Abstract
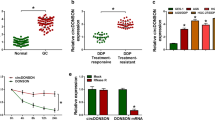
Gastric cancer remains a worldwide burden as the second leading cause of cancer-related death. Drug resistance of chemotherapy looms as a major clinical obstacle to successful treatment. Recent evidence indicated that miRNA-200c can restore the sensitivity of NSCLC cells to cisplatin and cetuximab. The expression of miRNA-200c and RhoE were investigated in gastric cancer tissues and cells (SGC7901 and SGC7901/DDP) by qRT-PCR. A luciferase reporter assay was done to understand the potential correlation between miRNA-200c and RhoE. Pre-miR-200c was transfected in SGC7901/DDP cells to confirm whether miRNA-200c could regulate RhoE expression. RhoE was knocked down to explore the role of RhoE on sensitivity of chemotherapy in gastric cancer by MTT. Western blot analysis was performed to further explore the mechanism of RhoE in regulating drug resistance. The results showed that miRNA-200c was significantly lower in cancerous tissues than those in the paired normal tissues, whereas the expression of RhoE was just the opposite. The significant difference of miRNA-200c and RhoE were observed between SGC7901 cells and SGC7901/DDP cells. miRNA-200c has target sites in the 3’-UTR of RhoE mRNA by luciferase reporter assay. Transfection of pre-miR-200c reduces RhoE expression. Meanwhile, the knockdown of RhoE enhanced the sensitivity of SGC7901/DDP cells and changed expression of some genes. These suggested that miRNA-200c regulated the sensitivity of chemotherapy to cisplatin (DDP) in gastric cancer by possibly targeting RhoE.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee JH, Kim KM, Cheong JH, Noh SH (2012) Current management and future strategies of gastric cancer. Yonsei Med J 53(2):248–257
Hudler P (2012) Genetic aspects of gastric cancer instability. Sci World J 2012:761909
Zhang H, Sun LL, Meng YL, Song GY, Hu JJ, Lu P, Ji B (2011) Survival trends in gastric cancer patients of Northeast China. World J Gastroenterol 17(27):3257–3262
Maconi G, Manes G, Porro GB (2008) Role of symptoms in diagnosis and outcome of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 14(8):1149–1155
Sun F, Lu X, Li H, Peng Z, Wu K, Wang G, Tong Q (2012) Special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1 regulates the multidrug resistance and invasion of human gastric cancer cells. Oncol Lett 4(1):156–162
Schoof CR, Botelho EL, Izzotti A, Vasques Ldos R (2012) MicroRNAs in cancer treatment and prognosis. Am J Cancer Res 2(4):414–433
Dontu G, de Rinaldis E (2010) MicroRNAs: shortcuts in dealing with molecular complexity? Breast Cancer Res 12(1):301
Davalos V, Moutinho C, Villanueva A, Boque R, Silva P, Carneiro F, Esteller M (2012) Dynamic epigenetic regulation of the microRNA-200 family mediates epithelial and mesenchymal transitions in human tumorigenesis. Oncogene 31(16):2062–2074
Roybal JD, Zang Y, Ahn YH, Yang Y, Gibbons DL, Baird BN, Alvarez C, Thilaganathan N, Liu DD, Saintigny P, Heymach JV, Creighton CJ, Kurie JM (2011) miR-200 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell invasion and metastasis by targeting Flt1/VEGFR1. Mol Cancer Res 9(1):25–35
Yu J, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Sato N, Kayashima T, Fujita H, Nakata K, Tanaka M (2010) MicroRNA, hsa-miR-200c, is an independent prognostic factor in pancreatic cancer and its upregulation inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion but increases cell proliferation. Mol Cancer 9:169
Ceppi P, Mudduluru G, Kumarswamy R, Rapa I, Scagliotti GV, Papotti M, Allgayer H (2010) Loss of miR-200c expression induces an aggressive, invasive, and chemoresistant phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Res 8(9):1207–1216
Chen J, Tian W, Cai H, He H, Deng Y (2012) Down-regulation of microRNA-200c is associated with drug resistance in human breast cancer. Med Oncol 29(4):2527–2534
Madigan JP, Bodemann BO, Brady DC, Dewar BJ, Keller PJ, Leitges M, Philips MR, Ridley AJ, Der CJ, Cox AD (2009) Regulation of Rnd3 localization and function by protein kinase C alpha-mediated phosphorylation. Biochem J 424(1):153–161
Riento K, Villalonga P, Garg R, Ridley A (2005) Function and regulation of RhoE. Biochem Soc Trans 33(Pt 4):649–651
Villalonga P, Guasch RM, Riento K, Ridley AJ (2004) RhoE inhibits cell cycle progression and Ras-induced transformation. Mol Cell Biol 24(18):7829–7840
Li K, Lu Y, Liang J, Luo G, Ren G, Wang X, Fan D (2009) RhoE enhances multidrug resistance of gastric cancer cells by suppressing Bax. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379(2):212–216
Issabekova A, Berillo O, Regnier M, Anatoly I (2012) Interactions of intergenic microRNAs with mRNAs of genes involved in carcinogenesis. Bioinformation 8(11):513–518
Hong L, Han Y, Lu Q, Zhang H, Zhao Q, Wu K, Fan D (2012) Drug resistance-related microRNAs in esophageal cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther 12(11):1487–1494
Burk U, Schubert J, Wellner U, Schmalhofer O, Vincan E, Spaderna S, Brabletz T (2008) A reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep 9(6):582–589
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, Bert AG, Wang J, Shannon MF, Goodall GJ (2008) A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 68(19):7846–7854
Jurmeister S, Baumann M, Balwierz A, Keklikoglou I, Ward A, Uhlmann S, Zhang JD, Wiemann S, Sahin Ö (2012) MicroRNA-200c represses migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by targeting actin-regulatory proteins FHOD1 and PPM1F. Mol Cell Biol 32(3):633–651
Lo WL, Yu CC, Chiou GY, Chen YW, Huang PI, Chien CS, Tseng LM, Chu PY, Lu KH, Chang KW, Kao SY, Chiou SH (2011) MicroRNA-200c attenuates tumour growth and metastasis of presumptive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma stem cells. J Pathol 223(4):482–495
Cochrane DR, Spoelstra NS, Howe EN, Nordeen SK, Richer JK (2009) MicroRNA-200c mitigates invasiveness and restores sensitivity to microtubule-targeting chemotherapeutic agents. Mol Cancer Ther 8(5):1055–1066
Leskelä S, Leandro-García LJ, Mendiola M, Barriuso J, Inglada-Pérez L, Muñoz I, Martínez-Delgado B, Redondo A, de Santiago J, Robledo M, Hardisson D, Rodríguez-Antona C (2010) The miR-200 family controls beta-tubulin III expression and is associated with paclitaxel-based treatment response and progression-free survival in ovarian cancer patients. Endocr Relat Cancer 18(1):85–95
Collett GP, Goh XF, Linton EA, Redman CW, Sargent IL (2012) RhoE is regulated by cyclic AMP and promotes fusion of human BeWo choriocarcinoma cells. PLoS One 7(1):e30453
Poch E, Miñambres R, Mocholí E, Ivorra C, Pérez-Aragó A, Guerri C, Pérez-Roger I, Guasch RM (2007) RhoE interferes with Rb inactivation and regulates the proliferation and survival of the U87 human glioblastoma cell line. Exp Cell Res 313(4):719–731
Cuiyan Z, Jie H, Fang Z, Kezhi Z, Junting W, Susheng S, Xiaoli F, Ning L, Xinhua M, Zhaoli C, Kang S, Bin Q, Baozhong L, Sheng C, Meihua X, Jie H (2007) Overexpression of RhoE in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) is associated with smoking and correlates with DNA copy number changes. Cancer Biol Ther 6(3):335–342
Klein RM, Higgins PJ (2011) A switch in RND3-RHOA signaling is critical for melanoma cell invasion following mutant-BRAF inhibition. Mol Cancer 10:114
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81172333).
Disclosure Statement
There were no competing financial interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Liang Chang, Fengjie Guo, Yudong Wang and Yalei Lv have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, L., Guo, F., Wang, Y. et al. MicroRNA-200c Regulates the Sensitivity of Chemotherapy of Gastric Cancer SGC7901/DDP Cells by Directly Targeting RhoE. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 20, 93–98 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-013-9664-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-013-9664-7