Abstract
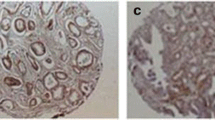
Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN, also named as CD147) is a multifunctional membrane glycoprotein over-expressed in many kinds of human solid tumors. It has been demonstrated to be involved in tumor invasion and angiogenesis. The aim of this study was to analyze the clinicopathological characteristics of the expression of CD147 in human prostate cancer (PCa), and to evaluate its clinical significance in the histologic classification and prognosis of PCa. CD147 protein expression in paraffin-embedded specimens gathered from 62 cases of PCa and 30 cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) were detected by the method of immunohistochemistry. The association of CD147 protein expression with the clinicopathological characteristics and with the prognosis of PCa was subsequently assessed. CD147 expression were positively expressed in 51/62 (82.3%) of PCa and 4/30 (13.3%) of BPH cases, respectively. The positive expression rate of CD147 in PCa tissues was significantly higher than that in BPH. The positive expression of CD147 was dramatically associated with TNM grade (p < 0.001), the depth of the prostatic wall invasion (p = 0.008), GLEASON Score (p = 0.001) and Histologic grade (p = 0.001). The patients with CD147 expression were associated with a poor prognosis of PCa (p = 0.01) and the survival rate of the patients with a strong positive expression of CD147 was the lowest (p = 0.01). The results suggest that the expression of CD147 may be an important feature of PCa and the detection of its expression may benefit us in the prediction of the prognosis of PCa.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schrgder FH, Wildhagen MF, ERSPC (2001) Screening for prostate cancer: evidence and perspectives. BJU Int 88:811–817
Holmberg L, Bill-Axelson A, Helgesen F (2002) A randomized trial comparing radical prostatectomy with watchful waiting in early prostate cancer. New Eng J Med 347:781–789
Hochreiter WW (2008) The issue of prostate cancer evaluation in men with elevated prostate-specific antigen and chronic prostatitis. Andrologia 40:130–133
Loeb S, Catalona WJ (2008) What to do with an abnormal PSA test. Oncologist 13:299–305
Kehinde EO, Maghrebi MA, Anim JT (2008) The importance of determining the aggressiveness of prostate cancer using serum and tissue molecular markers. Can J Urol 15:3967–3974
Wang L, Wu G, Yu L, Yuan J, Fang F, Zhai Z et al (2006) Inhibition of CD147 expression reduces tumor cell invasion in human prostate cancer cell line via rna interference. Cancer Biology & Therapy 5:608–614
Gabison EE, Mourah S, Steinfels E et al (2005) Differential expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (CD147) in normal and ulcerated corneas. Am. J. Pathol 166:209–219
Li Y, Shang P, Qian A et al (2003) Inhibitory effects of antisense RNA of HAb18G/CD147 on invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro. World J Gastroente 9:2174–2177
Sidhu SS, Mengistab AT, Tauscher AN, LaVail J, Basbaum C (2004) The microvesicle as a vehicle for EMMPRIN in tumorstromal interactions. Oncogene 23:956–963
Millimaggi D, Mari M, D’Ascenzo S, Carosa E, Jannini EA, Zucker S et al (2007) Tumor vesicle-associated CD147 modulates the angiogenic capability of endothelial cells. Neoplasia 9:349–357
Nabeshima K, Iwasaki H, Koga K, Hojo H, Suzumiya J, Kikuchi M (2006) Emmprin (basigin/CD147): matrix metalloproteinase modulator and multifunctional cell recognition molecule that plays a critical role in cancer progression. Pathol Int. 56:359–367
London CA, Sekhon HS, Arora V, Stein DA, Iversen PL, Devi GR (2003) A novel antisense inhibitor of MMP-9 attenuates angiogenesis, human prostate cancer cell invasion and tumorigenicity. Cancer Gene Ther 10:823–832
Mi Z, Oliver T, Guo H, Gao C, Kuo PC (2007) Thrombin-cleaved COOH (-) terminal osteopontin peptide binds with cyclophilin C to CD147 in murine breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 67:4088–4097
Kakehi Y (2003) Watchful waiting as a treatment option for localized prostate cancer in the PSA era. Jpn J Clin oncol. 33:1–5
Li QQ, Wang WJ, Xu JD, Cao XX, Chen Q, Yang JM et al (2007) Up-regulation of CD147 and matrix metalloproteinase-2, -9 induced by P-glycoprotein substrates in multidrug resistant breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci 98:1767–1774
Riethdorf S, Reimers N, Assmann V, Kornfeld JW, Terracciano L, Sauter G et al (2006) High incidence of EMMPRIN expression in human tumors. Int J Cancer 119:1800–1810
Biswas C, Zhang Y, DeCastro R, Guo H, Nakamura T, Kataoka H et al (1995) The human tumor cell-derived collagenase stimulatory factor (renamed EMMPRIN) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cancer Res 55:434–439
Caudroy S, Polette M, Nawrocki-Raby B, Cao J, Toole BP, Zucker S et al (2002) EMMPRIN-mediated MMP regulation in tumor and endothelial cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 19:697–702
Tang Y, Nakada MT, Kesavan P, McCabe F, Millar H, Rafferty P et al (2005) Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer stimulates tumor angiogenesis by elevating vascular endothelial cell growth factor and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Res 65:3193–3199
Biswas C (1982) Tumor cell stimulation of collagenase production by fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 109:1026–1034
Cozzi PJ, Wang J, Delprado W, Perkins AC, Allen BJ, Russell PJ et al (2005) MUC1, MUC2, MUC4, MUC5AC and MUC6 expression in the progression of prostate cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 22:565–573
Sun J, Hemler ME (2001) Regulation of MMP-1 and MMP-2production through CD147/extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer interactions. Cancer research 61:2276–2281
Marieb EA, Zoltan-Jones A, Li R (2004) Emmprin promotes anchorage-independent growth in human mammary carcinoma cells by stimulating hyaluronan production. Cancer Research. 64:1229–1232
Li HG, Xie DR, Shen XM (2005) Clinicopathological significance of expression of paxillin, syndecan-l and EMMPRIN in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 11:1445–1451
Lanyi M, Antonescu CR (2002) The precrystalline cytoplasmic granules of alveolar soft part sarcoma contain monocarboxylate transporter 1 and CD147. Am J Pathol 160:1215–1221
Seitz C, Djavan B (2006) Biological markers of prostate cancer. Ann Urol (Paris). 40:329–335
Zucker S, Hymowitz M, Rollo EE et al (2001) Tumorigenic potential of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer. Am J Pathol 158:1921–1928
Tang Y, Kesavan P, Marian T (2004) Tumor-stroma interaction:positive feedback regulation of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) expressio and matrix metalloproteinase-dependent generation of soluble EMMPRIN. Mol Cancer Res 2:73–80
Kanekura T, Chen X, Kanzaki T (2002) Basigin (CD147) is expressed on melanoma cells and induces tumor cell invasion by stimulating production of matrix metalloproteinases by fibroblasts. Int J Cancer 99:520–528
Jia L, Wang H, Qu S, Miao X, Zhang J (2008) CD147 regulates vascular endothelial growth factor-expression, tumorigenicity, and chemosensitivity to curcumin in hepatocellular carcinoma. IUBMB Life 60:57–63
Tang Y, Nakada MT, Rafferty P, McCabe FL, Millar H, Cunningham M et al (2006) Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by EMMPRIN via the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Mol Cancer Res 4:371–377
Madigan MC, Kingsley EA, Cozzi PJ, Delprado WJ, Russell PJ, Li Y (2008) The role of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer protein in prostate cancer progression. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57(9):1367–1379 doi:10.1007/s00262-008-0473-x
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No.04003650) and the Key Programs of Science and Technology of Guangzhou city (No. 200323 – E4053) and National High Technology Research and Development Project of China (No.2006AA02A245).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhao-dong Han, Xue-cheng Bi, and Wei-jun Qin contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Zd., Bi, Xc., Qin, Wj. et al. CD147 Expression Indicates Unfavourable Prognosis in Prostate Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 15, 369–374 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-008-9131-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-008-9131-z