Abstract
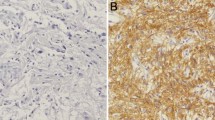
Medulloblastoma (MB) is the most common embryonal CNS tumor of childhood. Its survival rates have significantly improved over the years due to developments in diagnostic techniques and therapeutic strategies. However, it is still an important cause of cancer-related deaths in children. Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) is a member of the immunoglobulin family and a glycoprotein enriched on the surface of many types of tumor cells. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate whether the expression patterns of EMMPRIN may predict the clinical prognosis in MB. EMMPRIN expression in a series of 56 MB with various grades and pathological types was analyzed by immunohistochemical staining on paraffin-embedded sections. Then, the correlation of EMMPRIN expression patterns with clinical-pathological features of patients and its prognostic relevance were determined. Immunohistochemistry revealed that the positive expression rate of EMMPRIN in MB (75.0%, 42/56) was significantly higher than that in normal cerebellums (6.7%, 2/30, p < 0.001). In addition, EMMPRIN expression in MB was up-regulated in higher metastatic stage (p < 0.01), aggressive histopathological type (p < 0.005), necrosis (p < 0.01), as well as with undifferentiated tumor (p < 0.01). Furthermore, over-expression of EMMPRIN correlated significantly with poor prognosis (0.01 < p < 0.05) and represented an independent prognostic marker of overall survival on multivariate analysis (p = 0.01). Our study suggests that EMMPRIN expression was associated with the progression of MB and its over-activation may be an important predictor of poor survival in this patient cohort. Therefore, EMMPRIN may be regarded both as a prognostic factor and a therapeutic target for MB.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ris MD, Packer R, Goldwein J et al (2001) Intellectual outcome after reduced-dose radiation therapy plus adjuvant chemotherapy for medulloblastoma: a children’s cancer group study. J Clin Oncol 19:3470–6
Taylor RE, Bailey CC, Robinson K et al (2003) Results of a randomized study of preradiation chemotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for nonmetastatic medulloblastoma: the International Society of Paediatric Oncology/United Kingdom Children’s Cancer Study Group PNET-3 Study. J Clin Oncol 21:1581–91
Wolden SL, Dunkel IJ, Souweidane MM et al (2003) Patterns of failure using a conformal radiation therapy tumor bed boost for medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol 21:3079–83
Douglas JG, Barker JL, Ellenbogen RG et al (2004) Concurrent chemotherapy and reduced-dose cranial spinal irradiation followed by conformal posterior fossa tumor bed boost for average-risk medulloblastoma: efficacy and patterns of failure. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:1161–4
Gabison EE, Mourah S, Steinfels E (2005) Differential expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (CD147) in normal and ulcerated corneas. Am J Pathol 166:209–19
TangY KP, Nakada MT, Yan L (2004) Tumor-stroma interaction: positive feedback regulation of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) expression and matrix metalloproteinase-dependent generation of soluble EMMPRIN. Mol Cancer Res 2:73–80
Tang Y, Nakada MT, Kesavan P et al (2005) Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer stimulates tumor angiogenesis by elevating vascular endothelial cell growth factor and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Res 65:3193–9
Marieb EA, Zoltan-Jones A, Li R et al (2004) Emmprin promotes anchorage-independent growth in human mammary carcinoma cells by stimulating hyaluronan production. Cancer Res 64:1229–32
Yang JM, O’Neill P, Jin W et al (2006) Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (CD147) confers resistance of breast cancer cells to anoikis through inhibition of Bim. J Biol Chem 281:9719–27
Vignesw N, Beckers S, Waigel S et al (2006) Increased EMMPRIN (CD 147) expression during oral carcinogenesis. Exp Mol Pathol 80:147–59
Dai JY, Dou KF, Wang CH et al (2009) The interaction of HAb18G/CD147 with integrin α6β1 and its implications for the invasion potential of human hepatoma cells. BMC Cancer 9:337
Ishibashi Y, Matsumoto T, Niwa M et al (2004) CD147 and matrix metalloproteinase-2 protein expression as significant prognostic factors in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 101:1994–2000
Gershon TR, Becher OJ (2006) Medulloblastoma: therapy and biologic considerations. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 6:200–206
Jakacki RI (2005) Treatment strategies for high-risk medulloblastoma and supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Review of the literature. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl 1):44–52
Yang JM, Xu Z, Wu H (2003) Overexpression of extracellular matrixmetalloproteinase inducer in multidrug resistant cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 1:420–7
Thorns C, FellerAC MH (2002) EMMPRIN (CD147) is expressed in Hodgkin’s lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma. An immunohistochemical study of 60 cases. Anticancer Res 22:1983–6
Maria BL, Gupta N, Gilg AG et al (2008) Targeting hyaluronan interactions in spinal cord astrocytomas and diffuse pontine gliomas. J Child Neurol 23:1214–20
TsaiWC ChaoYC, Lee WH et al (2006) Inc reasing EMMPRIN and matriptase expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: tissue microarray analysis of immunohistochemical scores with clinicopathological parameters. Histopathology 49:388–95
Reimers N, ZafrakasK AssmannV et al (2004) Expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteases inducer on micrometastatic and primary mammary carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 10:3422–8
Davidson B, Konstantinovsky S, Nielsen S et al (2004) ltered expression of metastasis-associated and regulatory molecules in effusions from breast cancer patients: a novel model for tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res 10:7335–46
Davidson B, Goldberg I, Berner A et al (2003) EMMPRIN (extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer) is a novel marker of poor outcome in serous ovarian carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 20:161–9
Menashi S, Serova M, Ma L et al (2003) (2003) Regulation of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer matrix metalloproteinase expression by amphiregulin in transformed human breast epithelial cells. Cancer Res 63:7575–80
Jia L, Wei W, Cao J, Xu H, Miao X, Zhang J (2009) Silencing CD147 inhibits tumor progression and increases chemosensitivity in murine lymphoid neoplasm P388D1 cells. Ann Hematol 88:753–60
Kuang YH, Chen X, Su J et al (2009) RNA interference targeting the CD147 induces apoptosis of multi-drug resistant cancer cells related to XIAP depletion. Cancer Lett 276:189–95
Packer RJ, Rood BR, MacDonald TJ (2003) Medulloblastoma: present concepts of stratification into risk groups. Pediatr Neurosurg 39:60–7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Tongwei Chu and Xiaoyang Chen have offered the equal contribution to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, T., Chen, X., Yu, J. et al. Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer is a Negative Prognostic Factor of Pediatric Medulloblastoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 17, 705–711 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-011-9373-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-011-9373-z