Abstract
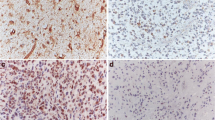
The aim of this study was to evaluate the expression of β-catenin in astrocytoma, and the clinical relevance and prognostic significance of the expression of β-catenin was also analyzed. Immunohistochemistry was performed on 63 resected astrocytoma tumor specimens to detect the expression of β-catenin. The correlation between the results of immuoexpression and the clinicopathologic parameters and patient survival was processed statistically. In 63 samples of astrocytoma, 36 cases were immunoreactive for β-catenin at cytoplasm, ten cases of astrocytoma were immunoreactive at cytomembrane, and four cases of astrocytoma were stained for β-catenin at nucleus. Spearman analysis showed that the distribution of β-catenin was not correlated with the grades of astrocytoma. However, the expression profiles were correlated with the patient’s 2-year survival, but not correlated with the grades, tumor size, sex, age, or tumor location. Patients with low β-catenin expression levels tended to be associated with a better prognosis than those who with high levels (p = 0.042). Our results suggest that β-catenin is useful for the prognosis evaluation of astrocytoma.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Louis DN (1997) A molecular genetic model of astrocytoma histopathology. Brain Pathol 7:755–764
Baeza N, Masuoka J, Kleihues P et al (2003) AXIN1 mutations but not deletions in cerebellar medulloblastomas. Oncogene 22:632–636
Collins VP (1995) Genetic alterations in gliomas. J Neurooncol 24:37–38
Nelson WJ, Nusse R (2004) Convergence of Wnt, beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science 303:1483–1487
Ilyas M (2005) Wnt signalling and the mechanistic basis of tumour development. J Pathol 205:130–144
Van Aken E, De Wever O, Correia da Rocha AS et al (2001) Defective E-cadherin/catenin complexes in human cancer. Virchows Arch 439:725–751
Lustig B, Behrens J (2003) The Wnt signaling pathway and its role in tumor development. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 129:199–221
Doucas H, Garcea G, Neal CP et al (2005) Changes in the Wnt signalling pathway in gastrointestinal cancers and their prognostic significance. Eur J Cancer 41:365–379
Ueta T, Ikeguchi M, Hirooka Y et al (2002) Beta-catenin and cyclin D1 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 9:1197–1203
Gerstein AV, Almeida TA, Zhao G et al (2002) APC/CTNNB1 (beta-catenin) pathway alterations in human prostate cancers. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 34:9–16
Ashihara K, Saito T, Mizumoto H et al (2002) Mutation of beta-catenin gene in endometrial cancer but not in associated hyperplasia. Med Electron Microsc 35:9–15
Utsuki S, Sato Y, Oka H et al (2002) Relationship between the expression of E-, N-cadherins and beta-catenin and tumor grade in astrocytomas. J Neurooncol 57:187–192
Henderson BR, Fagotto F (2002) The ins and outs of APC and beta-catenin nuclear transport. EMBO Rep 3:834–839
Novak A, Dedhar S (1999) Signaling through beta-catenin and Lef/Tcf. Cell Mol Life Sci 56:523–537
Akiyama T (2000) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 11:273–282
Polakis P (2000) Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev 14:1837–1851
Morin PJ (1999) beta-catenin signaling and cancer. Bioessays 21:1021–1030
Wijnhoven BP, Dinjens WN, Pignatelli M (2000) E-cadherin-catenin cell-cell adhesion complex and human cancer. Br J Surg 87:992–1005
Woo DK, Kim HS, Lee HS et al (2001) Altered expression and mutation of beta-catenin gene in gastric carcinomas and cell lines. Int J Cancer 95:108–113
Grabsch H, Takeno S, Noguchi T et al (2001) Different patterns of beta-catenin expression in gastric carcinomas: relationship with clinicopathological parameters and prognostic outcome. Histopathology 39:141–149
Zeng JZ, Hui Z, Rao HL, Zhang M, Hou J, Hui W, Qiu L (2004) Expression of cytoskeleton proteins α- and β-catenin in gliomas. China Cancer 11:0738–0740
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the State Key Laboratory of Cancer Biology grant, China (CBSKL 2005004 to QL) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30671087 to QL and 30700268 to JY). We are grateful to Dr Rui Liu for help in statistical analysis, to members in Qing Li’s laboratories for technical assistance and helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, LY., Jiang, LN., Li, FF. et al. Reduced β-catenin Expression is Associated with Good Prognosis in Astrocytoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 16, 253–257 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9219-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9219-0