Abstract
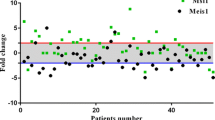
Homeobox genes play an overruling role in the regional cell fate determination during development. EVX1 is known as a new target gene of BMP signaling pathway, a group of morphogens which are making the largest subset within the transformation growth factor beta (TGF-β) superfamily. In this study, we aimed to enlighten the expression level of EVX1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and to disclose its apparent roles in maintenance and progression of the disease. The expression level of EVX1 was analyzed in fresh tumoral tissues in comparison with distant tumor-free tissues of 50 ESCC patients using relative comparative real-time PCR. The importance of EVX1 in development and cancer was also reviewed. EVX1 was underexpressed in 70 % of tumor samples. There was a significant correlation between down-regulation of EVX1 and lymph node metastasis of tumor cells (p = 0.027). Furthermore, EVX1 underexpression was significantly correlated with depth of tumor cell invasion (P = 0.037). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report highlighting EVX1 expression in ESCC to date. The clinicopathological relevance of EVX1 mRNA expression in ESCC targeted this gene as a new independent molecular marker for advanced tumor, which determine the characteristics and behavior of aggressive ESCC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruiz i Altaba A, Choi T, Melton DA (1991) Expression of the Xhox3 homeobox protein in xenopus embryos: blocking its early function suggests the requirement of Xhox3 for normal posterior development. Develop Growth Differ 33:651–669
Ruiz i Altaba A, Melton DA (1989a) Bimodal and graded expression of the xenopus homeobox gene Xhox3 during embryonic development. Development 106:173–183
Ruiz i Altaba A, Melton DA (1989b) Involvement of the xenopus homeobox gene Xhox3 in pattern formation along the anterior–posterior axis. Cell 57:317–326
Briata P, Van De Werken R, Airoldi I, Ilengo C, Di Blas E, Boncinelli E, Corte G (1995) Transcriptional repression by the human homeobox protein EVX1 in transfected mammalian cells. J Biophys Chem 270:27695–27701. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.46.27695
Hui X, Long-jiang L, Fang X, Bo H, Zhuang Z, Jiang W (2012) Differentially expressed homeobox genes in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma versus normal salivary gland tissue. Life Sci J 9(2):292–296
Guo X, Wang XF (2009) Signaling cross-talk between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res 19(1):71–88. doi:10.1038/cr.2008.302
Blanco Calvo M, Bolós Fernández V, Medina Villaamil V, Aparicio Gallego G, Díaz Prado S, Grande Pulido E (2009) Biology of BMP signalling and cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 11(3):126–137. doi:10.1007/S12094-009-0328-8
Zhang G, Mai R, Huang B (2010) ADH1B Arg47His polymorphism is associated with esophageal cancer risk in high-incidence Asian population: evidence from a meta-analysis. PLoS One 5(10):e13679. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013679
Baldwin, K. (2015). Esophageal Cancer. Retrieved from http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/277930-overview
Reya T, Clevers H (2005) Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature 434(7035):843–850. doi:10.1038/nature03319
Taipale J, Beachy PA (2001) The hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature 411(6835):349–354. doi:10.1038/35077219
Grier DG, Thompson A, Kwasniewska A, McGonigle GJ, Halliday HL, Lappin TR (2005) The pathophysiology of HOX genes and their role in cancer. J Pathol 205(2):154–171. doi:10.1002/path.1710
Zhai Y, Kuick R, Nan B, Ota I, Weiss SJ, Trimble CL, Fearon ER, Cho KR (2007) Gene expression analysis of preinvasive and invasive cervical squamous cell carcinomas identifies HOXC10 as a key mediator of invasion. Cancer Res 67(21):10163–10172. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2056
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C (2011) TNM classification of malignant tumours. Wiley, London
Garcia-Fernandez J (2005) The genesis and evolution of homeobox gene clusters. Nat Rev Genet 6(12):881–892. doi:10.1038/nrg1723
Rauch T, Wang Z, Zhang X, Zhong X, Wu X, Lau SK, Kernstine KH, Riggs AD, Pfeifer GP (2007) Homeobox gene methylation in lung cancer studied by genome-wide analysis with a microarray-based methylated CpG island recovery assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(13):5527–5532. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701059104
Osada S, Ohmori SY, Taira M (2003) XMAN1, an inner nuclear membrane protein, antagonizes BMP signaling by interacting with Smad1 in xenopus embryos. Development 130(9):1783–1794. doi:10.1242/dev.00401
Takebayashi-Suzuki K, Funami J, Tokumori D, Saito A, Watabe T, Miyazono K, Kanda A, Suzuki A (2003) Interplay between the tumor suppressor p53 and TGF beta signaling shapes embryonic body axes in xenopus. Development 130(17):3929–3939. doi:10.1242/dev.00615
Spyropoulos DD, Capecchi MR (1994) Targeted disruption of the even-skipped gene, evx1, causes early postimplantation lethality of the mouse conceptus. Genes Dev 8(16):1949–1961. doi:10.1101/gad.8.16.1949
Alev C, Wu Y, Kasukawa T, Jakt LM, Ueda HR, Sheng G (2010) Transcriptomic landscape of the primitive streak. Development 137(17):2863–2874. doi:10.1242/dev.053462
Bastian H, Gruss P (1990) A murine even-skipped homologue, Evx 1, is expressed during early embryogenesis and neurogenesis in a biphasic manner. EMBO J 9(6):1839–1852
Dush MK, Martin GR (1992) Analysis of mouse Evx genes: Evx-1 displays graded expression in the primitive streak. Dev Biol 151(1):273–287. doi:10.1016/0168-9525(92)90245-Y
Fuchtbauer EM (1995) Expression of M-twist during postimplantation development of the mouse. Dev Dyn 204(3):316–322. doi:10.1002/aja.1002040309
Wolf C, Thisse C, Stoetzel C, Thisse B, Gerlinger P, Perrin-Schmitt F (1991) The M-twist gene of Mus is expressed in subsets of mesodermal cells and is closely related to the xenopus X-twi and the drosophila twist genes. Dev Biol 143(2):363–373. doi:10.1016/0012-1606(91)90086-I
Kanai-Azuma M, Kanai Y, Gad JM, Tajima Y, Taya C, Kurohmaru M, Sanai Y, Yonekawa H, Yazaki K, Tam PP, Hayashi Y (2002) Depletion of definitive gut endoderm in Sox17-null mutant mice. Development 129(10):2367–2379
Yasunaga M, Tada S, Torikai-Nishikawa S, Nakano Y, Okada M, Jakt LM, Nishikawa S, Chiba T, Era T, Nishikawa S (2005) Induction and monitoring of definitive and visceral endoderm differentiation of mouse ES cells. Nat Biotechnol 23(12):1542–1550. doi:10.1038/nbt1167
Jones CM, Dale L, Hogan BL, Wright CV, Smith JC (1996) Bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP-4) acts during gastrula stages to cause ventralization of xenopus embryos. Development 122(5):1545–1554
Nostro MC, Cheng X, Keller GM, Gadue P (2008) Wnt, activin, and BMP signaling regulate distinct stages in the developmental pathway from embryonic stem cells to blood. Cell Stem Cell 2(1):60–71. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2007.10.011
Kalisz M, Winzi M, Bisgaard HC, Serup P (2012) Even-skipped homeobox 1 controls human ES cell differentiation by directly repressing goosecoid expression. Dev Biol 362:94–103. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.11.017
Yasuo H, Lemaire P (2001) Role of goosecoid, xnot and Wnt antagonists in the maintenance of the notochord genetic programme in xenopus gastrulae. Development 128(19):3783–3793
Luu O, Nagel M, Wacker S, Lemaire P, Winklbauer R (2008) Control of gastrula cell motility by the goosecoid/mix.1/siamois network: basic patterns and paradoxical effects. Dev Dyn 237(5):1307–1320. doi:10.1002/dvdy.21522
Hartwell KA, Muir B, Reinhardt F, Carpenter AE, Sgroi DC, Weinberg RA (2006) The Spemann organizer gene, goosecoid, promotes tumor metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(50):18969–18974. doi:10.1073/pnas.0608636103
Forghanifard MM, Moaven O, Farshchian M, Montazer M, Raeisossadati R, Abdollahi A, Moghbeli M, Nejadsattari T, Parivar K, Abbaszadegan MR (2012) Expression analysis elucidates the roles of MAML1 and Twist1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma aggressiveness and metastasis. Ann Surg Oncol 19(3):743–749. doi:10.1245/s10434-011-2074-8
Ansieau S, Morel AP, Hinkal G, Bastid J, Puisieux A (2010) TWISTing an embryonic transcription factor into an oncoprotein. Oncogene 29(22):3173–3184. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.92
Christiansen JJ, Rajasekaran AK (2006) Reassessing epithelial to mesenchymal transition as a prerequisite for carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res 66(17):8319–8326. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0410
Klymkowsky MW, Savagner P (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: a cancer researcher’s conceptual friend and foe. Am J Pathol 174(5):1588–1593. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2009.080545
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S, Itzykson RA, Come C, Savagner P, Gitelman I, Richardson A, Weinberg RA (2004) Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell 117(7):927–939. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.06.006
Sasaki K, Natsugoe S, Ishigami S, Matsumoto M, Okumura H, Setoyama T, Uchikado Y, Kita Y, Tamotsu K, Sakamoto A, Owaki T, Aikou T (2009) Significance of twist expression and its association with E-cadherin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 28:158. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-28-158
Yuen HF, Chan YP, Wong ML, Kwok WK, Chan KK, Lee PY, Srivastava G, Law SY, Wong YC, Wang X, Chan KW (2007) Upregulation of twist in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with neoplastic transformation and distant metastasis. J Clin Pathol 60(5):510–514. doi:10.1136/jcp.2006.039099
Du YC, Oshima H, Oguma K, Kitamura T, Itadani H, Fujimura T, Piao YS, Yoshimoto T, Minamoto T, Kotani H, Taketo MM, Oshima M (2009) Induction and down-regulation of Sox17 and its possible roles during the course of gastrointestinal tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology 137(4):1346–1357. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.06.041
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the colleagues at Division of Human Genetics for their kindly technical assistances.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mallak, A.J., Abbaszadegan, M.R., Khorasanizadeh, P.N. et al. Contribution of EVX1 in Aggressiveness of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 22, 341–347 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-015-0005-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-015-0005-x