Abstract
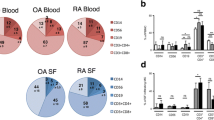
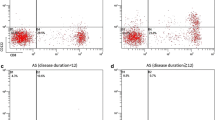
Rheumatoid arthritis is a multisystem disease with underlying immune mechanisms. Osteoarthritis is a debilitating, progressive disease of diarthrodial joints associated with the aging process. Although much is known about the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, our understanding of some immunologic changes remains incomplete. This study tries to examine the numeric changes in the T cell subsets and the alterations in the levels of some cytokines and adhesion molecules in these lesions. To accomplish this goal, peripheral blood and synovial fluid samples were obtained from 24 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, 15 patients with osteoarthritis and six healthy controls. The counts of CD4 + and CD8 + T lymphocytes were examined using flow cytometry. The levels of some cytokines (TNF-α, IL1-β, IL-10, and IL-17) and a soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) were measured in the sera and synovial fluids using enzyme linked immunosorbant assay. We found some variations in the counts of T cell subsets, the levels of cytokines and sICAM-1 adhesion molecule between the healthy controls and the patients with arthritis. High levels of IL-1β, IL-10, IL-17 and TNF-α (in the serum and synovial fluid) were observed in arthritis compared to the healthy controls. In rheumatoid arthritis, a high serum level of sICAM-1 was found compared to its level in the synovial fluid. A high CD4+/CD8+ T cell ratio was found in the blood of the patients with rheumatoid arthritis. In rheumatoid arthritis, the cytokine levels correlated positively with some clinicopathologic features. To conclude, the development of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis is associated with alteration of the levels of some cytokines. The assessment of these immunologic changes may have potential prognostic roles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maurer D, Felzmann T, Holter W, Petera P, Smolen J, Knapp W (1992) Evidence for the presence of activated CD4 T cells with naive phenotype in the peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol 87:429–434
Frye CA, Yocum DE, Tuan R, Suyana E, Seftor EA, Seftor RE, Khalkhali-Ellis Z, Moore TL, Hendrix MJ (1996) An in vitro model for studying mechanisms underlying synoviocyte-mediated cartilage invasion in rheumatoid arthritis. Pathol Oncol Res 2:157–166
Khalkhali-Ellis Z, Bulla GA, Schlesinger LS, Kirschmann DA, Moore TL, Hendrix MJ (1999) C1q-containing immune complexes purified from sera of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis patients mediate IL-8 production by human synoviocytes: role of C1q receptors. J Immunol 163:4612–4620
Choy EH, Connolly DJ, Rapson N, Jeal S, Brown JC, Kingsley GH, Panayi GS, Johnston JM (2000) Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and clinical effects of a humanized IgG1 anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody in the peripheral blood and synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 39:1139–1146
Khalkhali-Ellis Z, Roodman ST, Knutsen AP, Mueller KR, Chauhan B, Moore TL, Hendrix MJ (1998) Expression of macrophage markers by a population of T cells obtained from synovial fluid of a subgroup of patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 25:352–360
Kotake S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Matsuzaki K, Itoh K, Ishiyama S, Saito S, Inoue K, Kamatani N, Gillespie MT, Martin TJ, Suda T (1999) IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis is a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis. J Clin Invest 103:1345–1352
Zwerina J, Redlich K, Schett G, Smolen JS (2005) Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: targeting cytokines. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1051:716–729
Malemud CJ (2004) Cytokines as therapeutic targets for osteoarthritis. BioDrugs 18:23–35
Aigner T, Sachse A, Gebhard PM, Roach HI (2006) Osteoarthritis: pathobiology-targets and ways for therapeutic intervention. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 58:128–149
Zangerle PF, De Groote D, Lopez M, Meuleman RJ, Vrindts Y, Fauchet F, Dehart I, Jadoul M, Radoux D, Franchimont P (1992) Direct stimulation of cytokines (IL-1 beta, TNF-alpha, IL-6, IL-2, IFN-gamma and GM-CSF) in whole blood: II. Application to rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Cytokine 4:568–575
Ezawa K, Yamamura M, Matsui H, Ota Z, Makino H (1997) Comparative analysis of CD45RA- and CD45RO-positive CD4 + T cells in peripheral blood, synovial fluid, and synovial tissue in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Acta Med Okayama 51:25–31
Petrovic-Rackov L, Pejnovic N (2005) Clinical significance of IL-18, IL-15, IL-12 and TNF-alpha measurement in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 25:448–452
Firestein GS (2005) Immunologic mechanisms in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Rheumatol 11(3 Suppl):S39–44
Abramson SB, Amin A (2002) Blocking the effects of IL-1 in rheumatoid arthritis protects bone and cartilage. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41:972–980
Attur MG, Patel IR, Patel RN, Abramson SB, Amin AR (1998) Autocrine production of IL-1 beta by human osteoarthritis-affected cartilage and differential regulation of endogenous nitric oxide, IL-6, prostaglandin E2, and IL-8. Proc Assoc Am Physicians 110:65–72
Appel H, Neure L, Kuhne M, Braun J, Rudwaleit M, Sieper J (2004) An elevated level of IL-10- and TGFbeta-secreting T cells, B cells and macrophages in the synovial membrane of patients with reactive arthritis compared to rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 23:435–440
Verhoef CM, van Roon JA, Vianen ME, Bijlsma JW, Lafeber FP (2001) Interleukin 10 (IL-10), not IL-4 or interferon-gamma production, correlates with progression of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 28:1960–1966
Miossec P (2004) IL-17 in rheumatoid arthritis: a new target for treatment or just another cytokine? Joint Bone Spine 71:87–90
Ryu S, Lee JH, Kim SI (2006) IL-17 increased the production of vascular endothelial growth factor in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. Clin Rheumatol 25:16–20
Lindsley HB, Smith DD, Davis LS, Koch AE, Lipsky PE (1992) Regulation of the expression of adhesion molecules by human synoviocytes. Semin Arthritis Rheum 21:330–334
Cush JJ, Rothlein R, Lindsley HB, Mainolfi EA, Lipsky PE (1993) Increased levels of circulating intercellular adhesion molecule 1 in the sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 36:1098–1102
Gonzalez-Gay MA, Garcia-Unzueta MT, De Matias JM, Gonzalez-Juanatey C, Garcia-Porrua C, Sanchez-Andrade A, Martin J, Llorca J (2006) Influence of anti-TNF-alpha infliximab therapy on adhesion molecules associated with atherogenesis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 24:373–379
Albert DA, Huang G, Dubrow G, Brensinger CM, Berlin JA, Williams HJ (2004) Criteria for improvement in rheumatoid arthritis: alternatives to the American College of Rheumatology 20. J Rheumatol 31(5):856–866
Hussein MR, Hassan HI, Hofny ER, Elkholy M, Fatehy NA, Abd Elmoniem AE, Ezz El-Din AM, Afifi OA, Rashed HG (2005) Alterations of mononuclear inflammatory cells, CD4/CD8 + T cells, interleukin 1beta, and tumour necrosis factor alpha in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, peripheral blood, and skin of patients with systemic sclerosis. J Clin Pathol 58:178–184
Barrera P, Faure S, Prud’homme JF, Balsa A, Migliorini P, Chimenti D, Radstake TR, van de Putte LB, Pascual-Salcedo D, Westhovens R, Maenaut K, Alves H, Lopes-Vaz A, Stravopoulos C, Spyropoulou M, Fritz P, Bardin T, Charron D, Lepage V, Alibert, Martinez M, Cornelis F (2001) European genetic study on rheumatoid arthritis: is there a linkage of the interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-10 or IL-4 genes to RA? Clin Exp Rheumatol 19:709–714
Chabaud M, Page G, Miossec P (2001) Enhancing effect of IL-1, IL-17, and TNF-alpha on macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha production in rheumatoid arthritis: regulation by soluble receptors and Th2 cytokines. J Immunol 167:6015–6020
Petrovic-Rackov L (2006) Evaluation of the degree of clinical rheumatoid arthritis activity based on the concentrations of cytokines TNF-alpha, IL-12, IL-15, and IL-18 in serum and synovial fluid]. Vojnosanit Pregl 63:21–26
Brennan FM, Hayes AL, Ciesielski CJ, Green P, Foxwell BM, Feldmann M (2002) Evidence that rheumatoid arthritis synovial T cells are similar to cytokine-activated T cells: involvement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and nuclear factor kappaB pathways in tumor necrosis factor alpha production in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:31–41
Fossiez F, Djossou O, Chomarat P, Flores-Romo L, Ait-Yahia S, Maat C, Pin JJ, Garrone P, Garcia E, Saeland S, Blanchard D, Gaillard C, Das Mahapatra B, Rouvier E, Golstein P, Banchereau J, Lebecque S (1998) T cell interleukin-17 induces stromal cells to produce proinflammatory and hematopoietic cytokines. J Exp Med 183:2593–2603
Chabaud M, Fossiez F, Taupin JL, Miossec P (1998) Enhancing effect of IL-17 on IL-1-induced IL-6 and leukemia inhibitory factor production by rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes and its regulation by Th2 cytokines. J Immunol 161:409–414
Khalkhali-Ellis Z, Seftor EA, Nieva DR, Seftor RE, Samaha HA, Bultman L, De Larco JE, Ince A, Moore TL, Hendrix MJ (1997) Induction of invasive and degradative phenotype in normal synovial fibroblasts exposed to synovial fluid from patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: role of mononuclear cell population. J Rheumatol 24:2451–2460
Cush JJ, Splawski JB, Thomas R, McFarlin JE, Schulze-Koops H, Davis LS, Fujita K, Lipsky PE (1995) Elevated interleukin-10 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38:96–104
Macchioni P, Boiardi L, Casali B, Nicoli D, Farnetti E, Salvarani C (2000) Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) gene polymorphisms in Italian patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 18:553–558
Blann AD, Herrick A, Jayson MI (1995) Altered levels of soluble adhesion molecules in rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis and systemic sclerosis. Br J Rheumatol 34:814–819
Dolezalova P, Telekesova P, Nemcova D, Hoza J (2002) Soluble adhesion molecules ICAM-1 and E-selectin in juvenile arthritis: clinical and laboratory correlations. Clin Exp Rheumatol 20:249–254
Hanyuda M, Kasama T, Isozaki T, Matsunawa MM, Yajima N, Miyaoka H, Uchida H, Kameoka Y, Ide H, Adachi M (2003) Activated leucocytes express and secrete macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha upon interaction with synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis via a beta2-integrin/ICAM-1 mechanism. Rheumatology (Oxford) 42:1390–1397
Pigott R, Dillon LP, Hemingway IH, Gearing AJ (1992) Soluble forms of E-selectin, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 are present in the supernatants of cytokine activated cultured endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 187:584–589
Lindsley HB, Smith DD, Cohick CB, Koch AE, Davis LS (1993) Proinflammatory cytokines enhance human synoviocyte expression of functional intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). Clin Immunol Immunopathol 68:311–320
Fitzgerald JE, Ricalton NS, Meyer AC, West SG, Kaplan H, Behrendt C, Kotzin BL (1995) Analysis of clonal CD8 + T cell expansions in normal individuals and patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 154:3538–3547
Burmester GR, Stuhlmuller B, Keyszer G, Kinne RW (1997) Mononuclear phagocytes and rheumatoid synovitis. Mastermind or workhorse in arthritis? Arthritis Rheum 40:5–18
Benito MJ, Veale DJ, FitzGerald O, van den Berg WB, Bresnihan B (2005) Synovial tissue inflammation in early and late osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 64:1263–1267
Miltenburg AM, van Laar JM, de Kuiper R, Daha MR, Breedveld FC (1992) T cells cloned from human rheumatoid synovial membrane functionally represent the Th1 subset. Scand J Immunol 35:603–610
Rittner HL, Zettl A, Jendro MC, Bartz-Bazzanella P, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM (1997) Multiple mechanisms support oligoclonal T cell expansion in rheumatoid synovitis. Mol Med 3:452–465
Steiner G, Tohidast-Akrad M, Witzmann G, Vesely M, Studnicka-Benke A, Gal A, Kunaver M, Zenz P, Smolen JS (1999) Cytokine production by synovial T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 38:202–213
Franz JK, Kolb SA, Hummel KM, Lahrtz F, Neidhart M, Aicher WK, Pap T, Gay RE, Fontana A, Gay S (1998) Interleukin-16, produced by synovial fibroblasts, mediates chemoattraction for CD4 + T lymphocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol 28:2661–2671
Mamoune A, Durand V, Le Goff P, Pennec YL, Youinou P, Le Corre R (2000) Abnormal distribution of CD45 isoforms expressed by CD4 + and CD8 + T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Histol Histopathol 15:587–591
Hatachi S, Iwai Y, Kawano S, Morinobu S, Kobayashi M, Koshiba M, Saura R, Kurosaka M, Honjo T, Kumagai S (2003) CD4 + PD-1 + T cells accumulate as unique anergic cells in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. J Rheumatol 30:1410–1419
van Amelsfort JM, Jacobs KM, Bijlsma JW, Lafeber FP, Taams LS (2004) CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis: differences in the presence, phenotype, and function between peripheral blood and synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum 50:2775–2785
Mottonen M, Heikkinen J, Mustonen L, Isomaki P, Luukkainen R, Lassila O (2005) CD4 + CD25 + T cells with the phenotypic and functional characteristics of regulatory T cells are enriched in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol 140:360–367
Mallya RK, Mace BE (1981) The assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis using a multivariate analysis. Rheumatol Rehabil 20:14–17
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussein, M.R., Fathi, N.A., El-Din, A.M.E. et al. Alterations of the CD4+, CD8+ T Cell Subsets, Interleukins-1β, IL-10, IL-17, Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Soluble Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis: Preliminary Observations. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 14, 321–328 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-008-9016-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-008-9016-1