Abstract
Background
The ABCD2 score is increasingly being used to triage patients with transient ischemic attack (TIA). Whether the score can predict the need for in-hospital intervention (IHI), other than initiation of antiplatelets and statins, is unknown.
Aims
The ability of the ABCD2 score to predict IHI would strengthen the rationale to use it as a decision-making tool. We thus conducted this study to investigate the relationship between the ABCD2 score and IHI.
Methods
We analyzed prospectively collected data from consecutive TIA patients over 12 months. We determined ABCD2 upon admission and collected the results of in-hospital evaluation, treatments initiated during hospitalization, and follow-up status. We defined IHI as arterial revascularization or anticoagulation required during admission. We used chi-square for trend to examine the association between ABCD2 and IHI.
Results
We studied 121 patients. Fourteen (12%) had small infarcts on diffusion magnetic resonance imaging; 38 (31%) had a new risk factor recognized during admission [hyperlipidemia (n = 9), hypertension (1), diabetes (1), carotid stenosis ≥ 50% (16), other arterial occlusive lesions (7), and potential cardioembolic source (4)]. Their percentages increased with higher ABCD2 scores. However, among 12 patients (10%) with IHI, ABCD2 score categories were equally distributed (10% in 0–3, 9% in 4–5, and 10% in 6–7; p = 0.8). One patient (0.8%) worsened during hospitalization; none had a stroke during follow-up.
Conclusion
Patients with an ABCD2 score ≤ 3 had an equal chance of requiring IHI as those with a score of 4–7. The decision to admit TIA patients based on the ABCD2 score alone is not supported by our experience and requires further study.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Introduction
Because population-based studies have shown that the risk of stroke after a transient ischemic attack (TIA) is high [1], immediate evaluation and treatment is warranted. The ABCD2 score, which considers age, blood pressure, clinical features, duration of symptoms, and history of diabetes, has been shown to predict the short-term stroke risk after TIA and is being used to triage TIA patients [2]. Based on the presumed low risk of stroke within the first 2 days after a TIA, hospital admission may be unnecessary for most patients with a score ≤ 3 in the absence of atrial fibrillation (AF). Admission is, however, generally recommended for patients with a score ≥ 4 to ensure prompt evaluation and intervention to reduce the risk of subsequent early stroke [2, 3]. Recently, the EXPRESS and SOS-TIA studies showed that urgent evaluation and initiation of preventive treatments, such as antiplatelets, statins, anticoagulation, and carotid revascularization, greatly reduce the risk of early stroke after a TIA or minor stroke [4, 5]. Since antiplatelets and statins can be initiated in the emergency department or outpatient setting, the added benefit from hospital admission would be to facilitate timely detection and treatment of cardioembolic etiology requiring anticoagulation or arterial stenosis requiring revascularization.
Whether the ABCD2 score could also predict the need for urgent in-hospital intervention (IHI), i.e., anticoagulation and revascularization, other than antiplatelets and statins, is unknown. The score’s ability to predict IHI would strengthen the rationale for its use as a decision-making tool to determine which TIA patients should be admitted. We thus conducted this study to investigate the relationship between admission ABCD2 score and IHI during hospitalization.
Methods
We routinely admit all patients with suspected TIAs presenting to our emergency department for hospital observation, regardless of their ABCD2 score. We prospectively collected the data for consecutive patients admitted with TIAs to our service from July 2007 to July 2008. TIA was defined as a sudden onset of focal neurological deficits or amaurosis fugax, suspected to be of cerebrovascular origin, lasting less than 24 h and which has resolved prior to presentation to our emergency department. On admission, information on the symptoms and duration of TIA were obtained and the stroke fellows determined the ABCD2 score of each patient [2].
For each patient, we recorded the following information: (1) age and sex; (2) past medical history, especially TIA and stroke; (3) previously known vascular risk factors (AF, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, hyperlipidemia, and current smoking); (4) medications taken at the time of symptom onset (antiplatelets, statins, and anticoagulants); (5) the results of in-hospital evaluation(s), including newly diagnosed risk factors for stroke (arterial stenosis, AF, potential cardioembolic source, diabetes, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia); and (6) new treatments initiated during hospitalization including antiplatelets, statins, anticoagulation (either parenteral or oral), and carotid revascularization. Newly diagnosed hypertension was identified as systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg on repeated measurements. The threshold for the diagnosis of diabetes was set as a fasting plasma glucose level >126 mg/dl (7.0 mmol/l) or a casual plasma glucose >200 mg/dl (11.1 mmol/l). Hypercholesterolemia was defined as either total cholesterol >200 mg/dl or low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) >100 mg/dl, based on the current guidelines for stroke prevention [6].
The results of evaluations during admission were collected. As shown in Table 1, they included electrocardiogram (ECG), transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), transesophageal echocardiography (TEE), brain computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance (MR) studies including diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), carotid duplex sonography, MR angiography, or CT angiography, and electroencephalogram (EEG) when performed to exclude the possibility of a seizure. Many patients had more than one imaging modality. We also recorded the presence or absence of recurrent stroke-like symptoms during hospitalization and upon follow-up after discharge.
IHI was defined as arterial revascularization or initiation of anticoagulation during hospital admission due to arterial occlusive lesions or potential cardiac sources of emboli, thought to cause the TIA-like neurological symptoms. We excluded from analysis patients with known or documented AF upon presentation and those taking warfarin at the time of symptom onset, since these patients were either continued or started de novo on warfarin for presumed cardioembolism regardless of their ABCD2 scores or results of in-hospital work-up.
Statistical analysis
We determined the distribution of patients with newly diagnosed risk factors and IHI by ABCD2 scores, which were trichotomized into low- (1–3 points), medium- (4–5 points), and high-risk (6–7 points) groups. We used the Wilcoxon rank sum test for nonparametric and Fisher’s exact test for categorical comparisons. Risk associations were assessed by chi-square (χ2) for trend. A p < 0.05 was set for statistical significance. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS statistical software, version 15 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
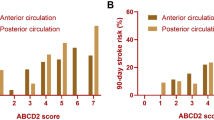
A total of 151 patients with suspected TIAs were admitted to the hospital during the study period. We excluded 30 patients with either known AF or those taking warfarin at the time of symptom onset from our analysis. The clinical characteristics of the remaining 121 TIA patients are shown in Table 1. The mean age was 65 ± 15 years and 55% were women. Antiplatelet therapy was either started de novo or changed from one antiplatelet agent to another in 53% of the patients during admission. Table 2 shows the distribution of patients with newly diagnosed risk factors and those requiring IHI by ABCD2 scores. Fifty-four patients (45%) had a score ≥ 4. Fourteen patients (12%) were found to have small infarcts on DWI, 57% (8/14) of whom had a score ≤ 3. Overall, a higher percentage (36%) was found to have infarcts among patients with a score of 6–7, compared to 12% among a score ≤ 3 and 5% among a score of 4–5. However, these differences were not significant (p for trend = 0.29).
The baseline 12-lead ECG was entirely normal in 97 of the 121 patients. Various ECG abnormalities ranging from ST-T wave changes, conduction defects, and voltage changes indicative of left ventricular hypertrophy were seen in the remaining 24 subjects. No patient had AF on telemetry during hospitalization. A potential cardioembolic source was revealed in four (3%) patients (three with right-to-left shunt and one with intracardiac thrombus) by echocardiography. Other risk factors newly recognized during admission included hyperlipidemia (7%, n = 9), hypertension (0.8%, n = 1), diabetes (0.8%, n = 1), carotid stenosis ≥ 50% (13%, n = 16), and other arterial occlusive lesions (6%, n = 7). The percentages of patients with newly recognized risk factors increased with higher ABCD2 scores (24% with ≤ 3, 37% with 4–5, and 55% with 6–7 points; p for trend = 0.02).
Ten percent of patients (12/121) required IHI. Seven percent (n = 9) had ≥ 50% ipsilateral carotid stenosis requiring urgent revascularization, and no patient received revascularization for <50% stenosis. The baseline characteristics of patients requiring revascularization were not significantly different from other patients. The attending clinicians decided to urgently anticoagulate two patients with other arterial occlusive lesions (one with carotid dissection and one with high-grade stenosis of the vertebral artery) and one with a thrombus on the mitral valve. IHI was equally distributed across all ABCD2 scores (10% in ≤ 3, 9% in 4–5, and 9% in 6–7; p for trend = 0.80). Table 3 shows the characteristics of patients with IHI vs those without IHI. There were no differences in individual components of the ABCD2 score between patients with and without IHI. A history of coronary artery disease (CAD) was more prevalent among IHI patients. The vast majority of patients with IHI were men. More patients with IHI were found to have small infarcts on DWI, compared with those without IHI (33 vs 9%; p = 0.03).
The mean length of hospitalization was 2.1 ± 2.1 days (range: 1–18), and increased with higher ABCD2 scores (p = 0.02). One patient (0.8%) worsened due to a new ischemic stroke during hospitalization; none had a stroke during an average of 48 ± 43 days follow-up period.
Discussion
In this cohort of TIA patients, we found no association between the ABCD2 score and the need for IHI. Patients with a score ≤ 3 had an equal chance of requiring IHI as those with higher scores.
Rapid evaluation and early intervention reduce the risk of stroke after a TIA [4, 5]. Treatments such as antiplatelet agents, statins, anticoagulation for patients with AF, and endarterectomy or stenting for patients with symptomatic carotid stenosis effectively prevent stroke after TIA [4, 5, 7–12]. Antiplatelets and statins can be easily and safely initiated in the emergency department or by the primary care physician as soon as a patient with TIA seeks medical attention, while adequate anticoagulation and timely endarterectomy or stenting often require hospitalization. Although the necessity of expedited evaluation and treatment of TIA patients is undisputed, routine hospital admission for all TIA patients may be unnecessary and cost ineffective. Therefore, a risk stratification score to determine which TIA patients should be admitted to the hospital should ideally be able to identify those patients who may require anticoagulation or carotid revascularization. In recent years, the ABCD2 score which was originally developed to predict the short-term risk of stroke after a TIA has become increasingly used to triage patients [2, 3]. However, the ability of the ABCD2 score to predict the need for IHI has not previously been studied.
We admit all patients with suspected TIAs at our institution for in-hospital observations and perform urgent diagnostic testing to determine the underlying cause for the TIA. This afforded us the opportunity to conduct the current study to examine the association between the ABCD2 score and IHI. Our finding of an equal distribution of IHI among patients with low, medium, and high ABCD2 scores suggests that the decision to admit patients with suspected TIAs for hospital observation based on the ABCD2 score alone is not justified. We also found that more than half of the patients with transient symptoms who had small infarcts on diffusion MRI had a low score of ≤ 3, indicating that the association between the ABCD2 score and DWI-positive TIA is poor. This is consistent with earlier reports indicating that patients with an ABCD score <4 still have a substantial probability of having radiographic evidence of acute infarction [13].
Only one patient (0.8%) experienced neurological worsening due to a new stroke during hospitalization in our study, and none was noted to have AF on telemetry. We perform urgent diagnostic testing to determine the TIA cause in our institution. Patients with relevant ipsilateral carotid stenosis > 50% generally undergo revascularization and patients with a cardioembolic source are started on anticoagulants during hospitalization. Antiplatelets and statins are either started or modified, as appropriate, in the emergency department for most patients. This aggressive approach is likely to account for our low stroke rate, which is similar to other studies in which TIA patients underwent urgent evaluation [4, 5] but much lower than other previous studies in which patients were less rapidly evaluated [14].
Our findings argue that hospital admission of TIA patients for the sole purposes of observation may be unnecessary; that telemetry, in patients with no clinical suspicion for a cardioembolic source and a normal sinus rhythm on 12-lead ECG without conduction or ST-T wave changes, is unlikely to yield significant abnormalities; and that the need for IHI is a more appropriate determinant for hospital admission rather than the individual patient’s short-term risk of subsequent stroke as assessed by the ABCD2 score. The most frequent findings leading to IHI among our patients was an ipsilateral carotid stenosis >50%, and only one patient had a cardioembolic source revealed by echocardiography which required anticoagulation during hospitalization. This suggests that imaging TIA patients for carotid occlusive disease should be urgently done in the emergency department. The importance of vascular imaging to identify high-risk TIA patients is highlighted by Hill et al. [14] and Lovett et al. [15] who showed that recurrent stroke risk varies between different etiologic subtypes of ischemic stroke and is highest in patients with large-artery atherosclerosis. The addition of results from an urgent diagnostic work-up, such as CT scan and MRI, improves the predictive ability of the ABCD2 score and suggests that a combined clinical and imaging assessment of brain and vessels has the potential to increase the efficient use of resources and rapidly evaluate the underlying etiology of the TIA patients [16, 17].
We found that patients with IHI had a higher rate of CAD, indicating that special attention should be paid to TIA patients with CAD. Carotid stenosis is common in CAD patients [18, 19]. We also found that IHI was less frequent among women than men. Women are more likely to be admitted to the hospital than men [20]. It is uncertain if the gender-based difference in IHI reflects the higher prevalence of arterial atherosclerosis in men or the admission of relatively more women with transient neurological symptoms that are not TIA.
The strength of our study lies in its prospective nature. However, our study also has limitations. The small number of patients, particularly those with a score of 4–7 and those requiring IHI, reduces the strength of our results. Although most of our patients were seen within the first 24 h of the onset of TIA symptoms, they were not all studied in a uniform manner or at a uniform time in their disease course. This variability in the time from symptom onset to evaluation and diagnostic methods may have influenced the testing results. Furthermore, our study is limited to patients seen at a single institution, which may limit its generalizability to other patient populations. Larger-scale studies are needed to validate our findings and to fully evaluate the predictive factors of IHI in TIA patients.
In conclusion, we found a poor association between admission ABCD2 score and the need for IHI in patients with TIA. The decision to admit or not admit patients with suspected TIAs for in-hospital observation based on the ABCD2 score alone is not supported by our experience and requires further study before it can be recommended as a tool to triage TIA patients. Our study highlights the fact that much depends on the capability to perform extensive evaluation in the emergency department using modern brain, vascular, and cardiac technologies to rapidly elucidate the pathophysiology of the TIA in individual patients.
References
Johnston SC, Gress DR, Browner WS et al (2000) Short-term prognosis after emergency department diagnosis of TIA. JAMA 284:2901–2906
Johnston SC, Rothwell PM, Nguyen-Huynh MN et al (2007) Validation and refinement of scores to predict very early stroke risk after transient ischaemic attack. Lancet 369:283–292
Bray JE, Coughlan K, Bladin C (2007) Can the ABCD Score be dichotomised to identify high-risk patients with transient ischaemic attack in the emergency department? Emerg Med J 24:92–95
Lavallée PC, Meseguer E, Abboud H et al (2007) A transient ischaemic attack clinic with round-the-clock access (SOS-TIA): feasibility and effects. Lancet Neurol 6:953–960
Rothwell PM, Giles MF, Chandratheva A et al (2007) Effect of urgent treatment of transient ischaemic attack and minor stroke on early recurrent stroke (EXPRESS study): a prospective population-based sequential comparison. Lancet 370:1432–1442
Sacco RL, Adams R, Albers G et al (2006) Guidelines for prevention of stroke in patients with ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Council on Stroke: co-sponsored by the Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention: the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline. Stroke 37:577–617
Johnston SC, Nguyen-Huynh MN, Schwarz ME et al (2006) National Stroke Association guidelines for the management of transient ischemic attacks. Ann Neurol 60:301–313
Fairhead JF, Rothwell PM (2005) The need for urgency in identification and treatment of symptomatic carotid stenosis is already established. Cerebrovasc Dis 19:355–358
Rothwell PM, Eliasziw M, Gutnikov SA et al (2003) Analysis of pooled data from the randomised controlled trials of endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis. Lancet 361:107–116
Amarenco P, Bogousslavsky J, Callahan A 3rd et al (2006) High-dose atorvastatin after stroke or transient ischemic attack. N Engl J Med 355:549–559
European Atrial Fibrillation Trial Study Group (1993) Secondary prevention in non-rheumatic atrial fibrillation after transient ischaemic attack or minor stroke. Lancet 342:1255–1262
Fairhead JF, Mehta Z, Rothwell PM (2005) Population-based study of delays in carotid imaging and surgery and the risk of recurrent stroke. Neurology 65:371–375
Cucchiara BL, Messe SR, Taylor RA et al (2006) Is the ABCD score useful for risk stratification of patients with acute transient ischemic attack? Stroke 37:1710–1714
Hill MD, Yiannakoulias N, Jeerakathil T et al (2004) The high risk of stroke immediately after transient ischemic attack: a population-based study. Neurology 62:2015–2020
Lovett JK, Coull AJ, Rothwell PM (2004) Early risk of recurrence by subtype of ischemic stroke in population-based incidence studies. Neurology 62:569–573
Coutts SB, Eliasziw M, Hill MD et al (2008) An improved scoring system for identifying patients at high early risk of stroke and functional impairment after an acute transient ischemic attack or minor stroke. Int J Stroke 3:3–10
Sciolla R, Melis F, SINPAC Group (2008) Rapid identification of high-risk transient ischemic attacks: prospective validation of the ABCD score. Stroke 39:297–302
Fassiadis N, Adams K, Zayed H et al (2008) Occult carotid artery disease in patients who have undergone coronary angioplasty. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 7:855–857
Seo WK, Yong HS, Koh SB et al (2008) Correlation of coronary artery atherosclerosis with atherosclerosis of the intracranial cerebral artery and the extracranial carotid artery. Eur Neurol 59(6):292–298
Coben JH, Owens PL, Steiner CA et al (2008) Hospital and demographic influences on the disposition of transient ischemic attack. Acad Emerg Med 15:171–176
Acknowledgements
Dr. Lou is supported by Zhejiang University Academic Stars Research Fellowship and grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30500175); Dr. Selim is supported in part by grants from the NINDS (1R01-NS 057127-01A1) and NIH (5R01-HL46690-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this paper are those of the author(s) and not those of the editors, editorial board or publisher.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0 ), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, M., Safdar, A., Edlow, J.A. et al. Can ABCD2 score predict the need for in-hospital intervention in patients with transient ischemic attacks?. Int J Emerg Med 3, 75–80 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12245-010-0176-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12245-010-0176-x