Abstract
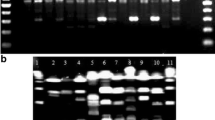
DNA fingerprinting methods, RAPD with 7 random primers, and rep-PCR using both BOXA1R and (GTG)5 ones, were used for the discrimination of 16 type and collection Bifidobacterium strains of 9 species of human origin, B. animalis ssp. animalis and B. animalis ssp. lactis and 7 Bifidobacterium strains collected in the Culture Collection of Dairy Microorganisms (CCDM). Both RAPD and rep-PCR methods provided similar results. The strains were identified as B. animalis ssp. lactis (6 strains) and B. adolescentis (1 strain). The reclassification of the collection strain CCM 3761 as B. pseudocatenulatum species (previously classified as B. adolescentis) was confirmed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARDRA:
-
amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis
- ATCC:
-
American Type Culture Collection
- CCDM:
-
Culture Collection of Dairy Microorganisms
- CCM:
-
Czech Collection of Microorganisms
- DSM:
-
Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen
- DSMZ:
-
Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen
- RAPD:
-
random amplified polymorphic DNA
- UPGMA:
-
unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean
References
Boylston T.D., Vinderola C.G., Ghoddusi H.B., Reinheimer J.A.: Incorporation of bifidobacteria into cheeses: challenges and rewards. Internat.Dairy J. 14, 375–387 (2004).
Cocconcelli P.S., Porro D., Galandini S., Senini L.: Development of RAPD protocol for typing of strains of lactic acid bacteria and enterococci. Lett.Appl.Microbiol. 21, 376–379 (1995).
Corroler D., Desmasures N., Gueguen M.: Correlation between polymerase chain reaction analysis of the histidine biosynthesis operon, randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis and phenotypic characterization of dairy Lactococcus isolates. Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol. 51, 91–99 (1999).
Delgado S., Mayo B.: Phenotypic and genetic diversity of Lactococcus lactis and Enterococcus spp. strains isolated from Northern Spain starter-free farmhouse cheeses. Internat.J.Food Microbiol. 90, 309–319 (2004).
Elmer G.W.: Probiotics: “Living drugs”. Am.J.Health Syst.Pharm. 58, 1101–1109 (2001).
Garro M.S., de Valdez G.F., de Giori G.S.: Temperature effect on the biological activity of Bifidobacterium longum CRL 849 and Lactobacillus fermentum CRL 251 in pure and mixed cultures grown in soymilk. Food Microbiol. 21, 511–518 (2004).
Gevers D., Huys G., Swigs J.: Applicability of rep-PCR fingerprinting for identification of Lactobacillus species. FEMS Microbiol.Lett. 205, 31–36 (2001).
Gueimonde M., Delgado S., Mayo B., Ruas-Madeido P., Margolles A., de los Reyes Gavilán C.G.: Viability and diversity of probiotic Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium populations included in commercial fermented milks. Food Res.Internat. 37, 839–850 (2004).
Isolauri E., Salminen S., Ouwehand A.C.: Probiotics. Best Pract.Res.Clin.Gastroenterol. 18, 299–313 (2004).
Křížová J., Španová A., Rittich B.: Evaluation of amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis (ARDRA) and species-specific PCR for identification of Bifidobacterium species. Syst.Appl.Microbiol. 29, 36–44 (2006).
Mårtensson O., Öste R., Holst O.: The effect of yoghurt culture on the survival of probiotic bacteria in oat-based, non-dairy products. Food Res.Internat. 35, 775–784 (2002).
Masco L., Huys G., Gevers D., Verbrugghen L., Swings J.: Identification of Bifidobacterium species using rep-PCR fingerprinting. Syst.Appl.Microbiol. 26, 557–563 (2003).
Matsuki T., Watanabe K., Tanaka R.: Genus-and species-specific PCR primers for the detection and identification of bifidobacteria, pp. 85–105 in G.W Tannock (Ed.): Probiotics and Prebiotics. Where Are We Going? Caister Academic Press, Wymondham 2002.
Mullié C., Romond M.-B., Izard D.: Establishment and follow-up of bifidobacterial species in the gut of healthy bottle-fed infants of 1–4 months age. Folia Microbiol. 51, 473–477 (2006).
Olive D.M., Bean P.: Principles and applications of methods for DNA-based typing of microbial organisms. J.Clin.Microbiol. 37, 1661–1669 (1999).
O’sullivan D.J., Kullen M.J.: Tracking of probiotic bifidobacteria in the intestine. Internat.Dairy J. 8, 513–525 (1998).
Pérez G, Cardell E., Zárate V.: Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis for differentiation of Leuconostoc mesenteroides subspecies isolated from Tenerife cheese. Lett.Appl.Microbiol. 34, 82–85 (2002).
Prodělalová J., Španová A., Rittich B.: Application of PCR, rep-PCR and RAPD techniques for typing of Lactococcus lactis strains. Folia Microbiol. 50, 150–154 (2005).
Reuter G., Klein G., Goldberg M.: Identification of probiotic cultures in food samples. Food Res.Internat. 35, 117–124 (2002).
Samaržija D., Sikora S., Redžepovic S., Antunac N., Havranek J.: Application of RAPD analysis for identification of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris strains isolated from artisanal cultures. Microbiol.Res. 157, 13–17 (2002).
Sambrook J., Russell D.W.: Molecular Cloning, 3rd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York 2001.
Trebichavský I., Šplíchal I.: Probiotics manipulate host cytokine response and induce antimicrobial peptides. Folia Microbiol. 51, 507–510 (2006).
Ventura M., van Sinderen D., Fitzgerald G.F., Zink R.: Insights into the taxonomy, genetics and physiology of bifidobacteria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 86, 205–223 (2004).
Versalovic J., Koeuth T., Lupski J.R.: Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to fingerprinting of bacterial genomes. Nucl.Acids Res. 19, 6823–6831 (1991).
Vincent D., Roy D., Mondou F., Déry C.: Characterisation of bifidobacteria by random DNA amplification. Internat.J.Food Microbiol. 43, 185–193 (1998).
Williams J.G.K., Kubelik A.R., Livak K.J., Rafalski J.A., Tingey S.V.: DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucl.Acids Res. 18, 6531–6535 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Křížová, J., Španová, A. & Rittich, B. RAPD and rep-PCR fingerprinting for characterization of Bifidobacterium species. Folia Microbiol 53, 99–104 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-008-0014-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-008-0014-1