Abstract
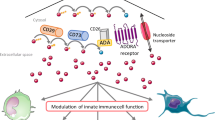
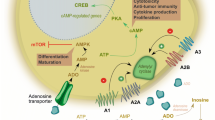
Adenosines, endogenous purine nucleosides, appear in the extracellular space under metabolically stressful conditions associated with ischemia, inflammation, and cell damage. Their activity on innate immunity is prevalently inhibitory and can develop both in infectious and neoplastic diseases. During cancer development, tumor cells that release high concentrations of adenosines can impair the function of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and assist tumor growth by neo-angiogenesis. We evaluated the influence of A2 adenosine receptor (A2AR) agonist on cytotoxic-cell response comparing human with other mammalian species (rodents, pigs, goats), both in healthy and in cancer conditions. The A2AR agonist developed dose-dependent inhibition of the cytotoxic activity of immune effector cells in all studied species. However, variability of the response was observed in relation to the species and the target cells that were used. Altogether, our data indicate that the A2AR plays a central role in adenosine-mediated inhibition of immune response to tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A2AR:
-
A2 adenosine receptor
- AR:
-
adenosine receptor
- CPCA:
-
5′-(N-cyclopropyl)carboxamidoadenosine
- FCS:
-
fetal calf serum
- GPCR:
-
G-protein-coupled receptor
- NK:
-
natural killer cells
- PBMC:
-
peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- SMC:
-
spleen mononuclear cells
- TIL:
-
tumor-infiltrating leukocyte
References
Bobek V., Boubelik M., Fiserova A., Luptovcova M., Vannucci L., Kacprzak G., Kolodzej J., Majewski A.M., Hoffman R.M.: Anticoagulant drugs increase natural killer cell activity in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 47, 215–223 (2005).
Borovansky J., Horak V., Elleder M., Fortyn K., Smith N.P., Kolb A.M.: Biochemical characterization of a new melanoma model — the minipig MeLiM strain. Melanoma Res. 13, 543–548 (2003).
Burnstock G.: The past, present and future of purine nucleotides as signaling molecules. Neuropharmacology 36, 1127–1139 (1997).
Cronstein B.N.: Adenosine, an endogenous anti-inflammatory agent. J.Appl.Physiol. 76, 5–13 (1994).
Fišerová A., Starec M., Kuldová M., Kovářů H., Páv M., Vannucci L., Pospíšil M.: Effects of D2-dopamine and α-adrenoceptor antagonists in stress induced changes on immune responsiveness of mice. J.Neuroimmunol. 130, 55–65 (2002).
Fredholm B.B., Ijzerman A.P., Jacobson K.A., Klotz K., Linden J.: International Union of Pharmacology. XXV. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors. Pharmacol.Rev. 53, 527–552 (2001).
Haskó G., Linden J., Cronstein B., Pacher P.: Adenosine receptors: therapeutic aspects for inflammatory and immune diseases. Nature Rev.Drug Discov. 7, 759–770 (2008).
Hoskin D.W., Reynolds T., Blay J.: 2-Chloroadenosine inhibits the MHC-unrestricted cytolytic activity of anti-CD3-activated killer cells: evidence for the involvement of a non-A1/A2 cell-surface adenosine receptor. Cell.Immunol. 159, 85–93 (1994).
Hoskin D.W., Mader J.S., Furlong S.J., Conrad D.M., Blay J.: Inhibition of T cell and natural killer cell function by adenosine and its contribution to immune evasion by tumor cells (review). Internat.J.Oncol. 32, 527–535 (2008).
Klinger M., Freissmuth M., Nanoff C.: Adenosine receptors: G protein-mediated signaling and the role of accessory proteins. Cell Signal. 14, 99–108 (2002).
Lokshin A., Raskovalova T., Huang X., Zacharia L.C., Jackson E.K., Gorelik E.: Adenosine-mediated inhibition of the cytotoxic activity and cytokine production by activated natural killer cells. Cancer Res. 66, 7758–7765 (2006).
Murphree L.J., Sullivan G.W., Marshall M.A., Linden J.: Lipopolysaccharide rapidly modifies adenosine receptor transcripts in murine and human macrophages: role of NF-κB in A2a adenosine receptor induction. Biochem.J. 391, 575–580 (2005).
Ohta A., Sitkovsky M.: Role of G-protein-coupled adenosine receptors in downregulation of inflammation and protection from tissue damage. Nature 414, 916–920 (2001).
Ohta A., Gorelik E., Prasad S.J., Ronchese F., Lukashev D., Wong M.K.K., Huang X., Caldwell S., Liu K., Smith P., Chen J., Jackson E.K., Apasov S., Abrams S., Sitkovsky M.V.: A2a adenosine receptor protects tumors from antitumor T cells. Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA 103, 13132–13137 (2006).
Priebe T., Platsoucas C.D., Nelson J.A.: Adenosine receptors and modulation of natural killer cell activity by purine nucleosides. Cancer Res. 50, 4328–4331 (1990).
Raskovalova T., Huang X., Sitkovsky M., Zacharia L.C., Jackson E.K., Gorelik E.: Gs Protein-coupled adenosine receptor signaling and lytic function of activated NK cells. J.Immunol. 175, 4383–4391 (2005).
Raskovalova T., Lokshin A., Huang X., Jackson E.K., Gorelik E.: Adenosine-mediated inhibition of cytotoxic activity and cytokine production by IL-2/NKp46-activated NK cells: involvement of protein kinase A isozyme I (PKA I). Immunol.Res. 36, 91–99 (2006).
Sitkovsky M.V.: Use of A2a adenosine receptor as a physiological immunosupressor and to engineer inflammation in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 65, 493–501 (2003).
Sitkovsky M.V., Lukashev D., Apasov S., Kojima H., Koshiba M., Caldwell C., Ohta A., Thiel M.: Physiological control of immune response and inflammatory tissue damage by hypoxia-inducible factors and adenosine A2a receptors. Ann.Rev. Immunol. 22, 657–682 (2004).
Trebichavský I., Šplíchal I., Šplíchalová A., Muneta Y., Mori Y.: Systemic and local cytokine response of young piglets to oral infection with Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium. Folia Microbiol. 48, 403–407 (2003).
Vannucci L., Huggins C.B., Mosca F.: A new experimental model for colorectal carcinogenesis in the rat. J.Environ.Pathol.Toxicol. Oncol. 13, 59–61 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuldová, M., Svoboda, J., Kovářů, F. et al. NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity modulation by A2 adenosine receptor agonist in different mammalian species. Folia Microbiol 54, 364–368 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-009-0051-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-009-0051-4