Am J Surg 186:397–399
Li S, Yang X, Zhang Y, Fan L, Zhang F, Chen L, Zhou Y, Chen X, Jiang J (2012) Assessment accuracy of core needle biopsy for hormone receptors in breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 135:325–334. doi:10.1007/s10549-012-2063-z
Sutela A, Vanninen R, Sudah M, Berg M, Kiviniemi V, Rummukainen J, Kataja V, Kärjä V (2008) Surgical specimen can be replaced by core samples in assessment of ER, PR and HER-2 for invasive breast cancer. Acta Oncol 47(1):38–46. doi:10.1080/02841860701441822
Seferina SC, Nap M, van den Berkmortel F, Wals J, Voogd AC, Tjan-Heijnen VC (2013) Reliability of receptor assessment on core needle biopsy in breast cancer patients. Tumour Biol 34:987–994. doi:10.1007/s13277-012-0635-5
Lorgis V, Algros MP, Villanueva C, Chaigneau L, Thierry-Vuillemin A, Nguyen T, Demarchi M, Bazan F, Sautiere JL, Maisonnette-Lescot Y, Ringenbach F, Bontemps P, Pivot X (2011) Discordance in early breast cancer for tumour grade, estrogen receptor, progesterone receptors and human epidermal receptor-2 status between core needle biopsy and surgical excisional primary tumour. Breast 20:284–287. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2010.12.007
Munch-Petersen HD, Rasmussen BB, Balslev E (2014) Reliability of histological malignancy grade, ER and HER2 status on core needle biopsy vs surgical specimen in breast cancer. APMIS 122:750–754. doi:10.1111/apm.12213
Chen X, Zhu S, Fei X, Garfield DH, Wu J, Huang O, Li Y, Zhu L, He J, Chen W, Jin X, Shen K (2015) Surgery time interval and molecular subtype may influence Ki67 change after core needle biopsy in breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 15:822. doi:10.1186/s12885-015-1853-1
Greer LT, Rosman M, Mylander WC, Hooke J, Kovatich A, Sawyer K, Buras RR, Shriver CD, Tafra L (2013) Does breast tumor heterogeneity necessitate further immunohistochemical staining on surgical specimens? J Am Coll Surg 216:239–251. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.09.007
Ough M, Velasco J, Hieken TJ (2011) A comparative analysis of core needle biopsy and final excision for breast cancer: histology and marker expression. Am J Surg 201:692–694. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2010.02.015
Zhang Z, Yuan P, Guo H, Zhao L, Ying J, Wang M, Zhao H, Pan Q, Xu B (2015) Assessment of hormone receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status in breast carcinoma using thin-prep cytology fine needle aspiration cytology FISH experience from China. Medicine (Baltimore) 94:e981. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000000981
Chen X, Sun L, Mao Y, Zhu S, Wu J, Huang O, Li Y, Chen W, Wang J, Yuan Y, Fei X, Jin X, Shen K (2013) Preoperative core needle biopsy is accurate in determining molecular subtypes in invasive breast cancer. BMC Cancer 13:390. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-390
Uy GB, Laudico AV, Carnate JM Jr, Lim FG, Fernandez AM, Rivera RR, Mapua CA, Love RR (2010) Breast cancer hormone receptor assay results of core needle biopsy and modified radical mastectomy specimens from the same patients. Clin Breast Cancer 10:154–159. doi:10.3816/CBC.2010.n.021
VandenBussche CJ, Cimino-Mathews A, Park BH, Emens LA, Tsangaris TN, Argani P (2015) Reflex estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 analysis of breast cancers in needle core biopsy specimens dramatically increases health care costs. Am J Surg Pathol 39:939–947. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000424
Douglas-Jones AG, Collett N, Morgan JM, Jasani B (2001) Comparison of core estrogen receptor (ER) assay with excised tumour: intratumoral distribution of ER in breast carcinoma. J Clin Pathol 54:951–955
Tamaki K, Sasano H, Ishida T, Miyashita M, Takeda M, Amari M, Tamaki N, Ohuchi N (2010) Comparison of core needle biopsy (CNB) and surgical specimens for accurate preoperative evaluation of ER, PgRand HER2 status of breast cancer patients. Cancer Sci 101:2074–2079. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01630.x
Melotti MK, Berg WA (2000) Core needle breast biopsy in patients undergoing anticoagulation therapy: preliminary results. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:245–249. doi:10.2214/ajr.174.1.1740245
Ozdemir A, Voyvoda NK, Gultekin S, Tuncbilek I, Dursun A, Yamac D (2007) Can core biopsy be used instead of surgical biopsy in the diagnosis and prognostic factor analysis of breast carcinoma? Clin Breast Cancer 7:791–795. doi:10.3816/CBC.2007.n.041
Hoda SA, Harigopal M, Harris GC, Pinder SE, Lee AH, Ellis IO (2003) Expert opinion: reporting needle core biopsies of breast carcinomas. Histopathology 43:84–90
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Science and Technology Supporting Plan of Science & technology Department of Sichuan Province, China (No:2015SZ0146).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
All of the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Wang, Z., Lv, Q. et al. Comparison of Core Needle Biopsy and Excision Specimens for the Accurate Evaluation of Breast Cancer Molecular Markers: a Report of 1003 Cases. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 23, 769–775 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0187-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0187-5