Abstract
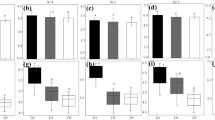
Functional diversity covers diverse functional traits of microorganisms in an ecosystem. Thus, we hypothesized that it could play an important role in the isolation of nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. These bacteria have been considered as biofertilizer for sustainable agriculture development. Soils were collected from different sites of agricultural field and performed several microbiological tests in which we observed considerable differences in heterotrophic microbial abundance and microbial activities among the microcosms. Functional diversity depends on both microbial richness and evenness. Based on the results of metabolic fingerprinting of the carbon sources of BiOLOG-ECO plates, richness and evenness was measured by determining Shannon diversity index and Gini coefficient, respectively. The results showed significant differences in both microbial richness and evenness, suggesting considerable variation of functional diversity among the microcosms. Thereafter, nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria were isolated on Burk’s and Pikovskaya media, respectively. The results revealed considerable variation of both types of bacterial abundance among the microcosms. Microcosm (T2) showing the highest functional diversity houses the maximum numbers of nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Similarly, the microcosm (T5) exhibiting the lowest functional diversity houses the minimum numbers of nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Thus, a strong positive correlation was observed between functional diversity and both types of bacterial abundance among the soil samples. Higher richness and evenness lead to the development of increased functional diversity that facilitates to accommodate substantial numbers of nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in soil. Taken together, the results demonstrated that functional diversity plays an important role in the isolation of nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from soil.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adnan M, Shah Z, Fahad S, Arif M, Alam M, Khan IA, Mian IA, Basir A, Ullah H, Arshad M, Rahman IU, Saud S, Ihsan MZ, Jamal Y, Amanullah, Hammad HM, Nasim W (2017) Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria nullify the antagonistic effect of soil calcification on bioavailability of phosphorus in alkaline soils. Sci Rep 7:16131. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16537-5
Bardi L, Malusà E (2012) Drought and nutritional stresses in plant: alleviating role of rhizospheric microorganisms. Abiotic stress: new research. Nova Science Publishers Inc., Hauppauge, pp 1–57. https://doi.org/10.2174/978160805058111101010039
Bhattarai KP, Mandal TN (2017) Effect of altitudinal variation on the soil characteristics in Sal (Shorea robusta gaertn.) forests of eastern Nepal. Int J Ecol Environ Sci 42:19–28. https://doi.org/10.3126/on.v14i1.16438
Chakraborty P, Joardar S, Ray S, Biswas P, Maiti D, Tribedi P (2018) 3,6-Di (pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazine (pytz)-capped silver nanoparticles (TzAgNPs) inhibit biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a potential approach toward breaking the wall of biofilm through reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 63:763–772. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-018-0620-5
Choi KH, Dobbs FC (1999) Comparison of two kinds of BiOLOG microplates (GN and ECO) in their ability to distinguish among aquatic microbial communities. J Microbiol Methods 36:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7012(99)00034-2
Clark CM, Flynn DF, Butterfield BJ, Reich PB (2012) Testing the link between functional diversity and ecosystem functioning in a Minnesota grassland experiment. PLoS One 7:e52821. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052821
Dey S, Tribedi P (2018) Microbial functional diversity plays an important role in the degradation of polyhydroxyl butyrate (PHB) in soil. 3 Biotech 8:171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1201-7
Goswami M, Bhattacharyya P, Mukherjee I, Tribedi P (2017) Functional diversity: an important measure of ecosystem functioning. Adv Microbiol 7:82–93. https://doi.org/10.4236/aim.2017.71007
Goswami M, Bhattacharyya P, Tribedi P (2017a) Addition of rubber to soil damages the functional diversity of soil. 3 Biotech 7:173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0854-y
Green VS, Stottb DE, Diacka M (2006) Assay for fluorescein diacetate hydrolytic activity: optimization for soil samples. Soil Biol Biochem 38:693–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.06.020
Gu Y, Wag P, Kong C (2009) Urease, invertase, dehydrogenase and polyphenoloxidase activities in paddy soils influenced by allelophatic rice variety. Eur J Soil Biol 45:436–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2009.06.003
Hoffman BM, Dean DR, Seefeldt LC (2009) Climbing nitrogenase: toward a mechanism of enzymatic nitrogen fixation. Acc Chem Res 42:609–619. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar8002128
Kaczynska G, Borowik A, Wyszkowska J (2015) Soil dehydrogenases as an indicator of contamination of the environment with petroleum products. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2642-9
Kayasth M, Gera R, Dudeja SS, Sharma PK, Kumar V (2014) Studies on salinization in Haryana soils on free-living nitrogen-fixing bacterial populations and their activity. J Basic Microbiol 54:170–179. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201200158
Laureto LMO, Cianciaruso MV, Samia DSM (2015) Functional diversity: an overview of its history and applicability. Natureza Conservação 13:112–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncon.2015.11.001
Mahanty T, Bhattacharjee S, Goswami M, Bhattacharyya P, Das B, Ghosh A, Tribedi P (2017) Biofertilizers: a potential approach for sustainable agriculture development. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:3315–3335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8104-0
Malusa E, Vassilev N (2014) A contribution to set a legal framework for biofertilizers. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:6599–6607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5828-y
Mason NW, Mouillot D, Lee WG, Wilson JB (2005) Functional richness, functional evenness and functional divergence: the primary components of functional diversity. Oikos 111:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2005.13886.x
Mazid M, Khan TA (2015) Future of bio-fertilizers in Indian agriculture: an overview. Int J Agric Food Res 3:10–23. https://doi.org/10.24102/ijafr.v3i3.132
Mehta S, Nautiyal CS (2001) An efficient method for qualitative screening of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Curr Microbiol 43:51–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002840010259
Nannipieri P, Ascher J, Ceccherini MT, Landi L, Pietramellara G, Renella G (2017) Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur J Soil Sci 68:12–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.2_12398
Panhwar QA, Othman R, Rahman ZA, Meon S, Ismail MR (2012) Isolation and characterization of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from aerobic rice. Afr J Biotechnol 11:2711–2719. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB10.2218
Park M, Kim C, Yang J, Lee H, Shin W, Kim S, Sa T (2005) Isolation and characterization of diazotrophic growth promoting bacteria from rhizosphere of agricultural crops of Korea. Microbiol Res 160:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2004.10.003
Salazar S, Sanchez L, Alvarez J, Valverde A, Galindo P, Igual J, Peix A, Santa-Regina I (2011) Correlation among soil enzyme activities under different forest system management practices. Ecol Eng 37:1123–1131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.02.007
Sarkar S, Tribedi P, Gupta AD, Saha T, Sil AK (2017) Microbial functional diversity decreases with sewage purification in stabilization ponds. Waste Biomass Valoriz 8:417–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9571-8
Satyaprakash M, Nikitha T, Reddi EUB, Sadhana B, Vani SS (2017) Phosphorous and phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant nutrition. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 6:2133–2144. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.604.251
Smith BE, Richards RL, Newton WE (eds) (2013) Catalysts for nitrogen fixation: nitrogenases, relevant chemical models and commercial processes. Springer Science & Business Media 1:340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8104-0
Stotzky G (ed) (2000) Soil biochemistry, volume 10. CRC Press, Boca Raton. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781482293364
Teng Y, Luo Y, Sun M, Liu Z, Li Z, Christie P (2010) Effect of bioaugmentation by Paracoccus sp. strain HPD-2 on the soil microbial community and removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from an aged contaminated soil. Bioresour Technol 101:3437–3443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.088
Tribedi P, Sil AK (2013) Bioaugmentation of polyethylene succinate contaminated soil with Pseudomonas sp. AKS2 results in increased microbial activity and better polymer degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:1318–1326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1080-0
Tribedi P, Sil AK (2013a) Founder effect uncovers a new axis in polyethylene succinate bioremediation during biostimulation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 346:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6968.12210
Tribedi P, Gupta AD, Sil AK (2015) Adaptation of Pseudomonas sp. AKS2 in biofilm on low-density polyethylene surface: an effective strategy for efficient survival and polymer degradation. Bioresour Bioprocess 2:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-015-0044-x
Wolińska A, Frąc M, Oszust K, Szafranek-Nakonieczna A, Zielenkiewicz U, Stępniewska Z (2017) Microbial biodiversity of meadows under different modes of land use: catabolic and genetic fingerprinting. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2318-2
Wolińska A, Kuźniar A, Zielenkiewicz U, Banach A, Izak D, Stępniewska Z, Błaszczyk M (2017a) Metagenomic analysis of some potential nitrogen-fixing bacteria in arable soils at different formation process. Microb Ecol 73:162–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0837-2
Zaidi A, Khan MS, Ahemad M, Oves M, Wani PA (2009) Recent advances in plant growth promotion by phosphate-solubilizing microbes. In: Khan MS et al (eds) Microbial strategies for crop improvement. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 23–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01979-1_2
Acknowledgements
The authors’ would like to express sincere gratitude to the learned experts for their immense guidance and cooperation in improving the manuscript. We sincerely thank Ms. Rakshita Dave, Ms. Sutirtha Dutta, and Mr. Debajjyoti Basu for vitally reading the manuscript. This current work has been supported by a grant in aid from the Department of Science and Engineering research board (SERB), DST, Govt. of India (sanction number YSS/2015/000387).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, P., Tribedi, P. Functional diversity performs a key role in the isolation of nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from soil. Folia Microbiol 64, 461–470 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-018-00672-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-018-00672-1