Abstract
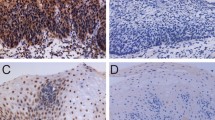
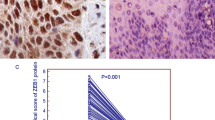
Prohibitin, a potential tumor suppressor, has been shown to be an anti- proliferative protein, a regulator of cell-cycle progression and in apoptosis. Recently, it was found to be over-expressed in breast cancer and gastric cancer, and it has been suggested as a biomarker in those diseases. To clarify the role and the prognostic significance of prohibitin expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), we analyzed the expression in ESCC and their corresponding nonneoplastic epithelia tissues by immunohistochemistry(IHC), Western blotting and real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction(QRT-PCR).The relationship between prohibitin expression and clinicopathological variables was examined by statistical analysis. The findings suggested the up-regulation of prohibitin play an important role in the carcinogenesis of ESCC. The over-expression of prihibitin was significantly correlated with the depth of tumor, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, lymphatic invasion and vascular invasion of ESCC. These results suggested that prohibitin(+), lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis could be the independent risk factors for worse prognosis in ESCC patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EC:
-
esophageal cancer
- ESCC:
-
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- IHC:
-
immunohistochemistry
- QRT-PCR:
-
real-time quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction
- TNM:
-
tumor, node, metastases
- AJCC:
-
American Joint Committee on Cancer
- TMA:
-
tissue microarray
- PBS:
-
phosphate buffer solution
- DAB:
-
diaminobenzidine
- PMSF:
-
phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride
- PVDF:
-
polyvinylidene difluoride
- HRP:
-
horseradish peroxidase
- ECL:
-
enhanced chemiluminescence
- RB:
-
retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein
- BPH:
-
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
References
Vizcaino AP, Moreno V, Lambert R, Parkin DM (2002) Time trends incidence of both major histologic types of esophageal carcinomas in selected countries, 1973–1995. Int J Cancer 99(6):860–868
Stoner GD, Gupta A (2001) Etiology and chemoprevention of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 22(11):1737–1746
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55(2):74–108
Piper PW, Bringloe D (2002) Loss of prohibitins, though it shortens the replicative life span of yeast cells undergoing division, does not shorten the chronological life span of G0-arrested cells. Mech Ageing Dev 123(4):287–295
Dell’Orco RT, McClung JK, Jupe ER, Liu XT (1996) Prohibitin and the senescent phenotype. Exp Gerontol 31(1–2):245–252
Jupe ER, Liu XT, Kiehlbauch JL, McClung JK, Dell’Orco RT (1996) The 39 untranslated region of prohibitin and cellular immortalization. Exp Cell Res 224(1):128–135
Kang X, Zhang L, Sun J et al (2008) Prohibitin: a potential biomarker for tissue-based detection of gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol 43(8):618–625
Dell’Orco RT, Jupe ER, Manjeshwar S et al (1997) Prohibitin: a new biomarker for breast tumors. Breast J 3:85–89
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID et al (2002) AJCC cancer staging manual, 6th edn. Springer-Verlag, New York
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A et al (1998) Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat Med 4(7):844–847
Gastl G, Spizzo G, Obrist P, Dünser M, Mikuz G (2000) Ep-CAM overexpression in breast cancer as a predictor of survival. Lancet 356(9246):1981–1982
Pancione M, Forte N, Sabatino L et al (2009) Reduced beta-catenin and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma expression levels are associated with colorectal cancer metastatic progression: correlation with tumor-associated macrophages, cyclooxygenase 2, and patient outcome. Hum Pathol 40(5):714–725
Allen JW, Richardson JD, Edwards MJ (1997) Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a review and update. Surg Oncol 6(4):193–200
Nijtmans LG, de Jong L, Artal Sanz M et al (2000) Prohibitins act as a membrane-bound chaperone for the stabilization of mitochondrial proteins. EMBO J 19(11):2444–2451
Coates PJ, Nenutil R, McGregor A et al (2001) Mammalian PHB proteins respond to mitochondrial stress and decrease during cellular senescence. Exp Cell Res 265(2):262–273
McClung JK, Jupe ER, Liu XT, Dell’Orco RT (1995) Prohibitin: potential role in senescence, development, and tumor suppression. Exp Gerontol 30(2):99–124
Ikonen E, Fiedler K, Parton RG, Simons K (1995) Prohibitin, an antiproliferative protein, is localized to mitochondria. FEBS Lett 358(3):273–277
Wang S, Nath N, Adlam M, Chellappan S (1999) Prohibitin, a potential tumor suppressor, interacts with RB and regulates E2F function. Oncogene 18(23):3501–3510
Wang KJ, Wang RT, Zhang JZ (2004) Identification of tumor markers using two- dimensional electrophoresis in gastric carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 10(15):2179–2183
Ummanni R, Junker H, Zimmermann U et al (2008) Prohibitin identified by proteomic analysis of prostate biopsies distinguishes hyperplasia and cancer. Cancer Lett 266(2):171–185
Asamoto M, Cohen SM (1994) Prohibitin gene is overexpressed but not mutated in rat bladder carcinomas and cell lines. Cancer Lett 83(1–2):201–207
Jupe ER, Liu XT, Kiehlbauch JL, McClung JK, Dell’Orco RT (1996) Prohibitin in breast cancer cell lines: loss of antiproliferative activity is linked to 3′untranslated region mutations. Cell Growth Differ 7(7):871–878
Pickens A, Orringer MB (2003) Geographical distribution and racial disparsity in esophageal cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 76(4):S1367–1369
Acknowledgements
This work was supported partly by a grant from the Innovation Project of Central South University (No.2340-76208). We would like to thank Dr. Zhen Zhang for his technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, HZ., Wang, JS., Wang, P. et al. Increased Expression of Prohibitin and its Relationship with Poor Prognosis in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 16, 515–522 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9242-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9242-1